






Knee Aspiration & Injection Trainer with Ultrasound Capabilities (Dark Skin Tone)
Skin Tone
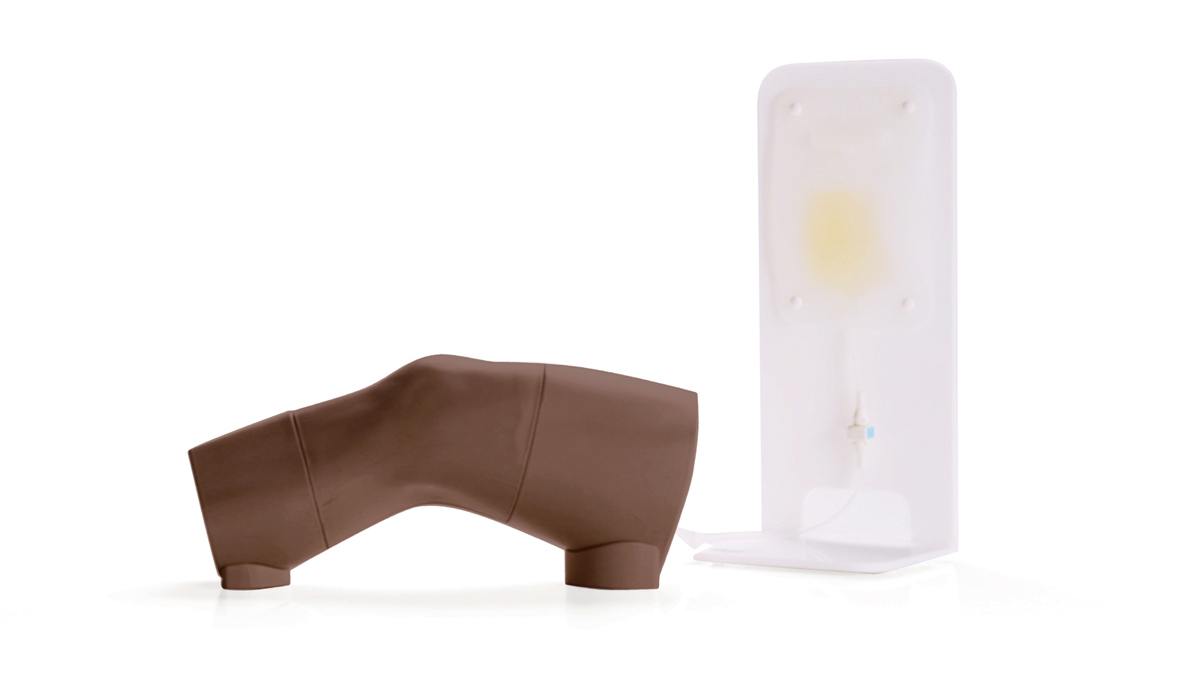
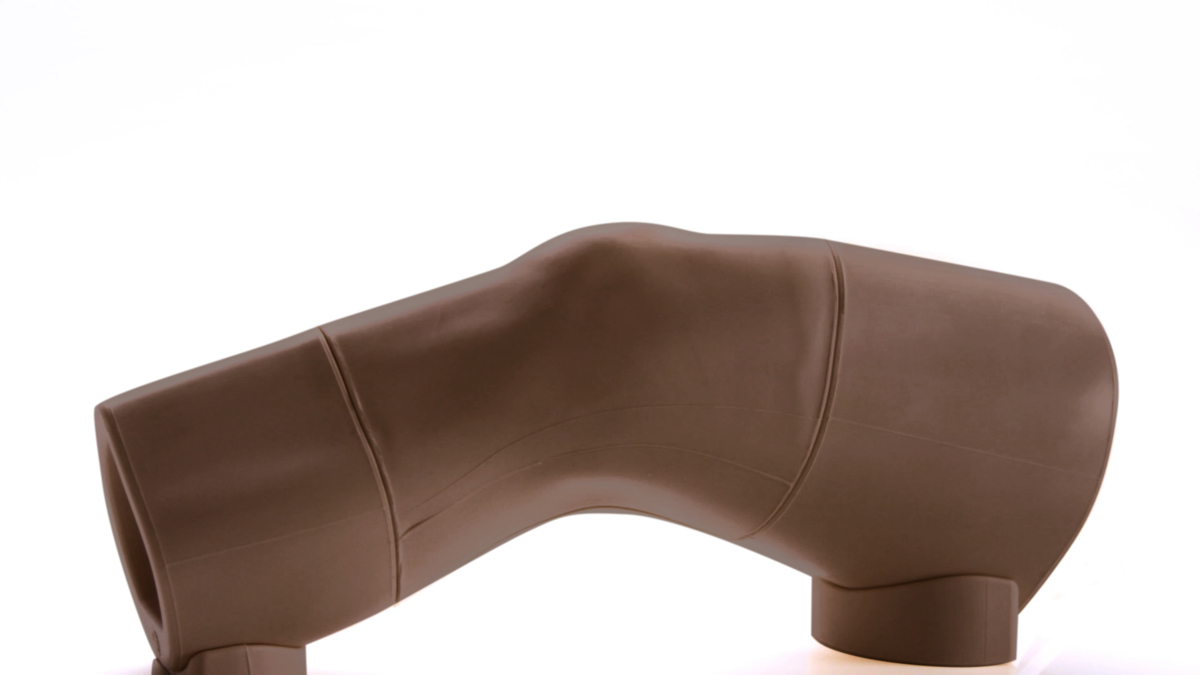
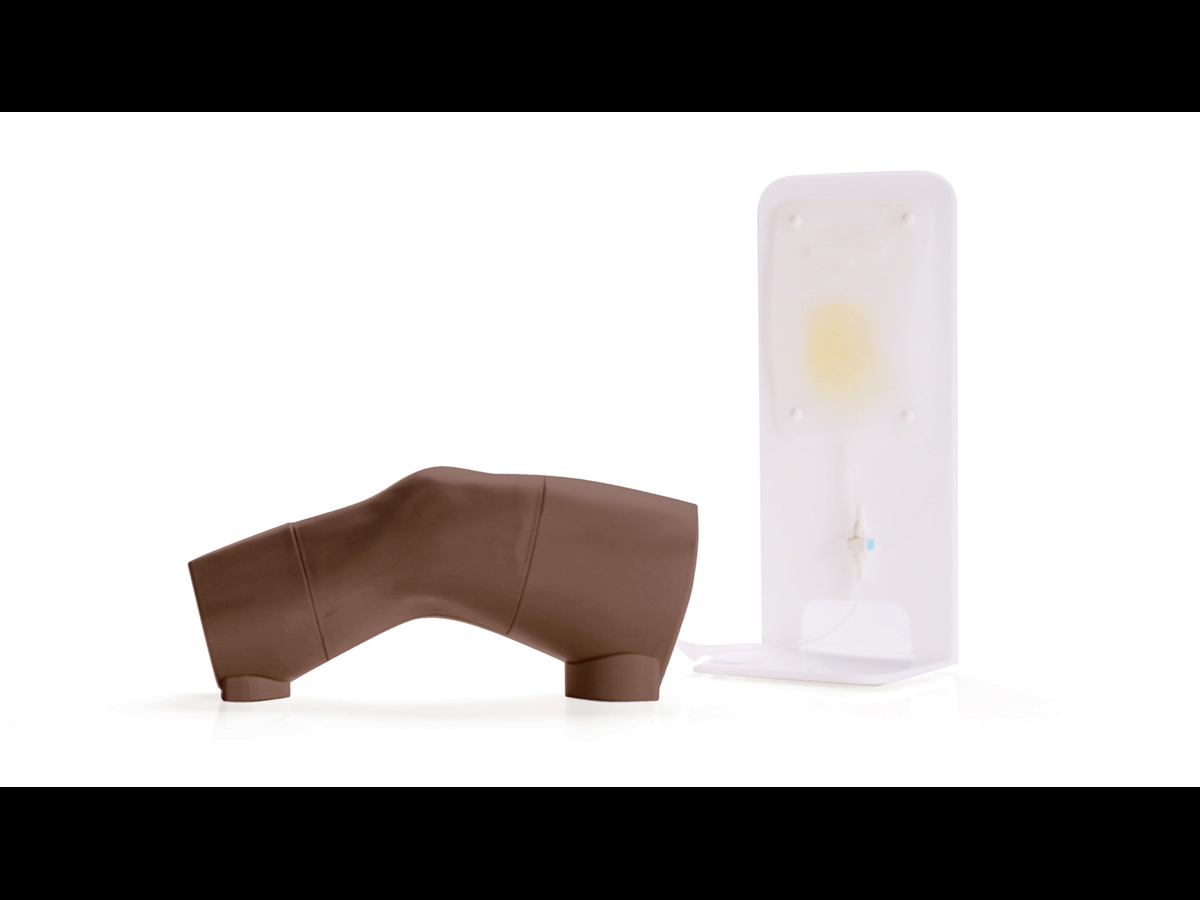
