News
Joint Injections for Pain Relief
24 March 2021
Joint pain, called arthralgia, can be either short term or chronic. It may be accompanied by inflammation, swelling, and tenderness at the site. One thing that cannot be denied is that joint pain can adversely affect daily activities of life, even to the point of debilitation.
Clinically, it may be easy to pinpoint the location of the pain but trying to determine the cause is not always as clear, as pain can be caused by joints or the surrounding ligaments, tendons, or muscles. Single joint pain can occur at any age, most often related to injury or infection. Treating the cause of injury or providing medication for the infection or inflammation along with immobilizing the joint for a few days is generally all that is needed to restore normal function and pain relief.1
When a patient feels pain in multiple joints at the same time, the cause is likely to be termed arthritis. There are many different acute diagnoses, including rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis, but may also include conditions like Lyme disease, gonorrhea, gout, and streptococcal infections. Chronic arthritis may be a continuation of flare-ups from the original acute diagnosis, and can happen in children, but are more common in adults.1
An overarching diagnosis for the cause of joint pain in the aging population is Osteoarthritis (OA), officially defined as the “degeneration of joint cartilage and the underlying bone, most common from middle age onward.”2 According to the World Health Organization (WHO) “the disease most commonly affects the joints in the knees, hands, feet, and spine and is relatively common in shoulder and hip joints. While OA is related to ageing, it is also associated with a variety of both modifiable and nonmodifiable risk factors, including: obesity, lack of exercise, genetic predisposition, bone density, occupational injury, trauma, and gender”.3 Statistically, it is estimated that “10% to 15% of all adults aged over 60 have some degree of OA, with prevalence higher among women than men”.3 Furthermore, despite ongoing research and initiatives related to the treatment of OA, “there is no pharmaceutical product that can halt or reverses the onset of OA”.3
Treatments that have had some success in relieving the pain of OA include injections of medication directly into the painful joint spaces, lasting approximately 2-3 months. While the use of corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid (HA) injections have been used for years, newer approaches are currently being researched, including the injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and placental tissue matrix (PTM) into the joints.4 It goes without saying that success in improved joint injection options that may alleviate the need for surgery would be welcomed by most patients.
