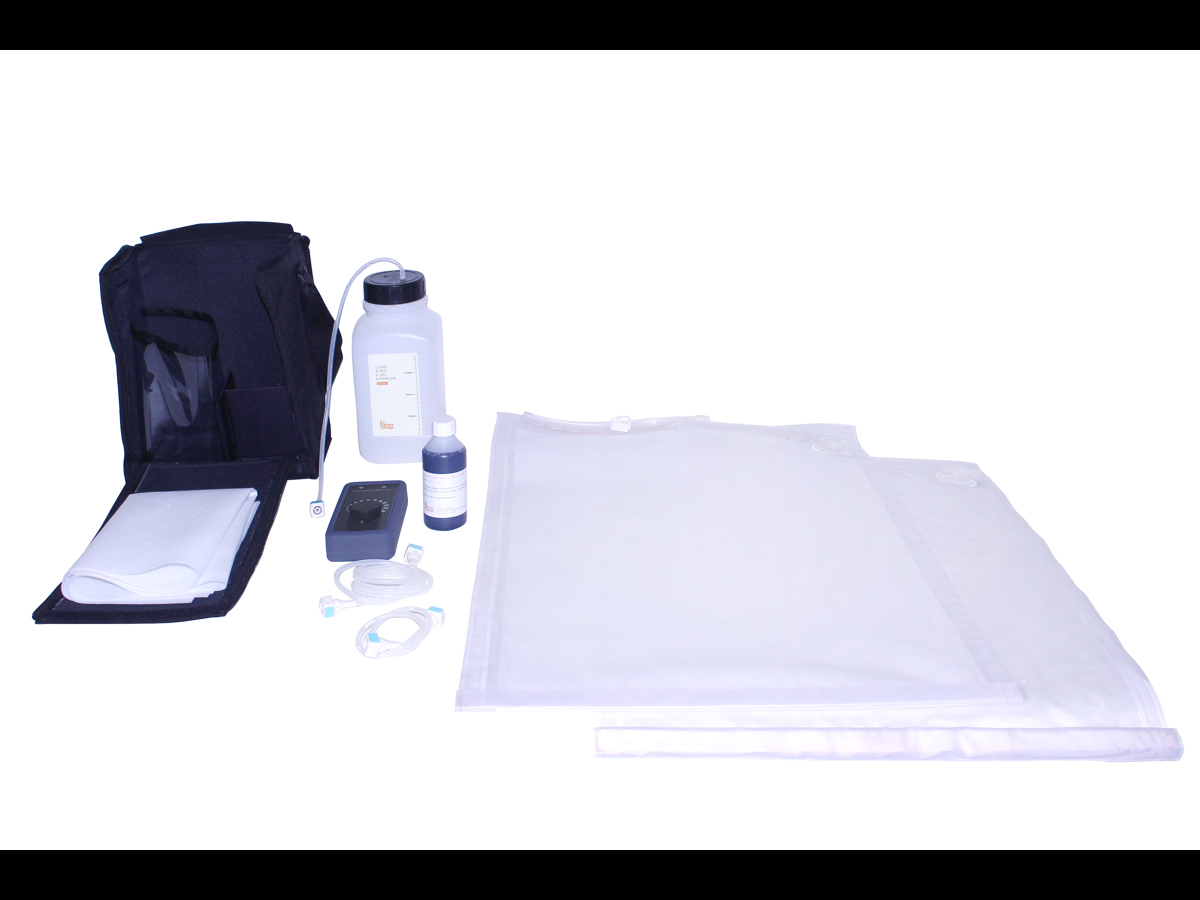








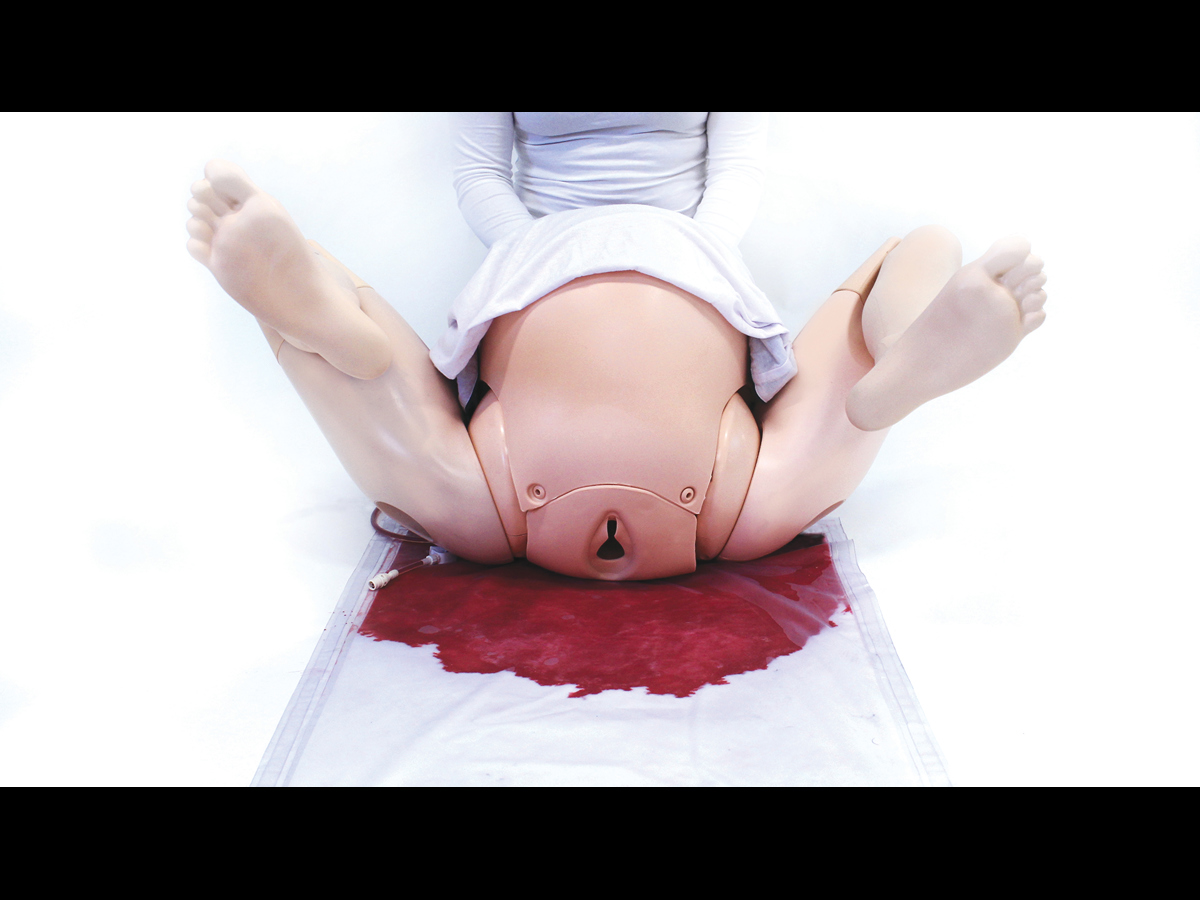
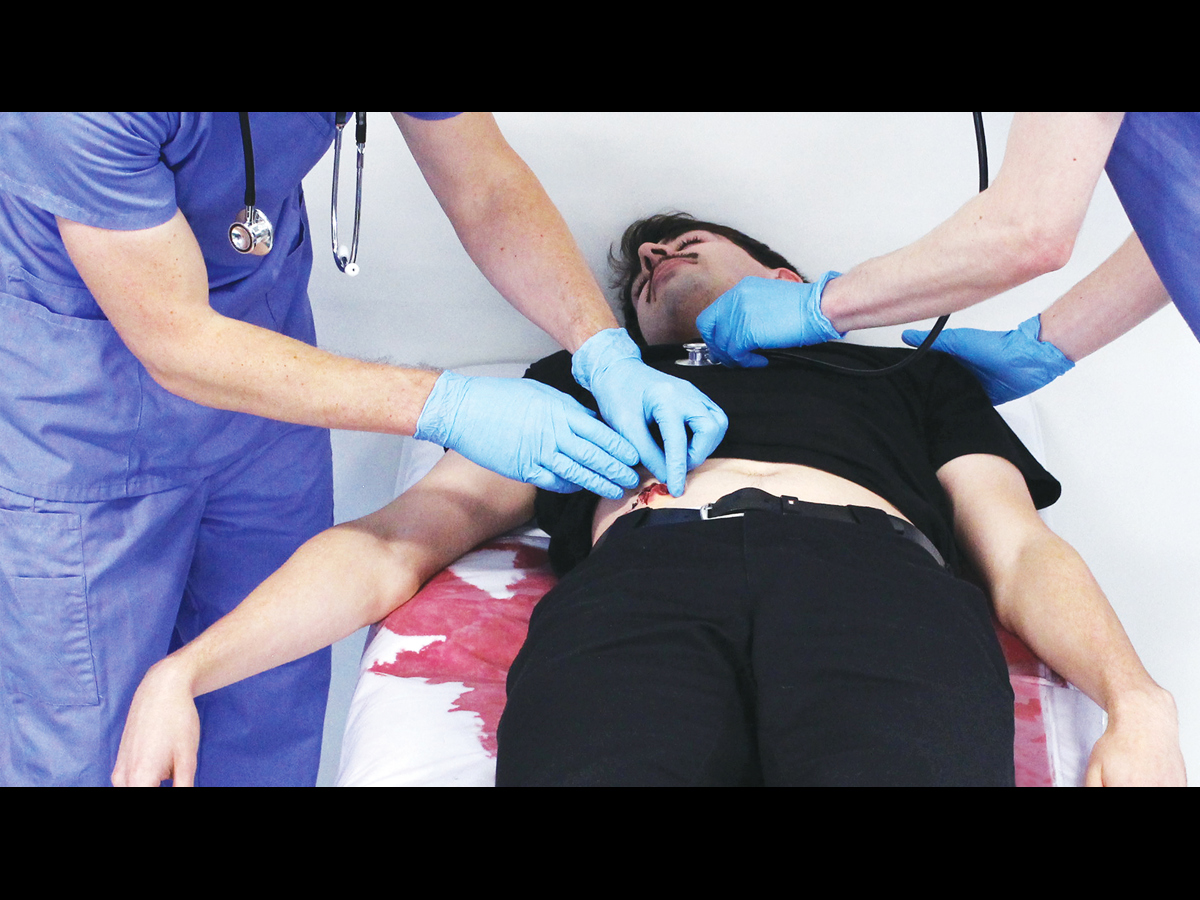


Clean Bleed® Mat – Blood and Fluid Loss Simulator
Adding to cart...
Added to cart