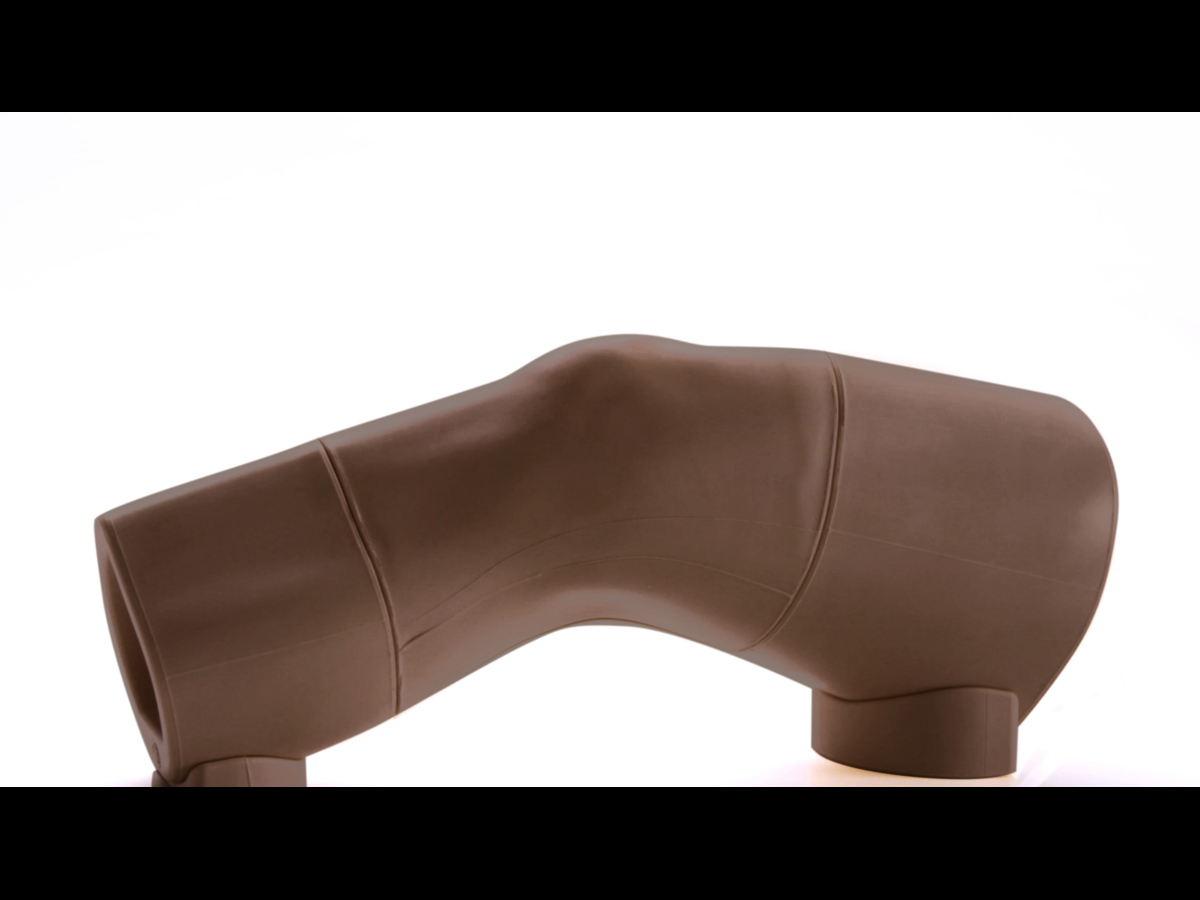
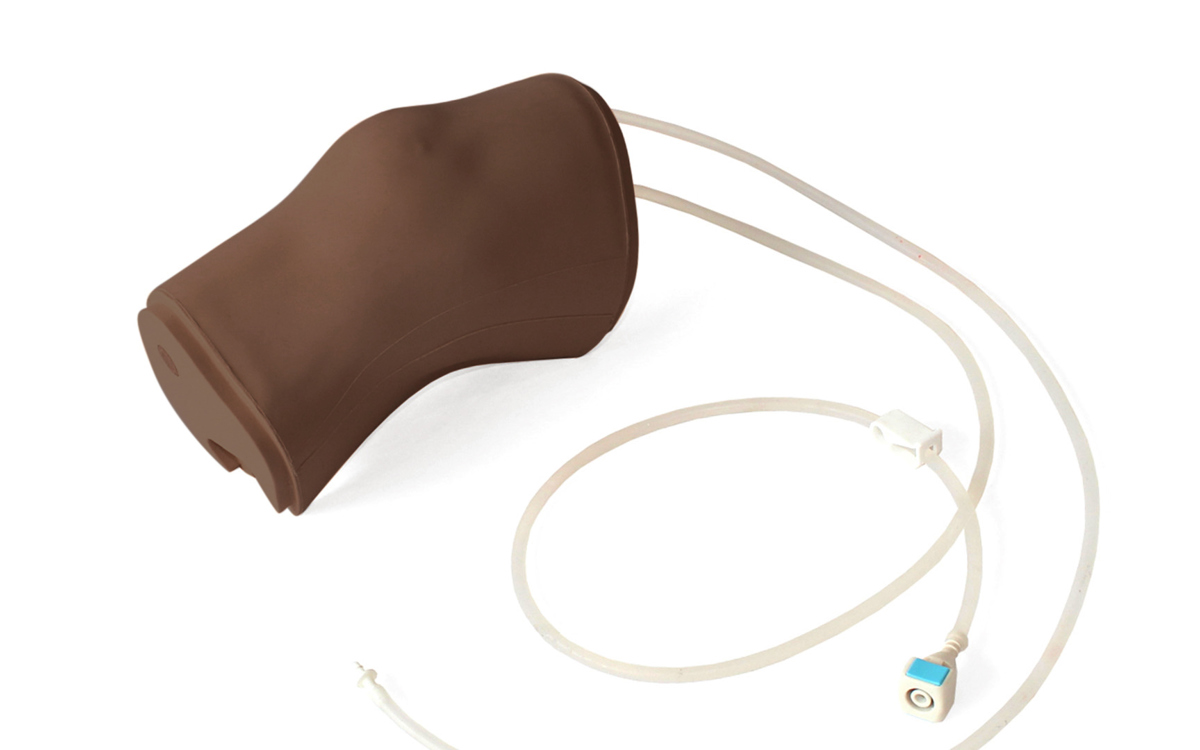
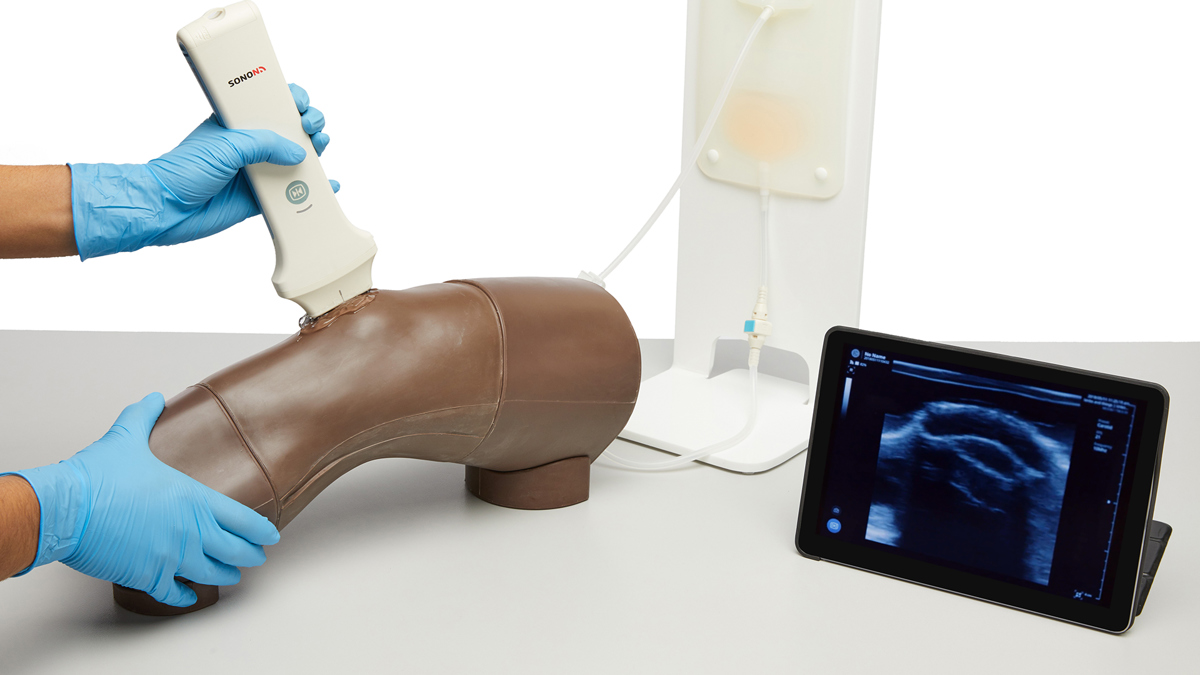
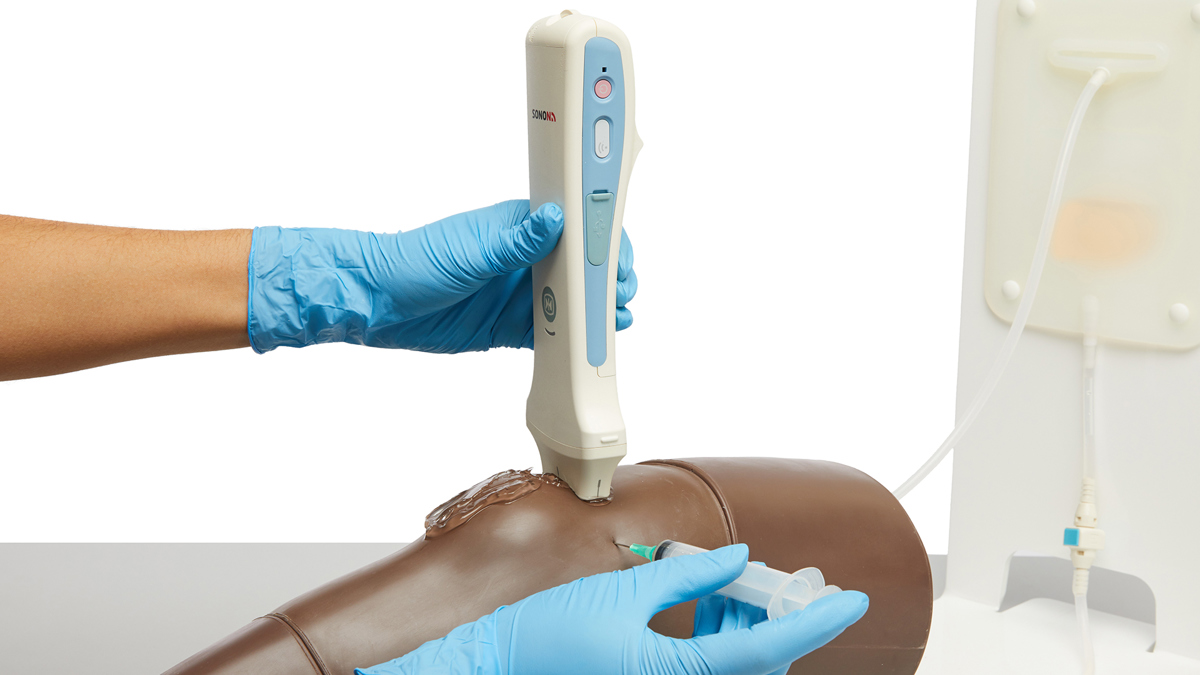
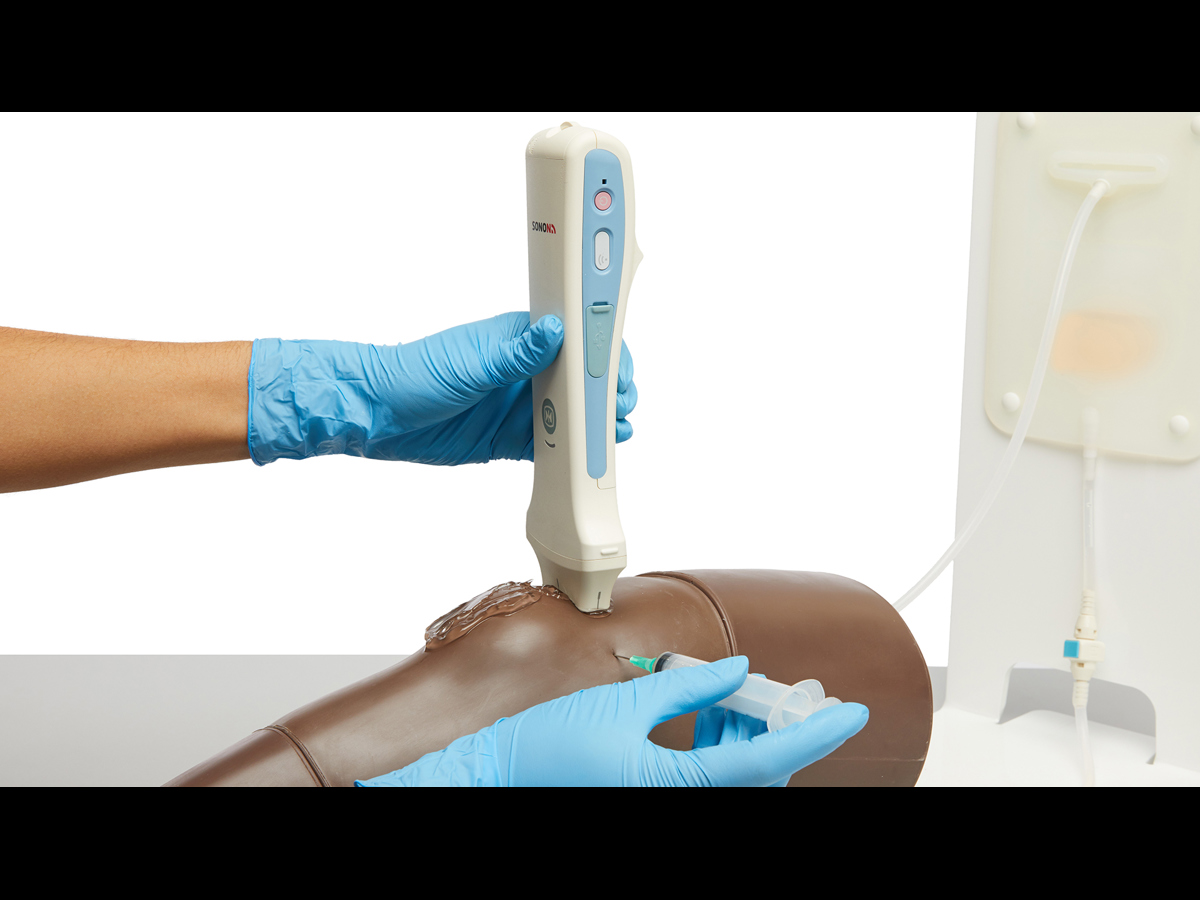
An anatomically accurate adult knee model for injection and aspiration of synovial fluid from the knee joint, from both the lateral and medial aspects, using palpation or ultrasound guidance.
