Ultrasound Range
To support with student training, we have created a range of ultrasound compatible simulators that allow realistic practice. Our models are designed to be used repeatably, allowing for continual practice until students are both competent and confident in their ability to interpret ultrasound images.
Choose your clinical focus
Diagnostic Ultrasound
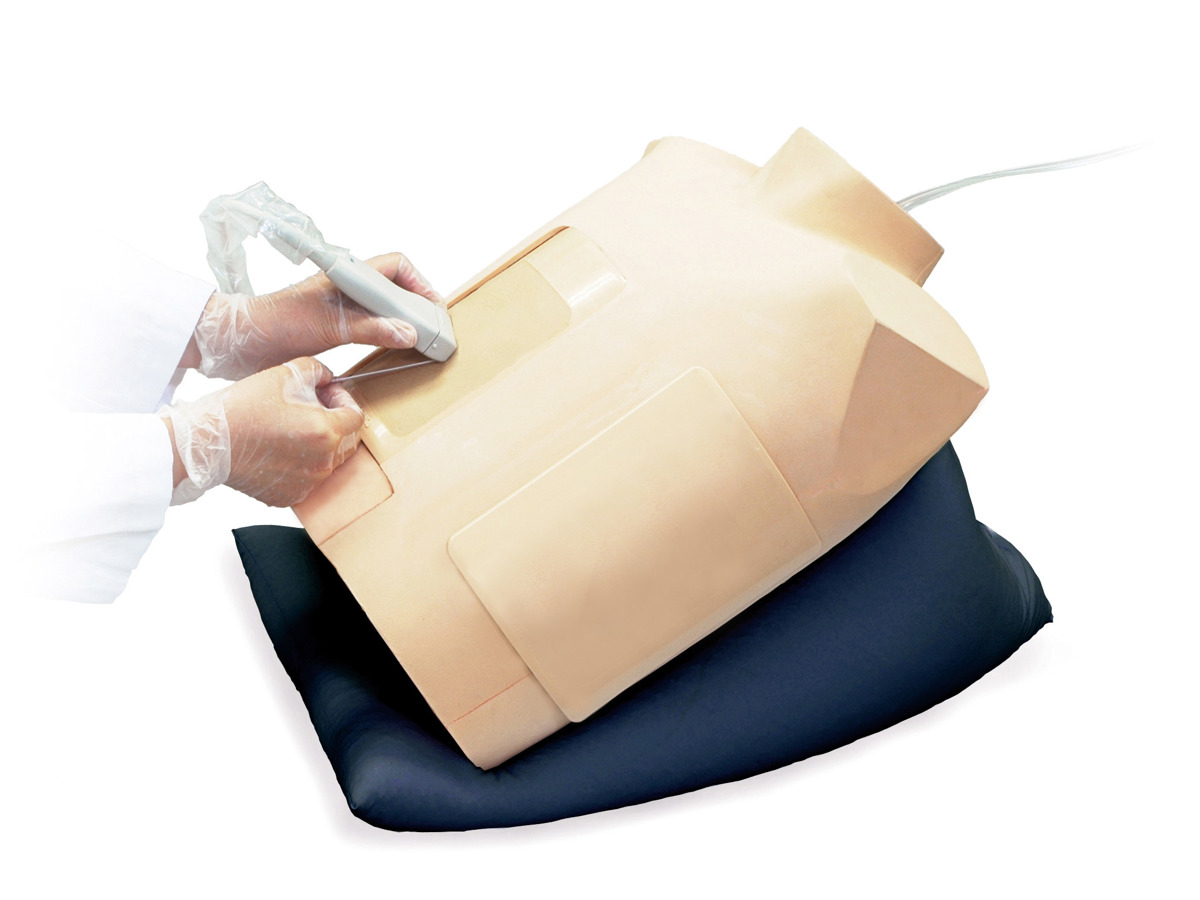
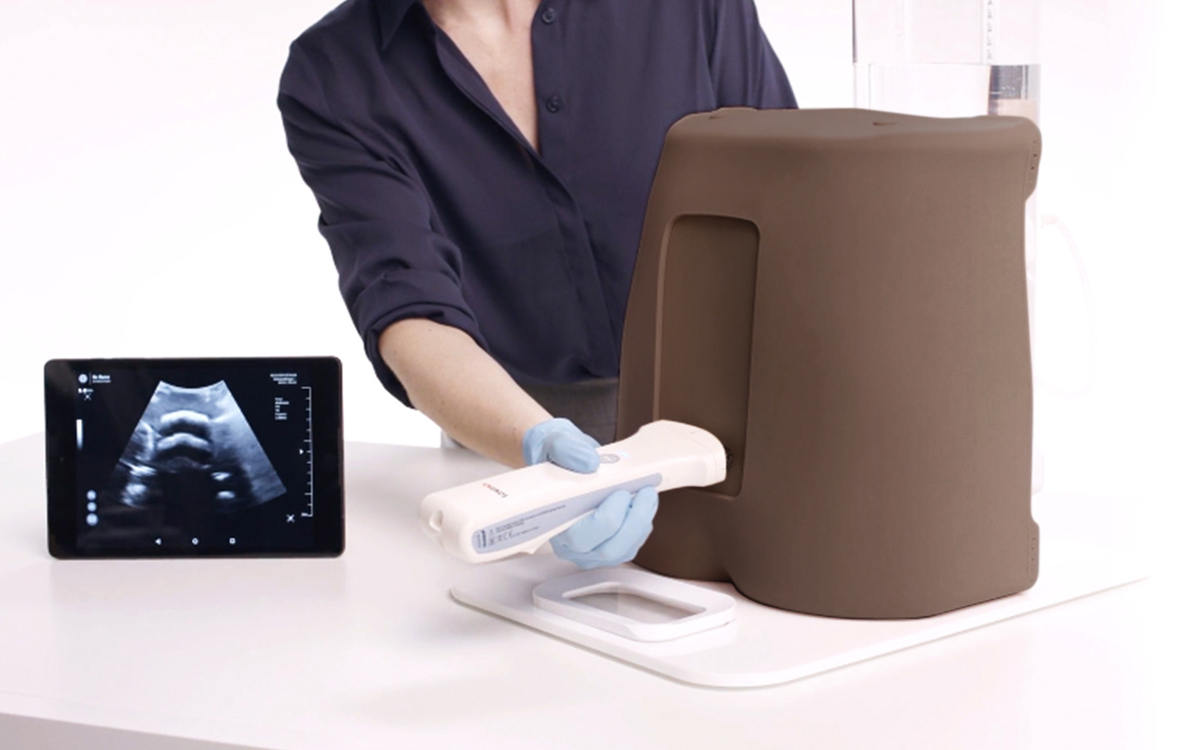
Diagnostic ultrasound is a safe, non-invasive medical imaging technique that allows doctors to diagnose medical conditions within the body. A handheld ultrasound device is used to send sound waves into the body, and these echo off tissue, organs, muscles, and blood vessels. The device picks up the echoes and renders a real-time image on a connected screen for diagnosis.

What sort of evaluations can be made during a diagnostic ultrasound?