Sorry, something went wrong adding the product to the cart.
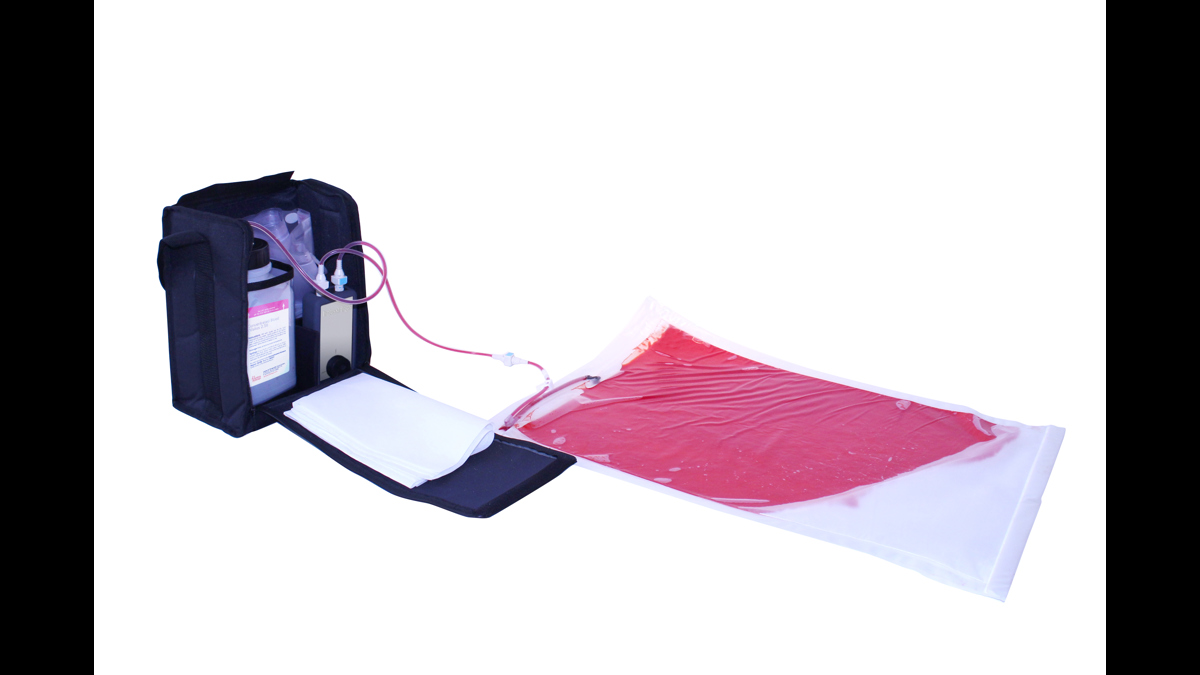
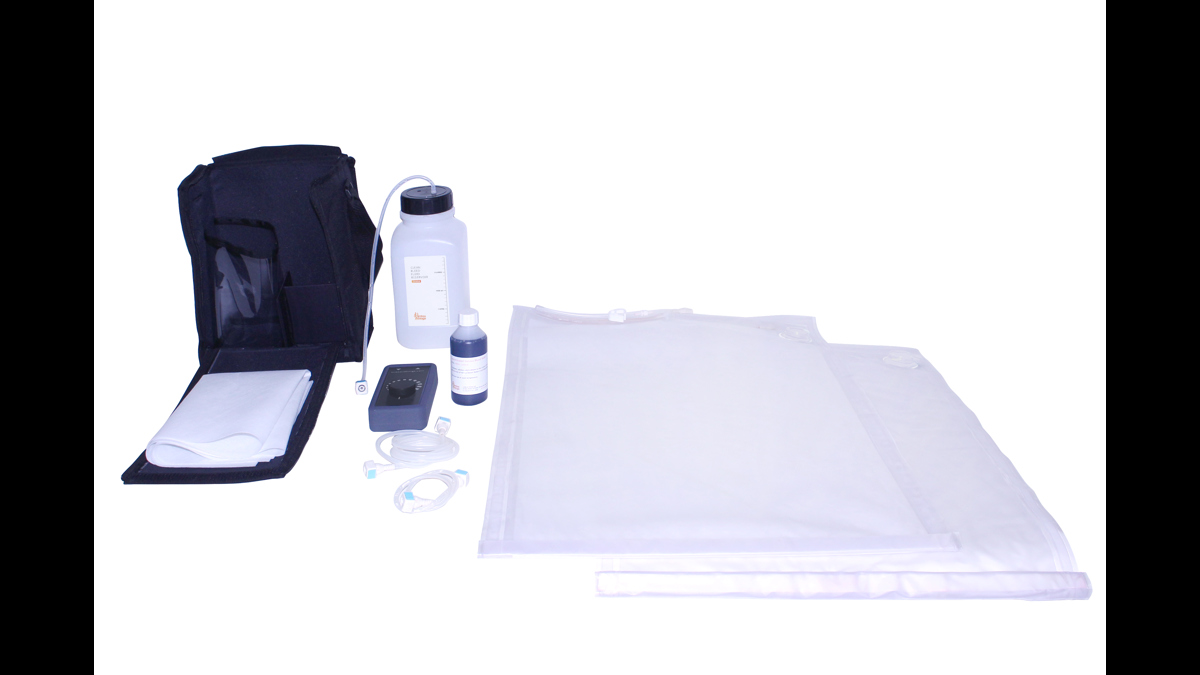
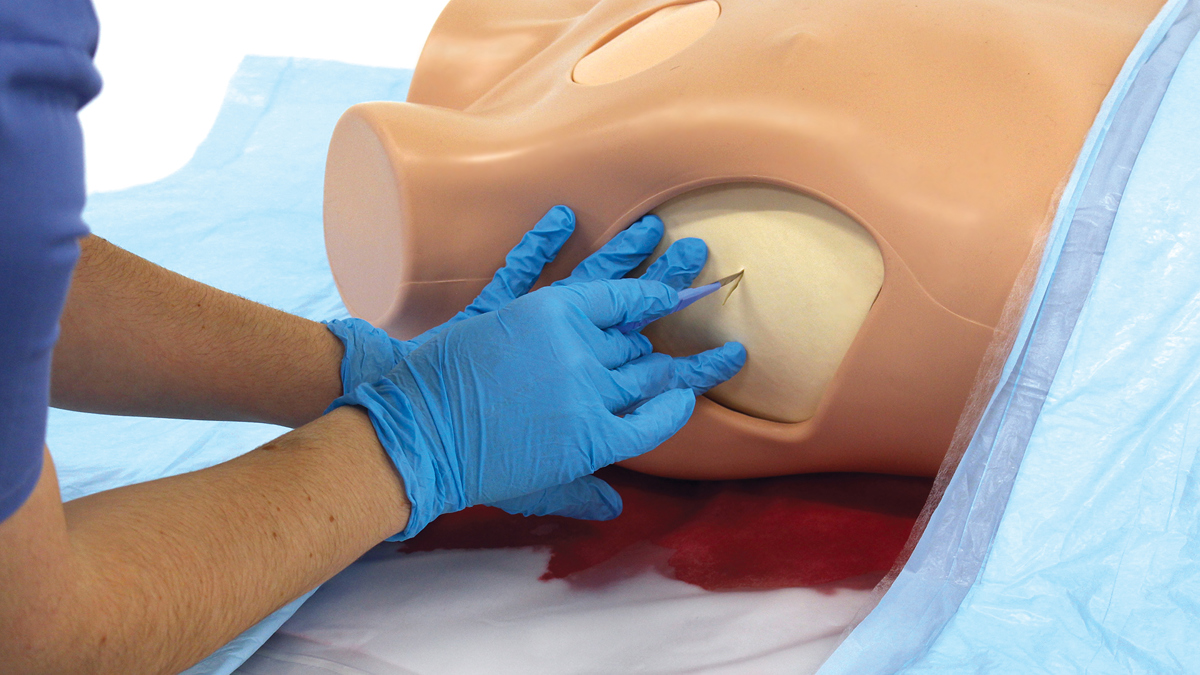
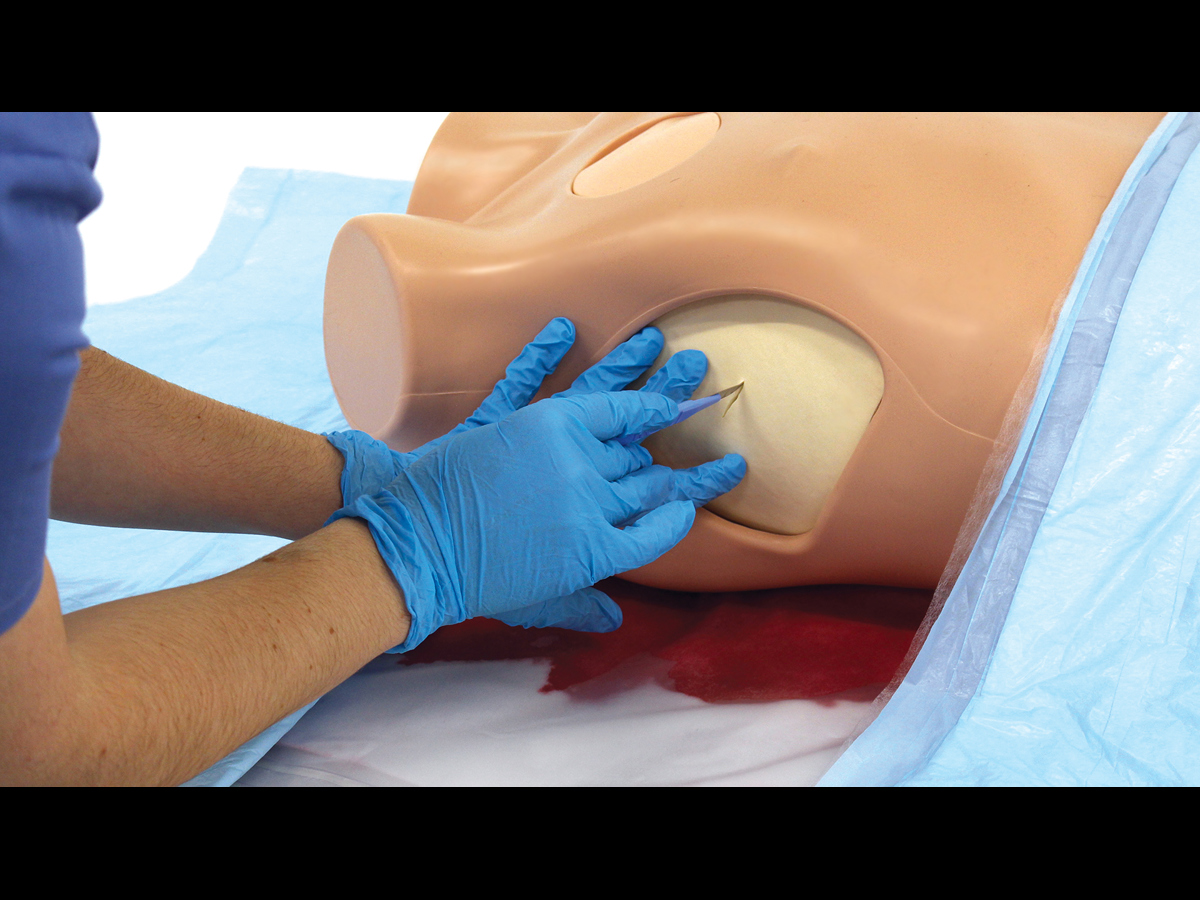
The Clean Bleed® Mat has been designed to support all simulation scenarios. This product can be used with any brand of trainer where external blood or fluid loss is a key indicator and measure of the emergency being simulated.