While patients can seek treatment from pain centers, emergency departments, and orthopedic specialists, many family physicians also provide injections to patients in community clinics and offices. With the number of aging adults increasing globally and the increased number of potential injections that will ease OA pain, even more practitioners will need to be trained to administer joint injections, including mid-level providers like Physician Assistants/Associates, and Advanced Practice Nurses around the world.
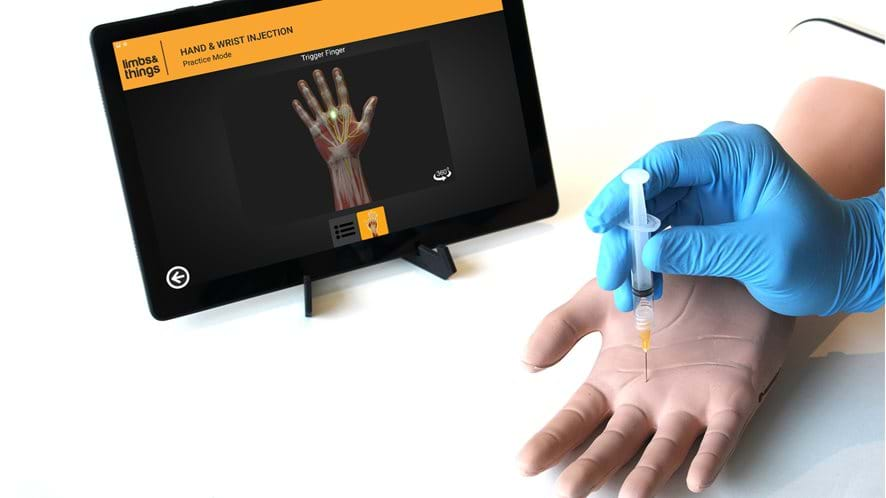
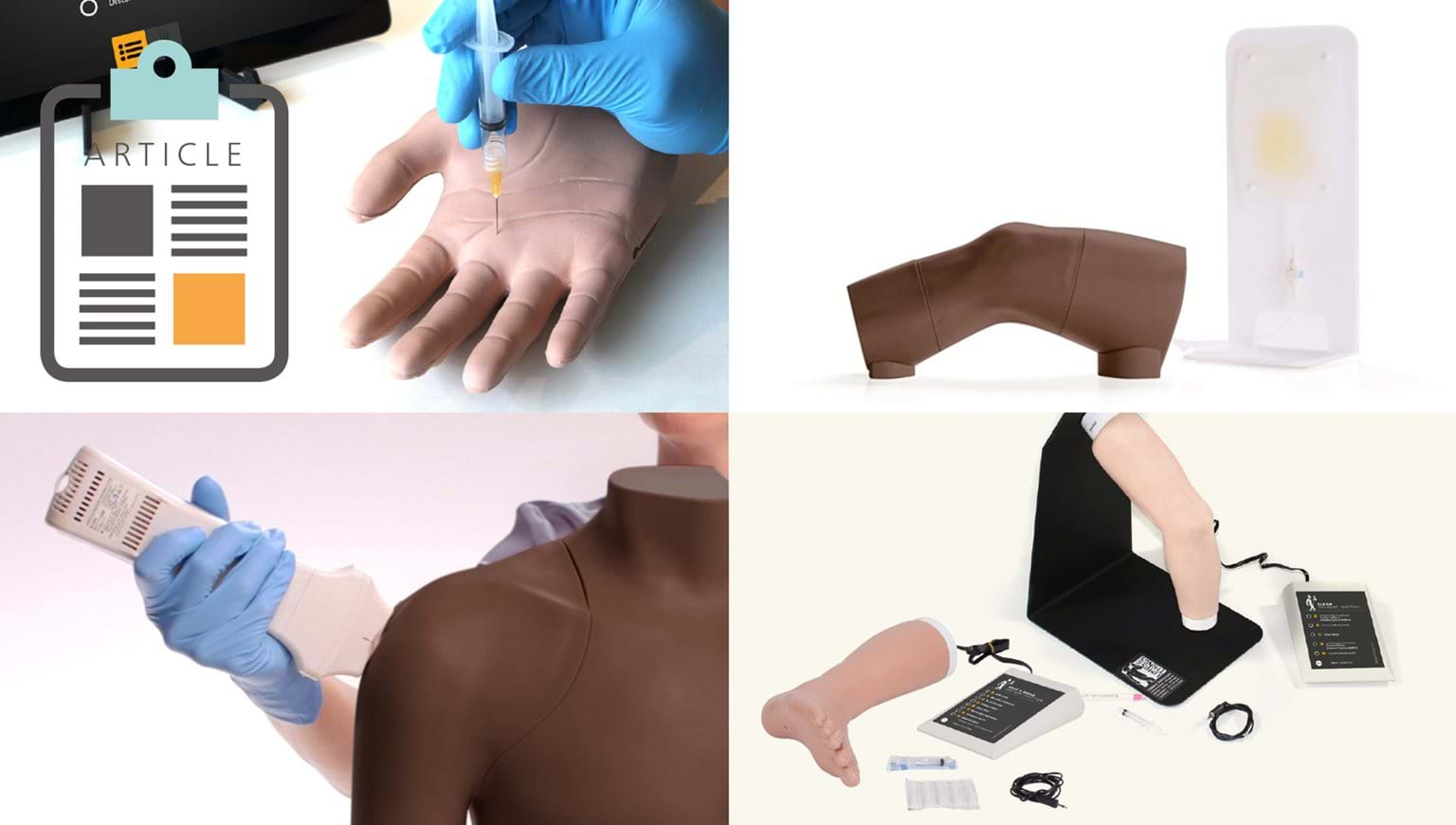
The Limbs & Things Joint Injection Range has many years of proven success in providing training to all levels of providers needing to obtain or maintain their skills in joint injection. New to the existing range is the updated Hand & Wrist Trainer, with added functionality and technology for instant feedback to the trainee. Suitable for all levels of training, the new Hand & Wrist Injection Trainer allows trainees and clinicians to practice and teach injections in five different locations within the hand and wrist. An anatomically correct representation of a man’s hand with important landmarks and underlying structures, the palpation-guided trainer allows for injections into the Carpal Tunnel, De Quervain’s Sheath, Trigger Finger, First Carpometacarpal Joint, and the Distal Radioulnar Joint, whilst the presence of the Median Nerve adds another level of realism and complexity. The trainer comes equipped with an Android tablet, which works in unison with our newly developed app. The app, coupled with innovative sensory technology, provides learners with wireless, real-time feedback from the procedure. An Interactive Anatomy element allows users to rotate the detailed model anatomy 360 degrees so each injection site can be viewed and analyzed from several angles.
Other popular trainers in the range include the palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Shoulder, Elbow, Foot & Ankle, and the most popular palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Knee Joint Injection models.
As always, Limbs & Things is committed to providing training tools for practitioners to provide accurate and safe treatments to patients with competence and confidence. For more information about our joint injection range, contact our team.
References:
1: Merck Manual: Joint Pain: Single Joint/Many Joints
2: Oxford Languages Dictionary
3: WHO: Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion: osteoarthritis
4: Cleveland Clinic: Injections That May Ease Your Joint Pain