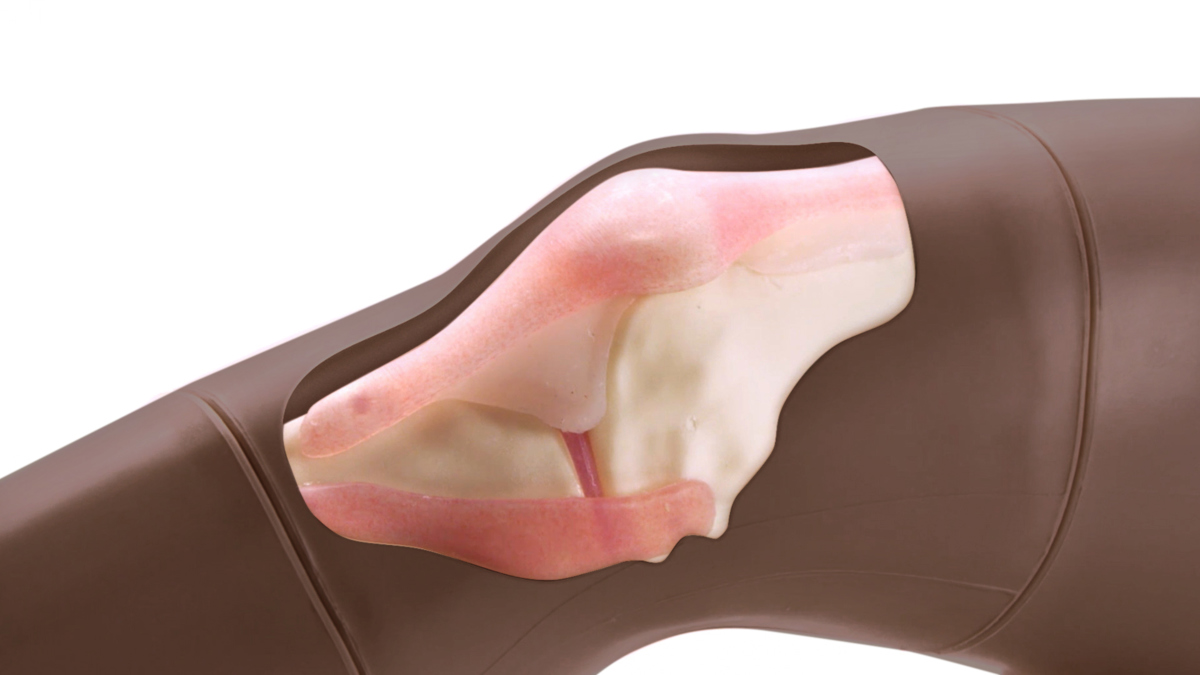
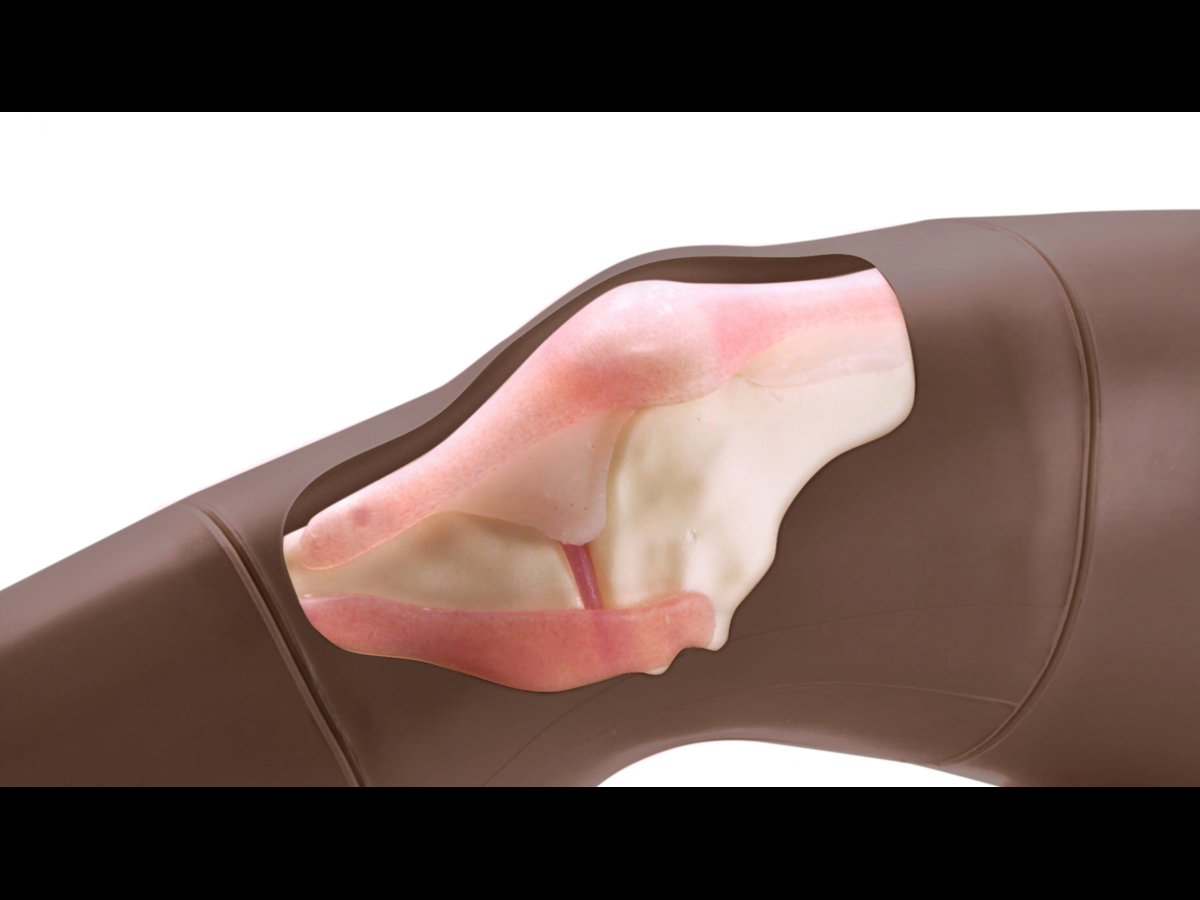
The robust sealed knee includes: knee joint, patella, patellar tendon and the suprapatellar space.