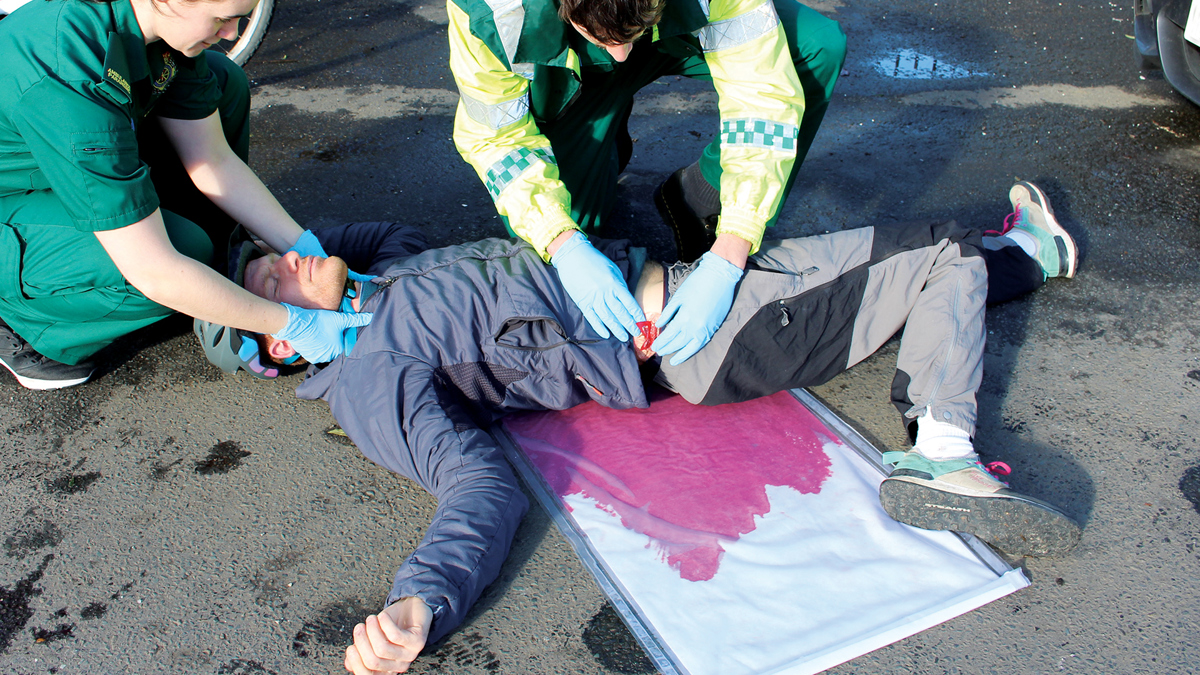
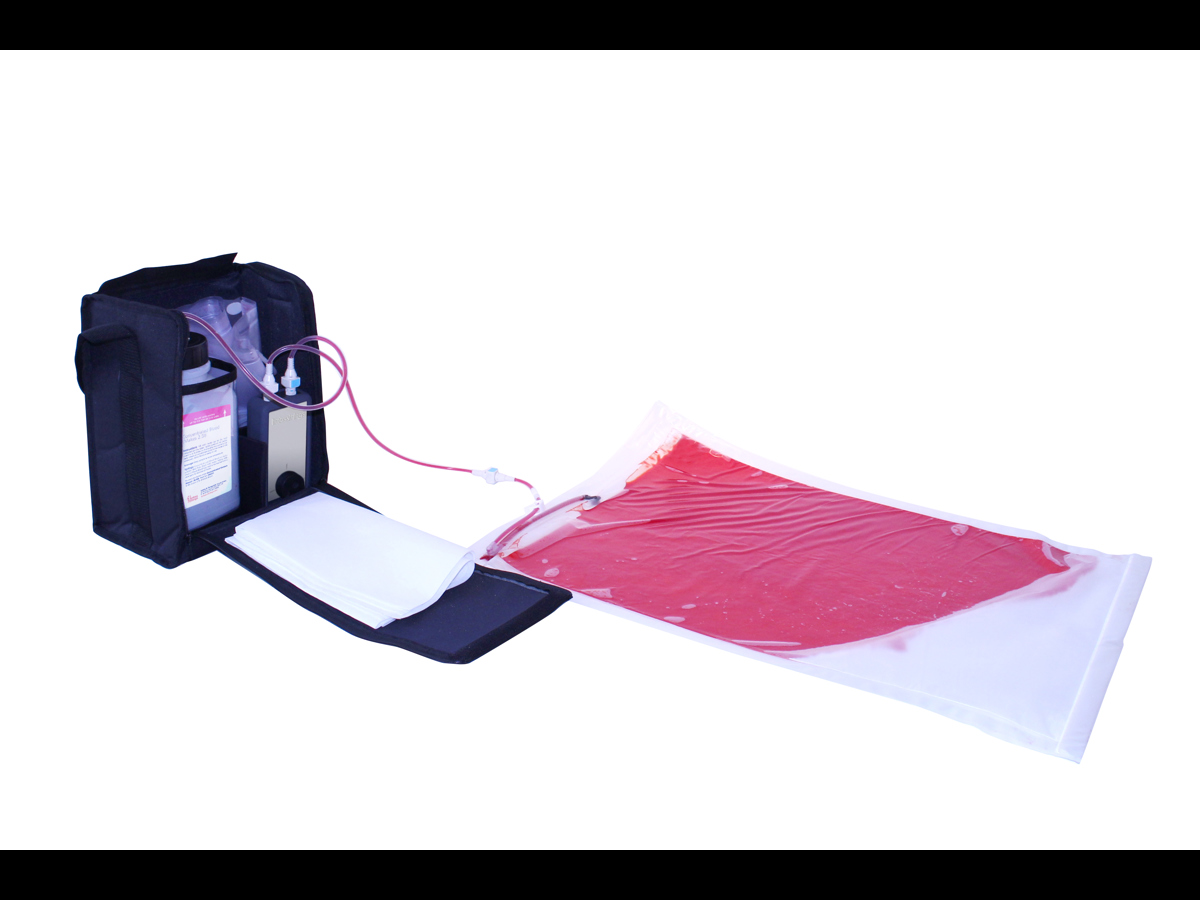
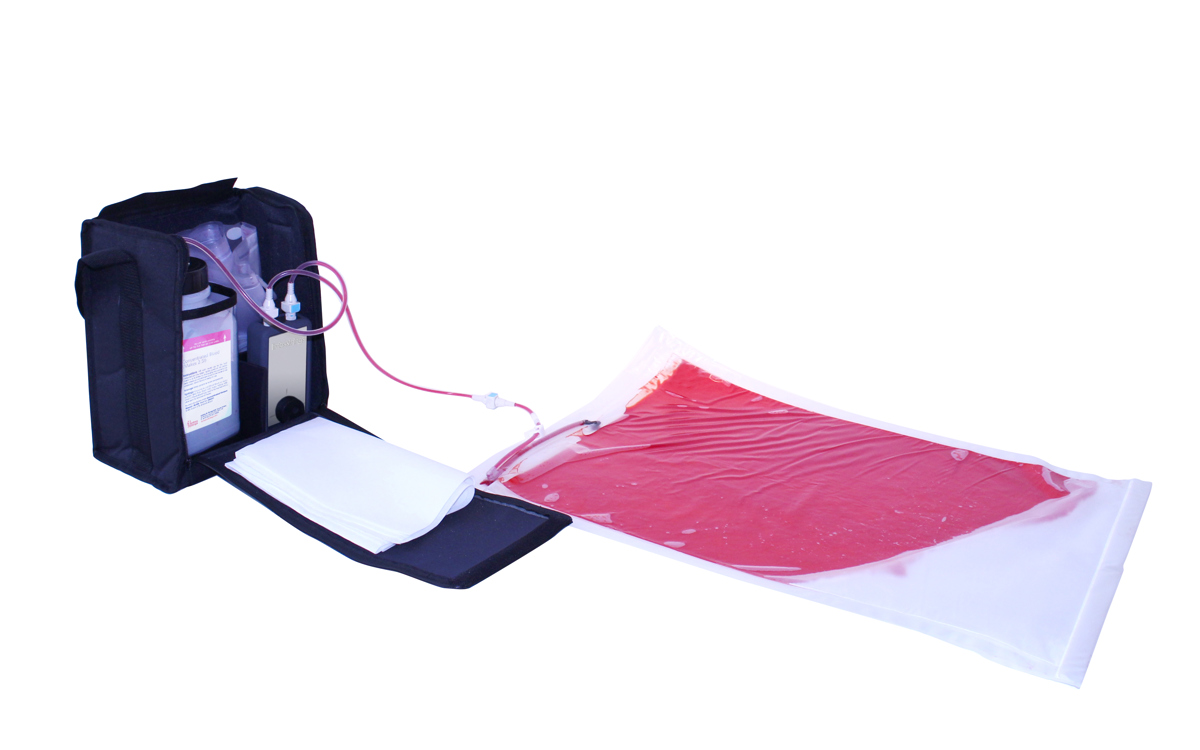
Easily set up in as little as 2 minutes, the patented Clean Bleed® Mat allows for a mess-free blood loss simulation. Accurately mimic a range of blood loss rates for a wide variety of clinical scenarios, including: post-partum haemorrhaging, post-operative wounds, gunshot trauma and arterial bleeds. With adjustable flow capability, realistic scenarios can be created based on the actions of the trainee.
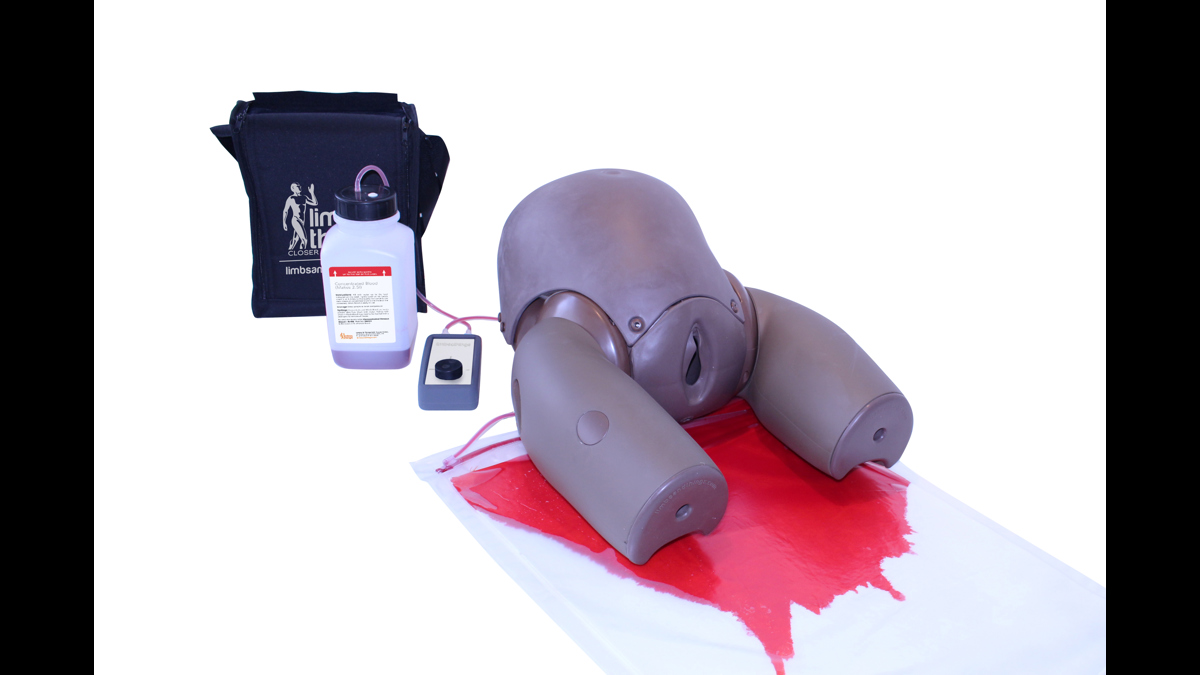
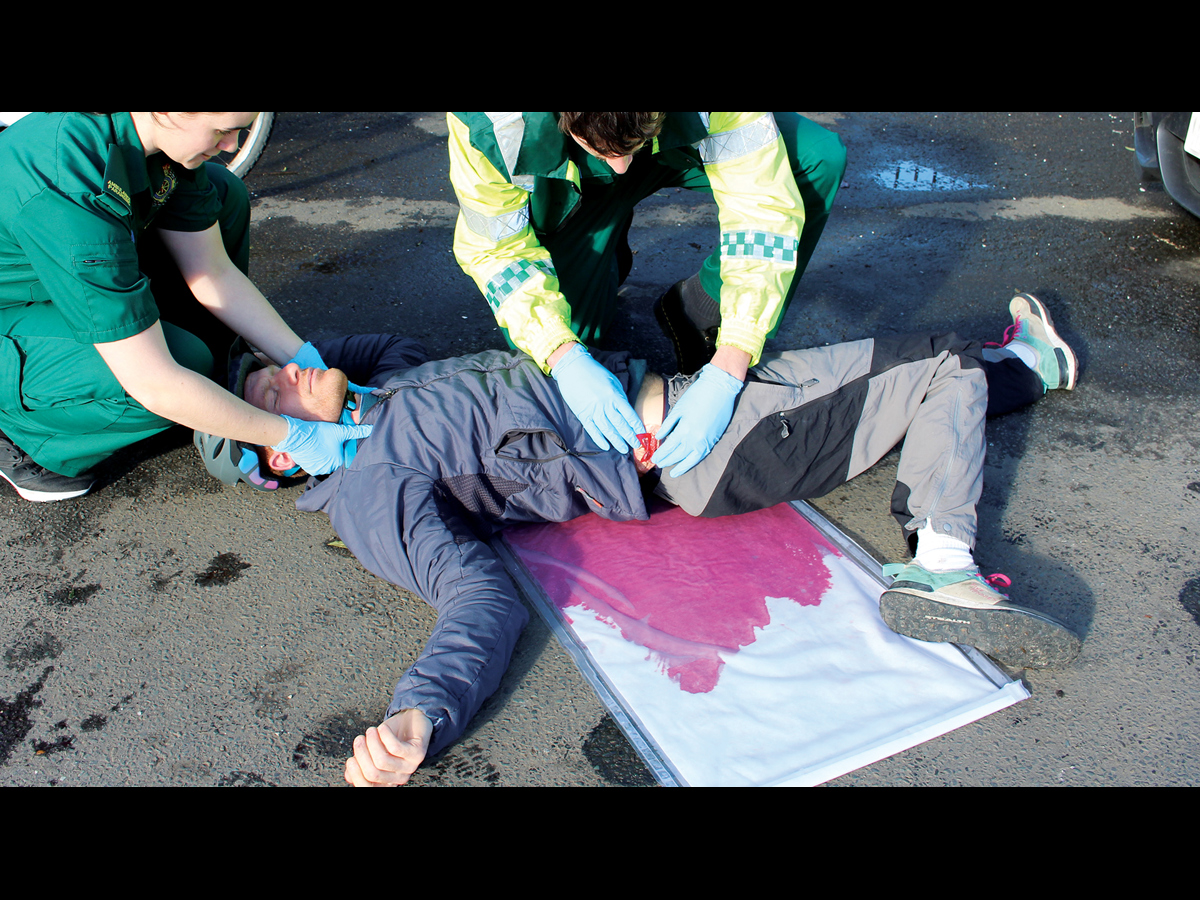
The Clean Bleed® Mat can be used in conjunction with any brand task trainers, full body manikins, or simulated patients, as well as being suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. For