- Soft tissue injuries: Identifying sprains, tears, and inflammation in muscles, tendons, and ligaments
- Organ health: Checking the health of organs in the abdomen and pelvis, such as the liver, kidneys, and reproductive organs like ovaries
- Evaluating blood vessels: Checking for issues in arteries and veins, including the carotid arteries
- Monitoring pregnancy: Prenatal care to monitor fetal development and health
- Real-time assessment: Identify the source of pain or see how structures are working in motion
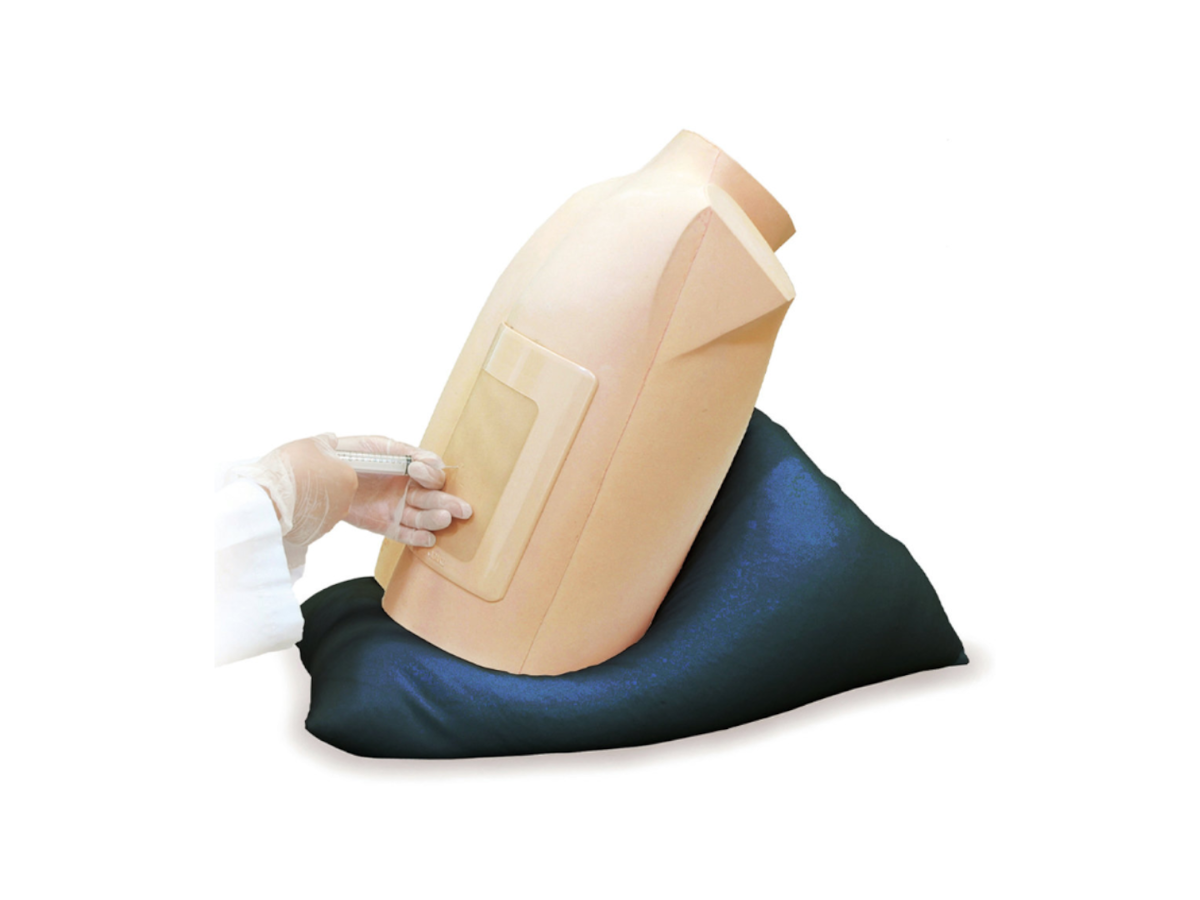
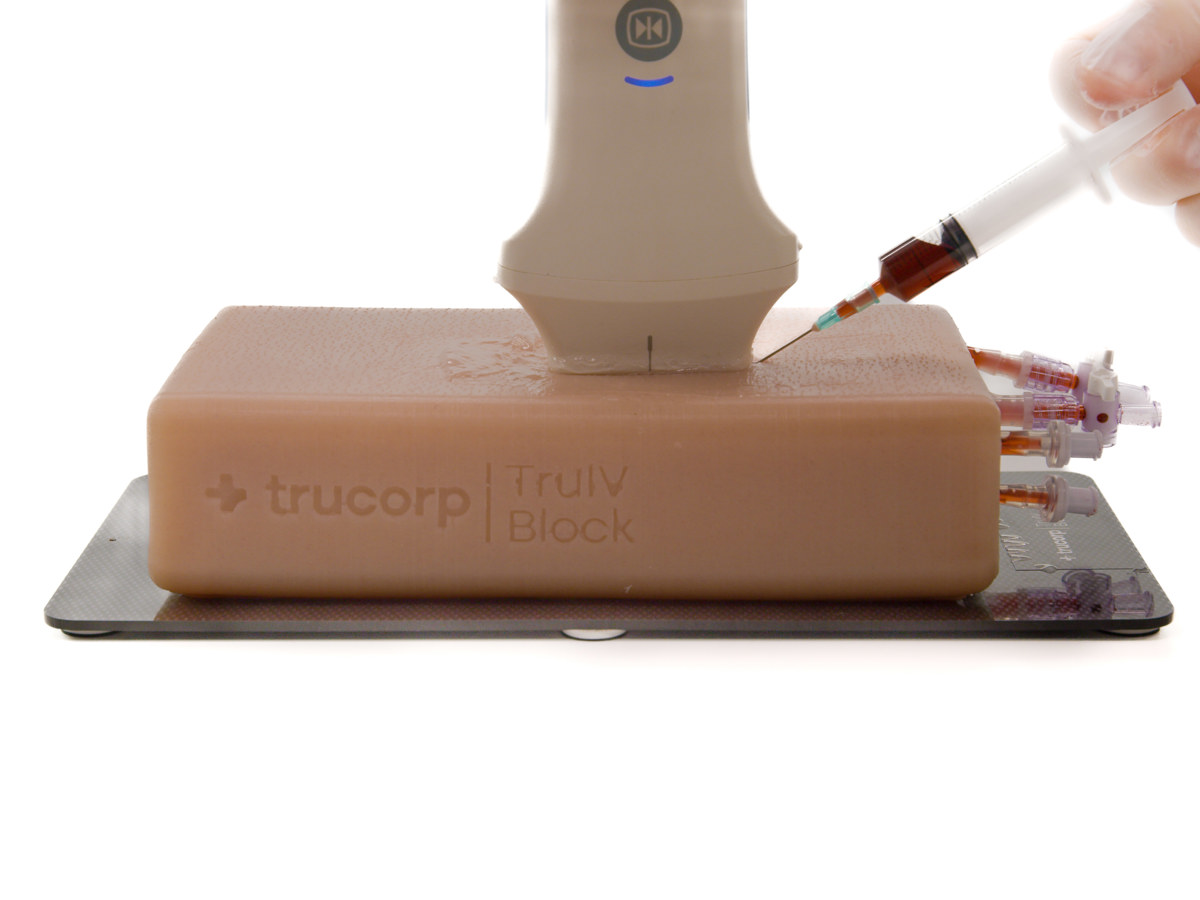
Procedural Ultrasound
Procedural ultrasound is performed to guide or assist a medical procedure, rather than solely to diagnose or evaluate anatomy. It combines real-time imaging with hands-on procedural intervention, allowing clinicians to visualize internal structures dynamically while performing procedures to improve accuracy, safety, and patient outcomes.

What sort of procedures are done under ultrasound guidance?
- Vascular access: Central venous catheterization (CVC), peripheral IV insertion (including difficult access), and arterial line placement
- Therapeutic drainage: Thoracentesis (removal of pleural fluid), paracentesis (removal of peritoneal fluid), abscess drainage or aspiration, pericardiocentesis (removal of fluid from the pericardial sac)
- Anesthesia and pain management: Peripheral nerve blocks, epidural and spine injections, joint and tendon sheath injections
- Biopsies and tissue sampling: Biopsies of the liver, kidney, thyroid or lymph nodes, and fine-needle aspiration (FNA) of superficial or deep lesions
- Guidance in Critical Care: Lumbar puncture, epidural placement, bladder catheterization, percutaneous tracheostomy, cardiac or lung procedures such as – pericardial effusion drainage, or pneumothorax before needle decompression