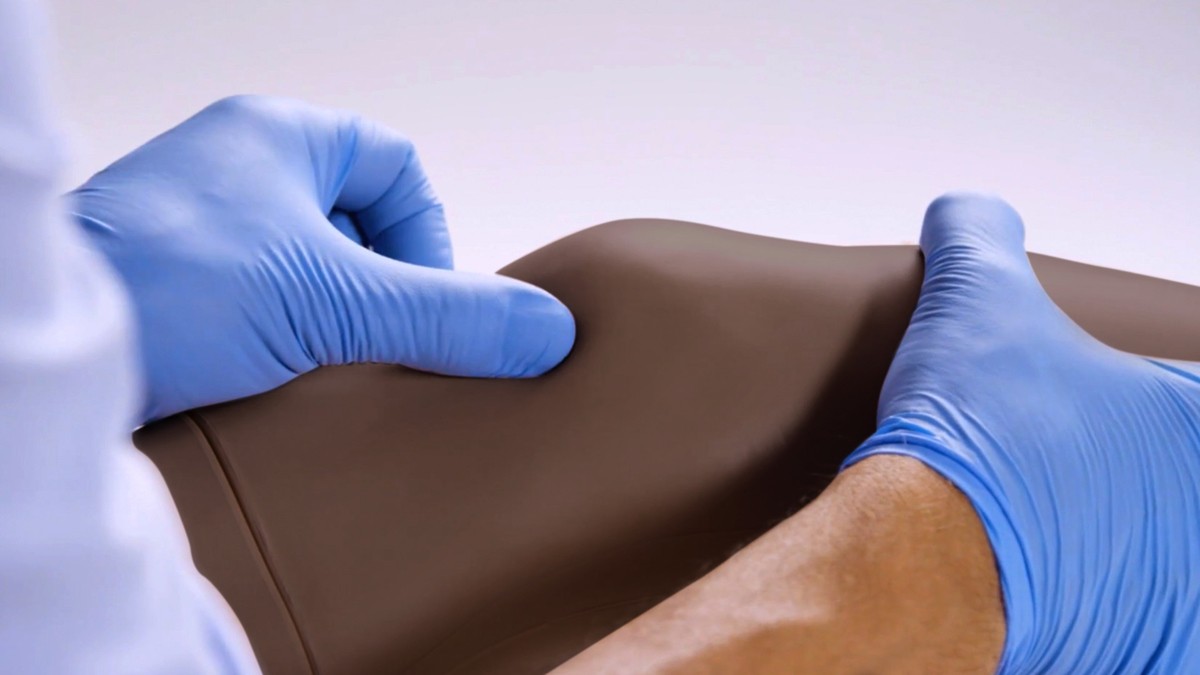
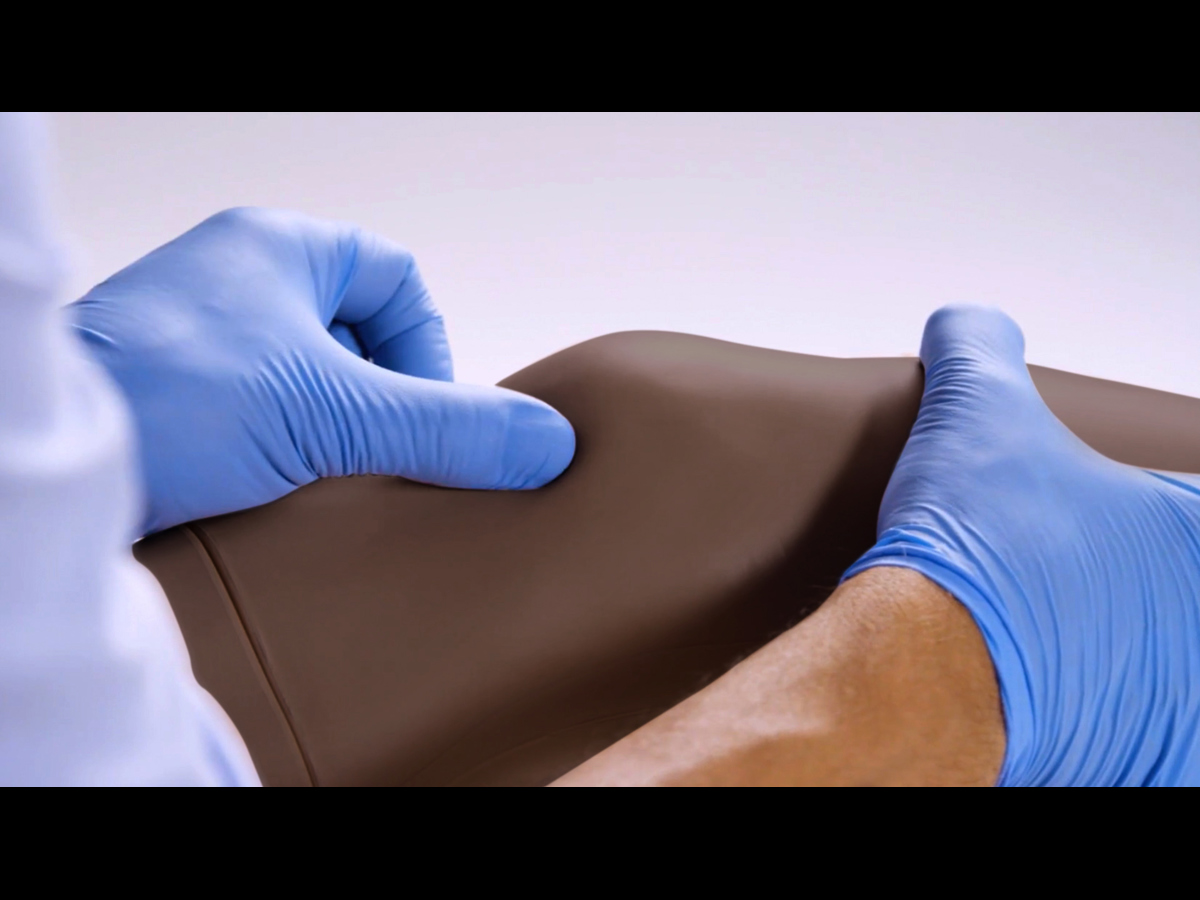
Discrete muscle, skin and fat layers, provide realistic tissue and needle response, while key anatomical landmarks are realistic to palpate. This enables trainees to improve their accuracy of injection and aspiration through repeatable practise.
Performing knee aspirations and injections are fundamental skills required for Internal Medical Trainees, as well as Rheumatologists, Doctors practising General Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgeons*
An anatomically accurate adult knee model for injection and aspiration of synovial fluid from the knee joint, from both the lateral and medial aspects, using palpation or ultrasound guidance.
The robust sealed knee includes: knee joint, patella, patellar tendon and the suprapatellar space.
Discrete muscle, skin and fat layers, provide realistic tissue and needle response, while key anatomical landmarks are realistic to palpate. This enables trainees to improve their accuracy of injection and aspiration through repeatable practise.
Performing knee aspirations and injections are fundamental skills required for Internal Medical Trainees, as well as Rheumatologists, Doctors practising General Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgeons*
This model was evaluated by Charles Wakeley (Bristol Royal Infirmary, UK) and Andrew Grainger (Leeds Teaching Hospitals, UK).