ease of use, this product comes with two lengths of tubing to allow for the fluid reservoir and pump to be placed further away from the training area.
The Clean Bleed® Mat has been designed to support all simulation scenarios. This product can be used with any brand of trainer where external blood or fluid loss is a key indicator and measure of the emergency being simulated.
Easily set up in as little as 2 minutes, the patented Clean Bleed® Mat allows for a mess-free blood loss simulation. Accurately mimic a range of blood loss rates for a wide variety of clinical scenarios, including: post-partum haemorrhaging, post-operative wounds, gunshot trauma and arterial bleeds. With adjustable flow capability, realistic scenarios can be created based on the actions of the trainee.
The Clean Bleed® Mat can be used in conjunction with any brand task trainers, full body manikins, or simulated patients, as well as being suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. For ease of use, this product comes with two lengths of tubing to allow for the fluid reservoir and pump to be placed further away from the training area.
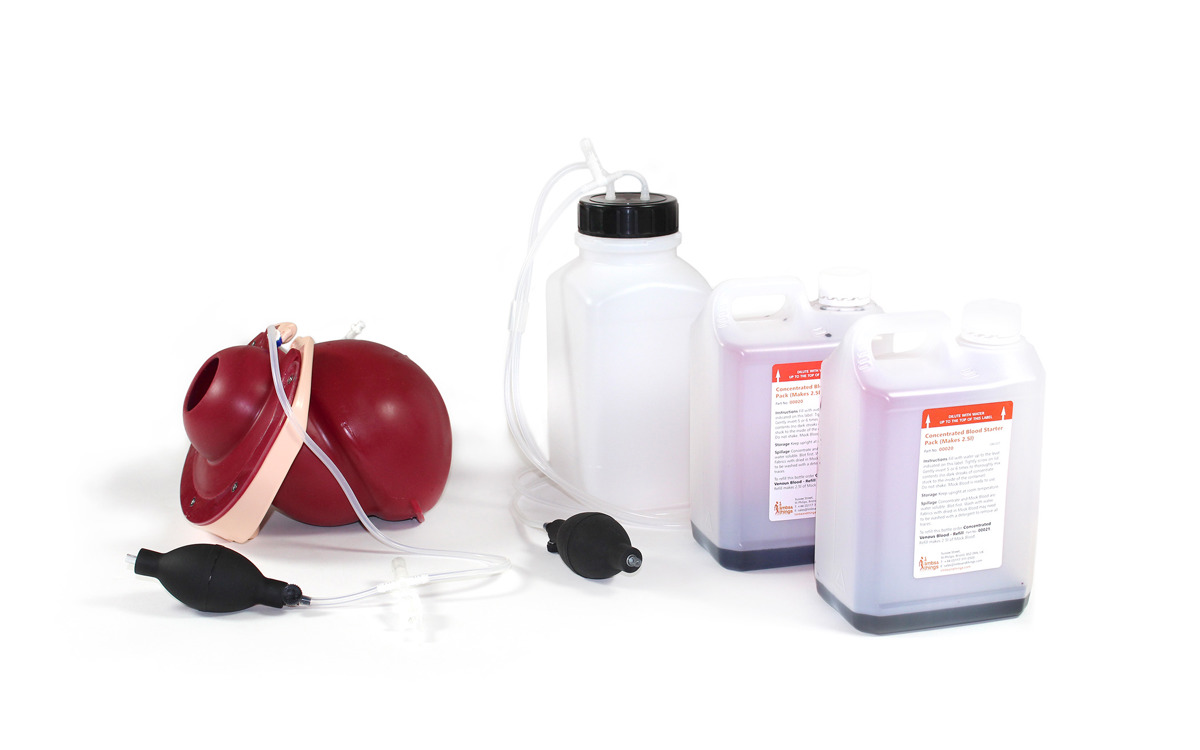
The internal mat can be removed, allowing trainees to weigh the blood or fluid loss as they would in a clinical setting. Our mats are specifically designed to allow easy clean up, including a 2-way pump system that ensures the fluid can be pumped back into the reservoir for reuse. This means a cost effective, mess-free way of using blood flow to aid in diagnosis.