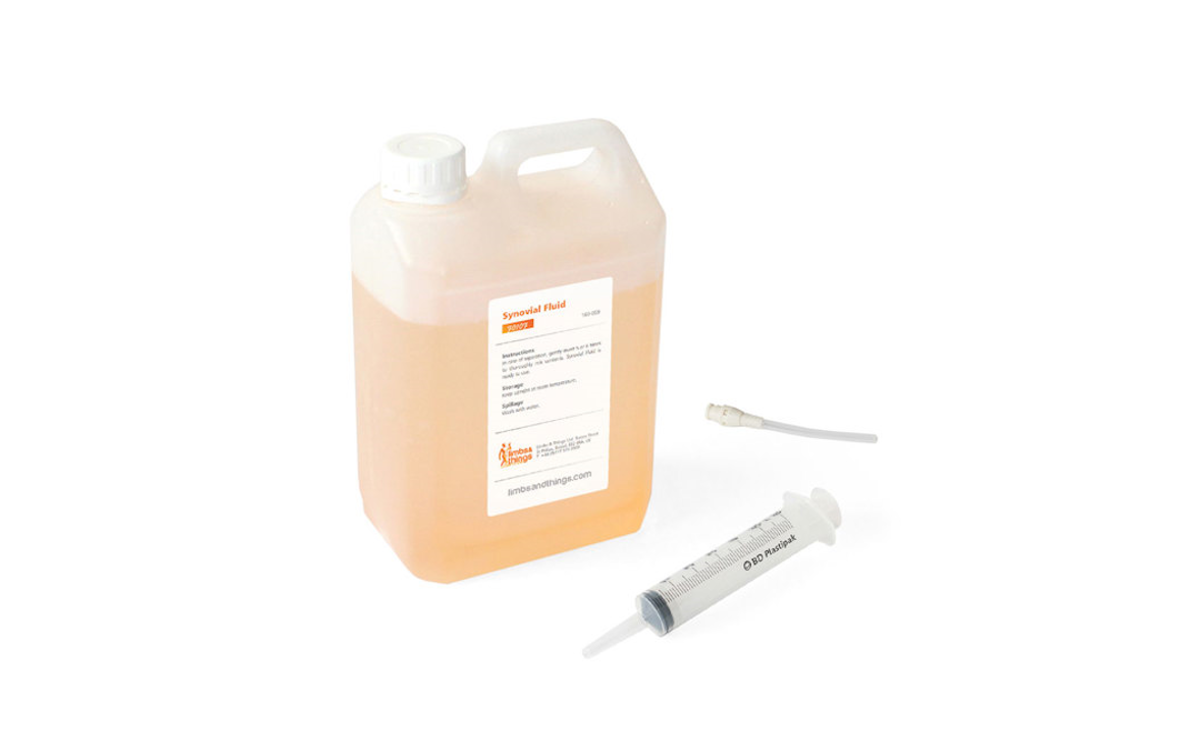
The Synovial Fluid used with this product now contains a new preservative which is approved for use by EU cosmetic regulations which means that it is safe for extended skin contact.
We still recommend the use of gloves, as the pigments may stain skin and clothes.
*Specialty Training Curriculum for Core Medical Training, Joint Royal Colleges of Physicians Training Board, 2009, amended 2013 / Section 5 Practical Procedures, Specialty Training Curriculum for Rheumatology, Joint Royal Colleges of Physicians Training Board, 2010 / Section: Applied Clinical Skills: General, Page 55, Specialist Training in Trauma & Orthopaedics Curriculum, 2013
Overview
- 1,000+ stabs per module with 21 gauge needle
- Precise, palpable anatomy with bony landmarks
- Robust, sealed knee unit that holds all anatomy
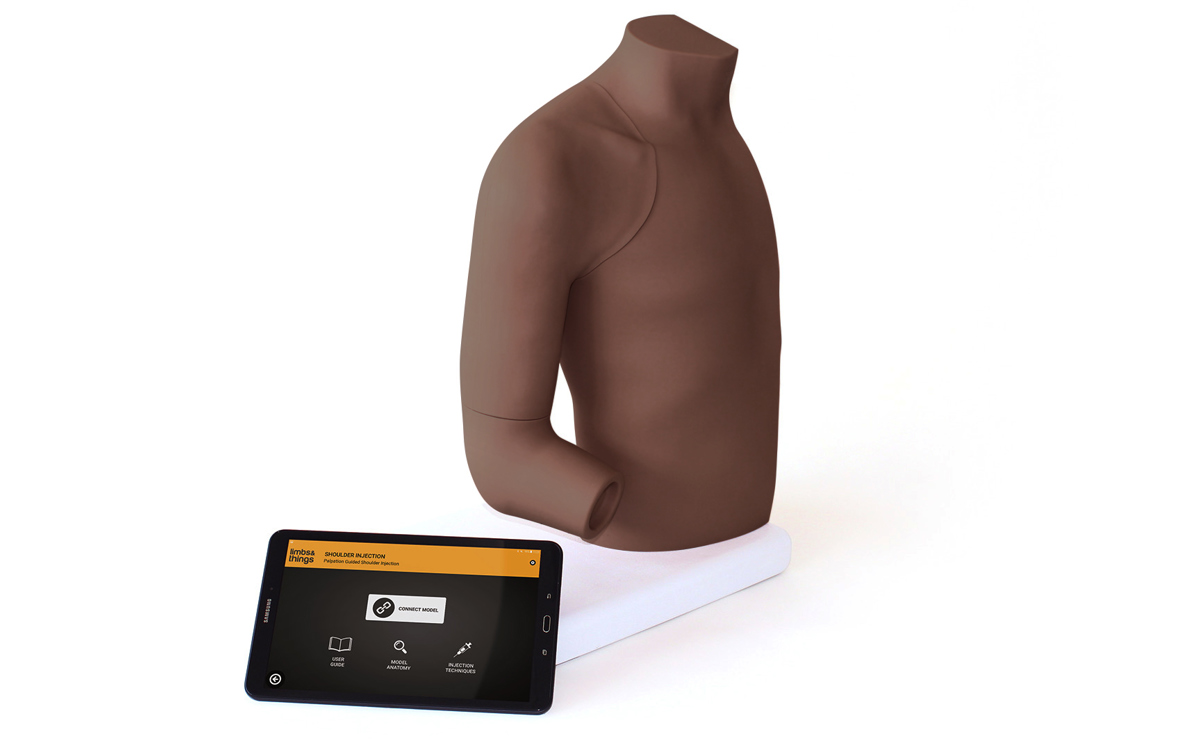
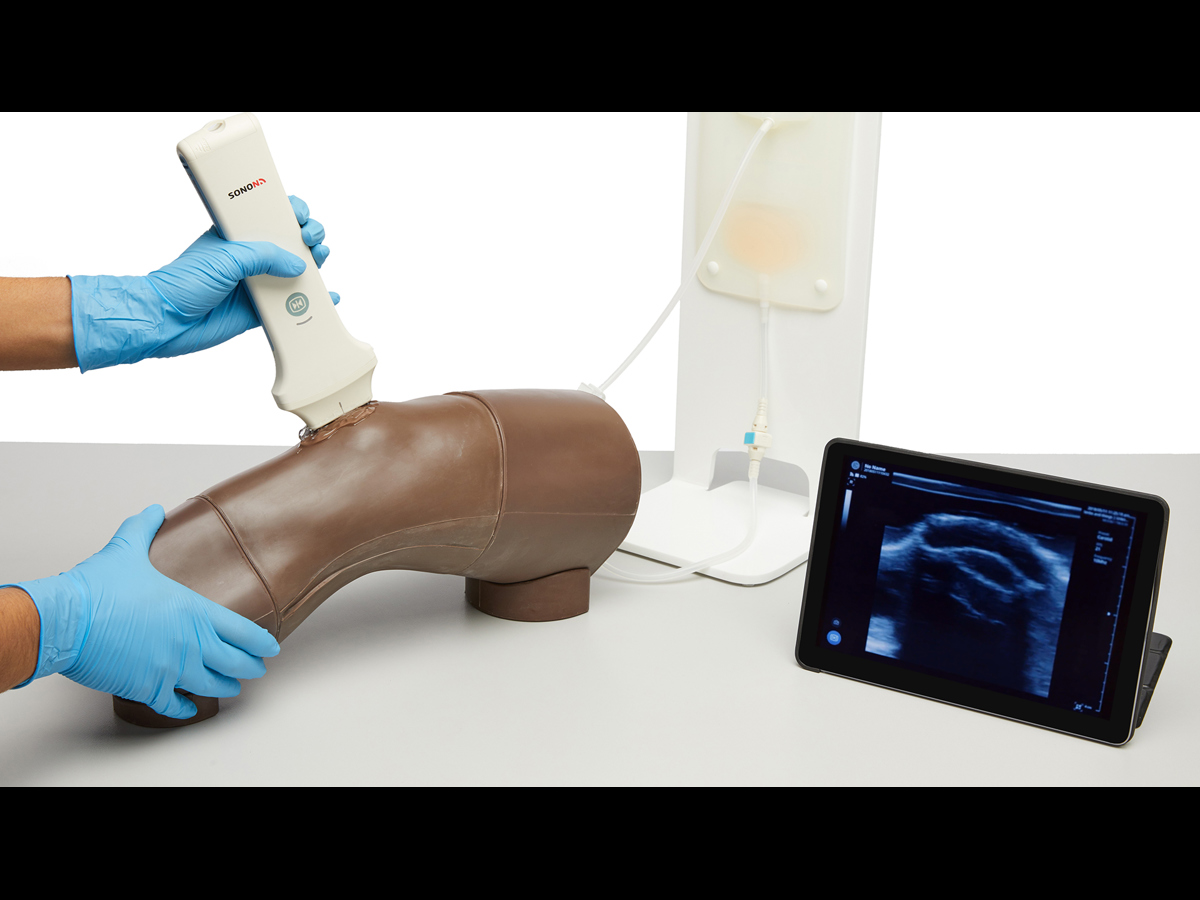
- Key internal landmarks visible under ultrasound
- Compatible with all standard ultrasound machines
- Echolucent material allows aspiration and injection under ultrasound guidance or using the palpation method
- Suitable for Undergraduate and Postgraduate medical study
- Knee skin is watertight
Realism
- Discrete muscle and skin layers provide realistic tissue and needle response
- Anatomically accurate synovial sac and palpable patella
- Realistic color and consistency of synovial fluid
Versatility
- Can be used with leg supports for supine position, or without leg supports for side of bed position
- Caters for ultrasound-guided techniques as well as palpation
- Separate Fluid Bag & Stand ensure the model is easy to use and mobile
- Clear indicator on Fluid Bag to prevent overfilling
Cleaning
- Clean off any residual ultrasound gel from the knee injection trainer
- Skin surface should be cleaned with a soft, damp cloth, using warm water and mild detergent
- Empty any remaining fluid from the knee once the procedure is complete
- Allow knee injection model to dry before storing
Safety
- This product is latex free
- If the model sustains damage, refer all servicing to qualified servicing personnel
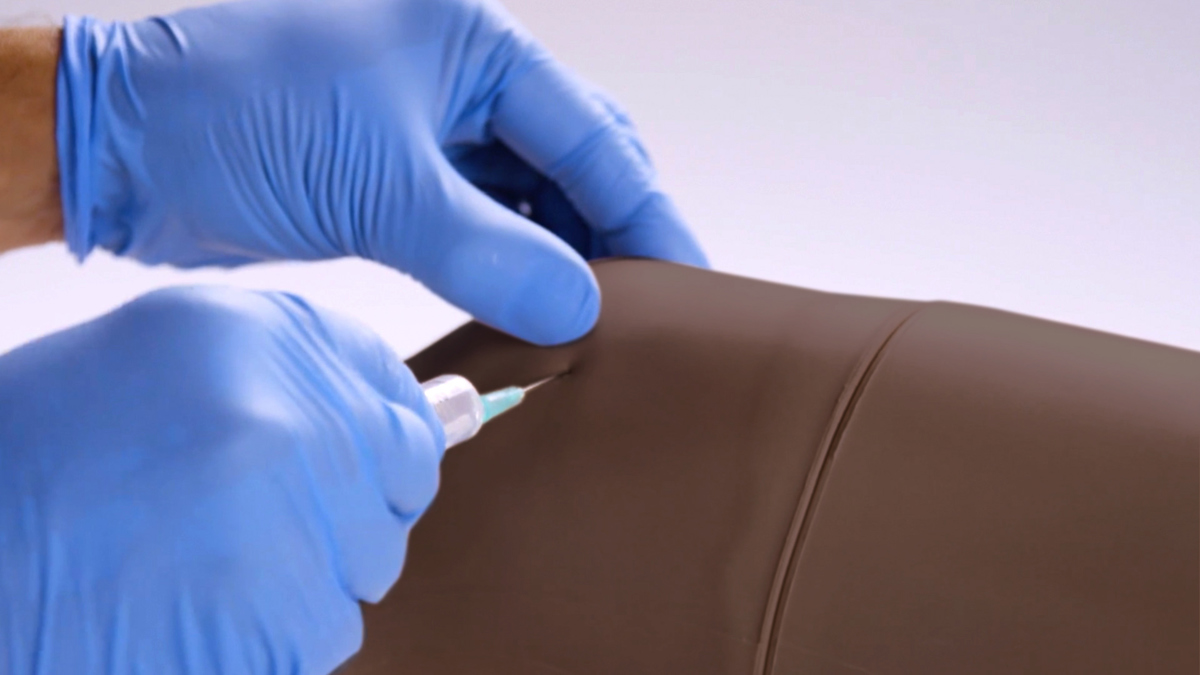
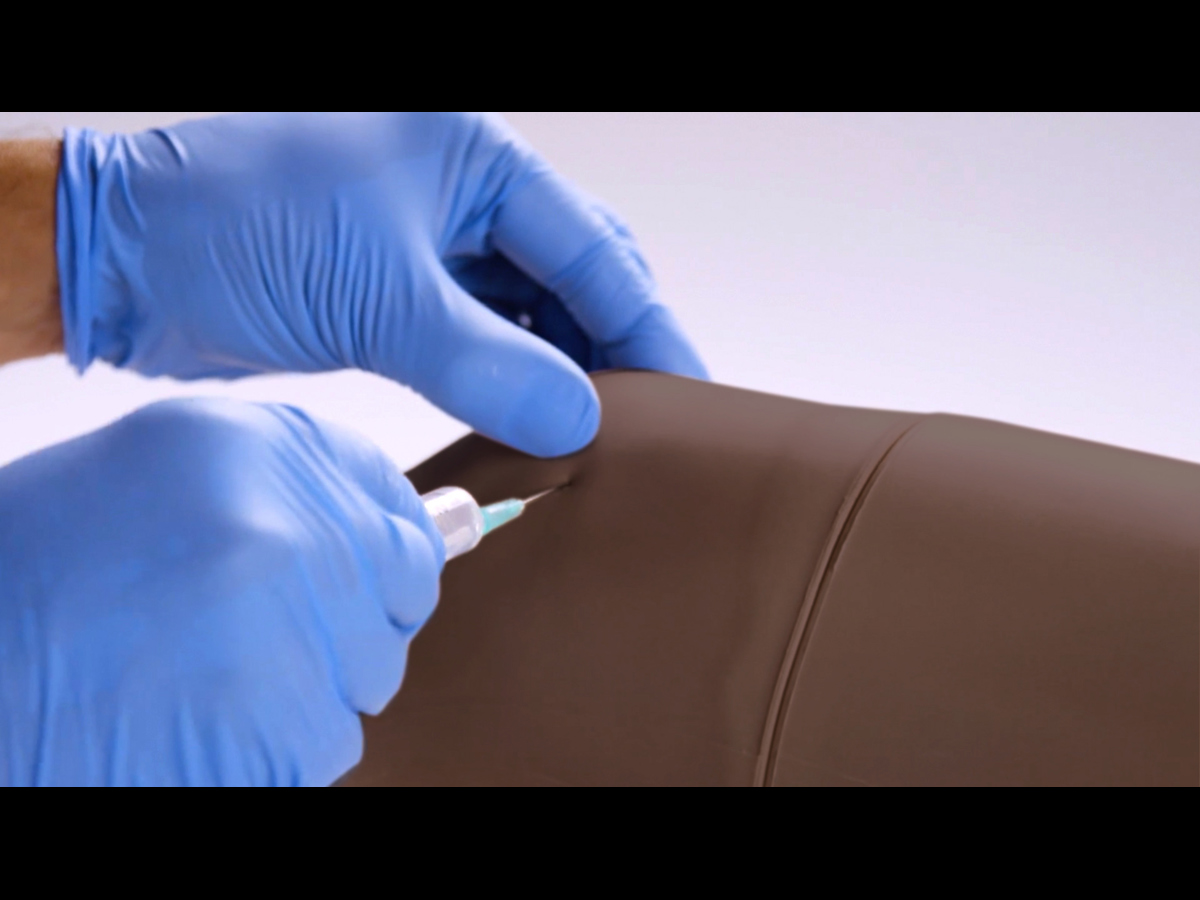
- During practice injections, be sure to remove the needle at the same angle as inserted, removing at an angle can cause the knee skin to split
- We advise that you do not use simulator if the skin of the knee is torn
- Always store/dispose of needles safely in the sharps bin supplied or a suitable alternative
- While the new Synovial Fluid in this product contains a new preservative (approved for use by EU cosmetic regulations) meaning it is safe for extended skin contact, we still recommend the use of gloves while using this product
Simulated Patient
- This knee model can be used with a simulated patient to practice knee joint aspiration and injection
Anatomy
Key anatomical landmarks are realistic to palpate:
- Skin
- Subcutaneous fat, quadriceps tendon & patellar ligament
- Prefemoral fat pad
- Suprapatellar fat pad
- Hoffa’s or Infrapatellar fat pad
- Femur
- Medial & lateral collateral ligament
- Tibia
- Patella
- Joint space & synovial recess
- Meniscus
- Muscle mass of quadriceps
Skills Gained
- Injection into joint cavity
- Aspiration of synovial fluid from both the lateral and medial aspects
- Competence using ultrasound technology to perform
- systematic scanning techniques and examination of the knee joint
- Identification of anatomical landmarks using ultrasound guidance or the palpation method
- Patient positioning and management
- Recognition of joint effusion
- Ballottement
Works with the following products:
References
AAFP Residency Guidelines, Musculoskeletal and Sports Medicine, Reprint No. 265 (p.4): Indications, limitations, contraindications, and informed consent for office-based musculoskeletal procedures such as: a. Common joint aspirations b. Common joint injections c. Common injections for bursitis d. Common injections for tendinopathy
Core Curriculum Outline for Rheumatology Fellowship Programs, American College of Rheumatology, 2015 "Demonstrtae competency in obtaining synovial fluid from diarthrodial joints, bursae, and tenosynovial structures."
Association of American Medical Colleges:Recommendations for Clinical Skills Curricula for Undergraduate Medical Education,Appendix B; Clinical Testing and Procedural Skills p.23 "Knee examination (including manoeuvres); Musculoskeletal Joint Aspiration Technique; Joint Fluid Examination."
Adult-Gerontology Acute Care And Primary Care NP Competencies 2016, p.42 Primary care practice skills which includes, but is not limited to: • Joint aspiration and injection. Nurse Practitioner (NP) and Physician Assistant (PA) Rheumatology Curriculum Outline, American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and Association of Rheumatology Health Professionals (ARHP), 2017, p.8 Perform procedures, as agreed upon by the supervising/collaborating rheumatologist and NP/PA: 2. Joint and soft tissue injections (adult) a. Indications and contraindications b. Large and medium joints (i.e., knee)
Nurse Practitioner (NP) and Physician Assistant (PA) Rheumatology Curriculum Outline, American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and Association of Rheumatology Health Professionals (ARHP), 2017, p.8 Perform procedures, as agreed upon by the supervising/collaborating rheumatologist and NP/PA: 2. Joint and soft tissue injections (adult) a. Indications and contraindications b. Large and medium joints (i.e., knee)
RAGCP Lifelong Learning Curriculum: Appropriate Procedures (2016): guided and unguided musculoskeletal injections (eg trigger point, joint, bursal, intra-articular, carpal tunnel, nerve blocks) The RACGP Curriculum for Australian General Practice 2011: Musculoskeletal Medicine, Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. Identify and acquire musculoskeletal procedural skill competency levels appropriate for the required service provision level, eg. if performing joint injections ensure skill competency level has been acquired.