Overview
- Controllable flow rates of between 50ml and 600ml per minute for realistic blood loss simulation
- Blood loss can be measured either visually, or by weighing
- Simple and easy set up takes just 2 minutes
- Provides mess-free blood loss simulation training
- Suitable for use with simulated patients, task trainers and full body manikins
- Quick release bag allows trainees to replace the bag quickly, as they would in a real-life scenario
- Absorbent pad behaves as an inco pad would
- Housed in a carry bag
Realism
- Unique sealed blood flow, heightens the realism for simulated scenarios
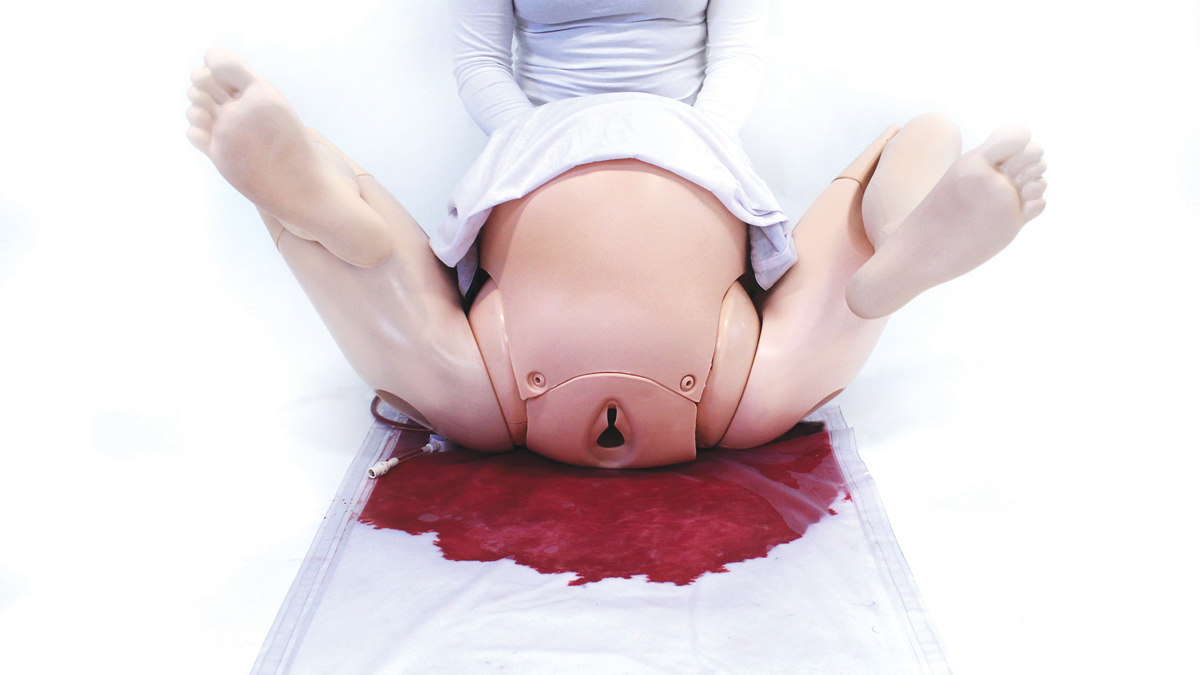
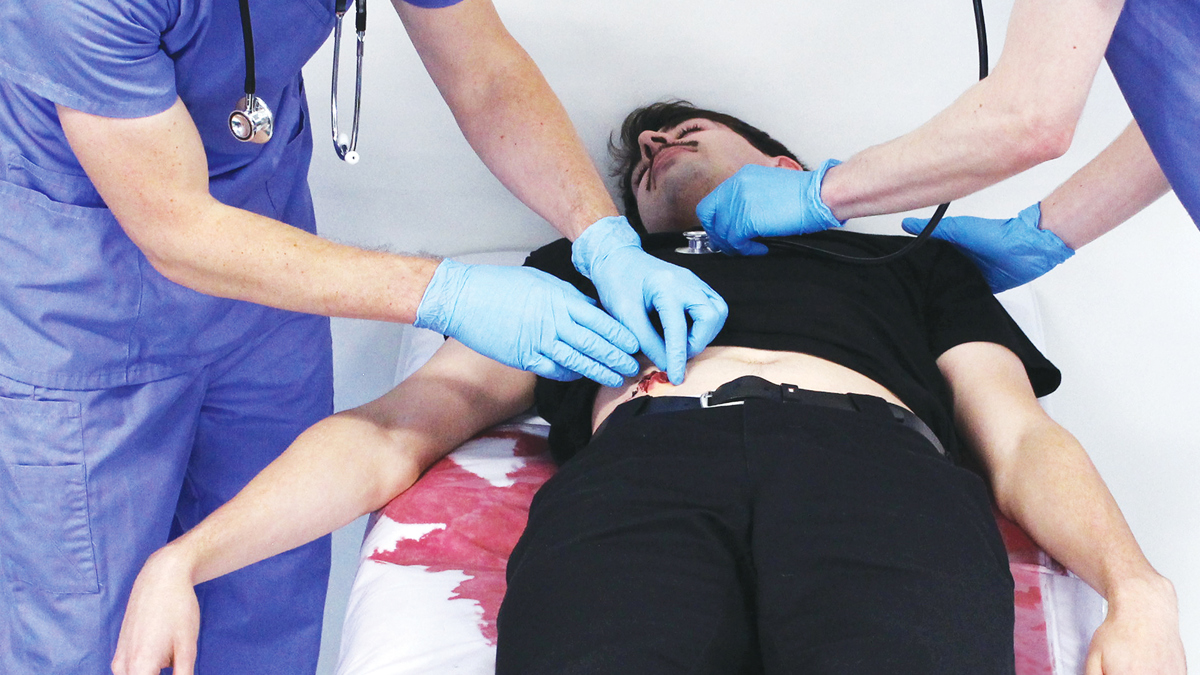
- Create high flow examples, such as: vaginal trauma (including post-partum haemorrhage or meconium fluid); abdominal, chest and neck trauma; loss of limb and post-operative bleeds
- Create low flow examples, such as: head or peripheral trauma; post-operative bleeds; meconium fluid
Versatility
- The Clean Bleed Mat can be used in conjunction with simulated patients, task trainers or full-body manikins
- Can be used to simulate a range of fluids
- Portable and durable for use in both indoors and outdoors
- Bag allows for the use of standard sized inco pads (60cm x 90cm)
Safety
- This product is latex free
- The blood used with this product now contains a new preservative which is approved for use by EU cosmetic regulations which means that, once diluted, it is safe for extended skin contact. We still recommend the use of gloves, as the pigments may stain skin and clothes.