Royal Australasian College of Physicians, Rheumatology Advanced Training Curriculum, Royal Australasian College of Physicians, 2013, p.8 "be competent in the use of appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, including joint and soft tissue injection and aspiration."
ACSEP CURRICULUM, Australasian College of Sports and Exercise Physicians, 2017 Demonstrate proficient and appropriate use of procedural skills, both diagnostic and therapeutic. Assessment: Direct Observation of Procedural Skills (DOPS): Knee joint injection/aspiration Ultrasound guided injection (optional)
NHS National Practitioner Program: Matrix Specification for the Physician Associate (2016). p.105: Skills: Perform knee aspiration using aseptic technique causing minimal distress to patient
Specialty Training Curriculum for Core Medical Training, 2013 CMTs should try to gain at least some experience and independent competency if possible in procedure relating to knee aspiration.
Section: Applied Clinical Skills: General, Page 55, Specialist Training in Trauma & Orthopaedics Curriculum, 2013 “A trainee must be able to demonstrate their competence in the procedures of aspiration and injection of knee joint”.
Specialty Training Curriculum for Sport and Exercise Medicine, Joint Royal Colleges of Physicians Training Board, August 2010, p.53 Skills (mandatory): Safely inject major joints including shoulder, elbow, knee and ankle
The RCGP Curriculum: Professional & Clinical Modules, The Royal College of General Practitioners, 2016, p.327 You may also consider attending courses offering joint injection training.
Specialty Training Curriculum for Rheumatology, Joint Royal Colleges of Physicians Training Board, 2010 ,p.24 Practical procedures: to aspirate and inject joints competently using the appropriate techniques Competency is required in all of the following procedures: o Knee: Joint: Tibio-femoral Soft tissue: Bursal injections.
Clinical Radiology Specialty Training Curriculum, The Royal College of Radiologists, 2019. Ultrasound guided.
Can this knee aspiration and injection model be injected with fluid?
This knee model can be injected with fluids to aid in the practice of administering anti-inflammatory agents. This is commonly done for inflammatory joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, tendonitis, bursitis and, occasionally, osteoarthritis.
With the additional ultrasound capabilities, users can visualise the introduction of fluid to confirm the correct needle placement.
Does the knee trainer allow for suprapatellar bogginess simulation?
Yes, an accumulation of fluid in the suprapatellar region can be created, this will indicate positive results for ballottement.