Skills Gained
- Visual inspection and body assessment
- Identification and assessment of speed and color of bleed or flow
- Assessment of the speed and relevance of trainee interventions
- Quantifying blood loss (QBL)
- Ability to initiate rapid transfusion protocol if haemorrhage is suspected
- Use of PPE to protect against bodily fluids
- Assessment of the ongoing patient condition and impact of prior interventions on the patient
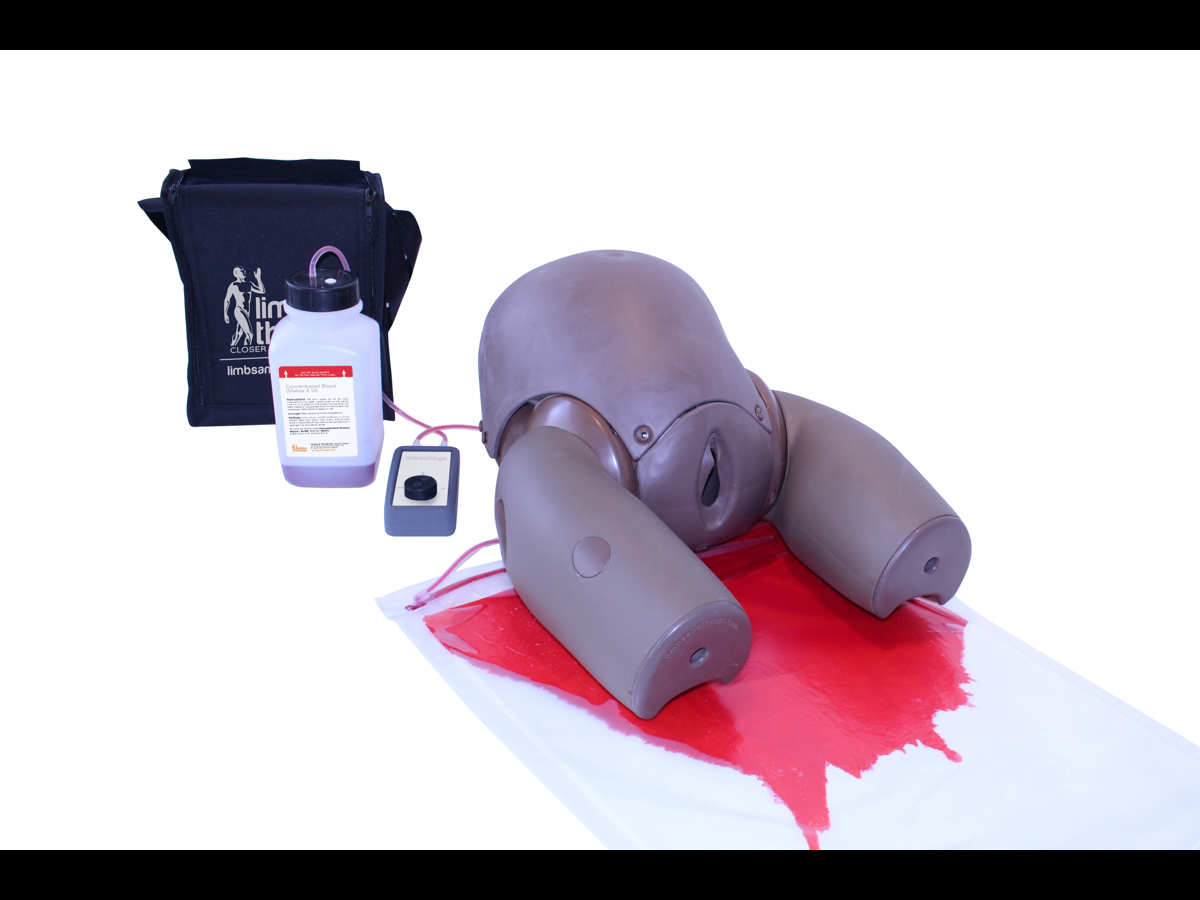
Product Contains
This product also contains:
- Tubes & Connectors Set
- Fluid Reservoir
- Clean Bleed Pump
Works with the following products:
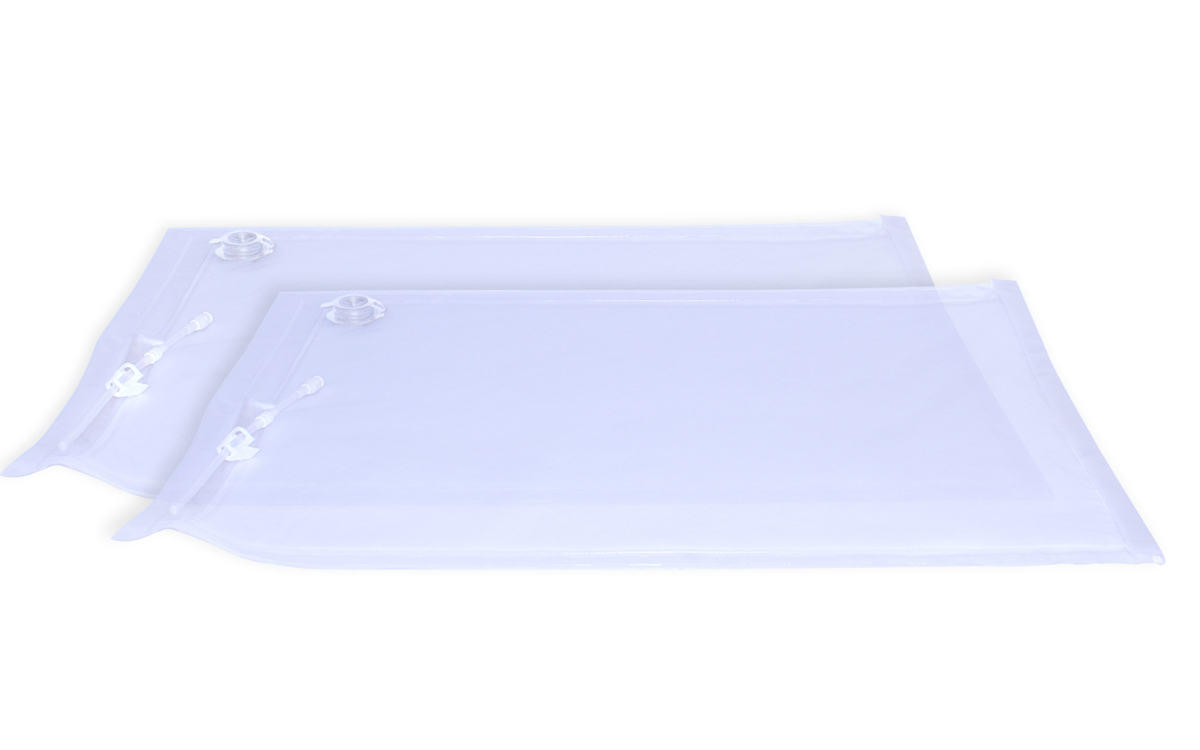

Clean Bleed® Bag (x2)

Clean Bleed® Absorbency Pad (x10)

Clean Bleed® Carry Case
-
Light
-
Dark
Birthing Simulator PROMPT Flex - Advanced (Light Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
Birthing Simulator PROMPT Flex - Standard (Light Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
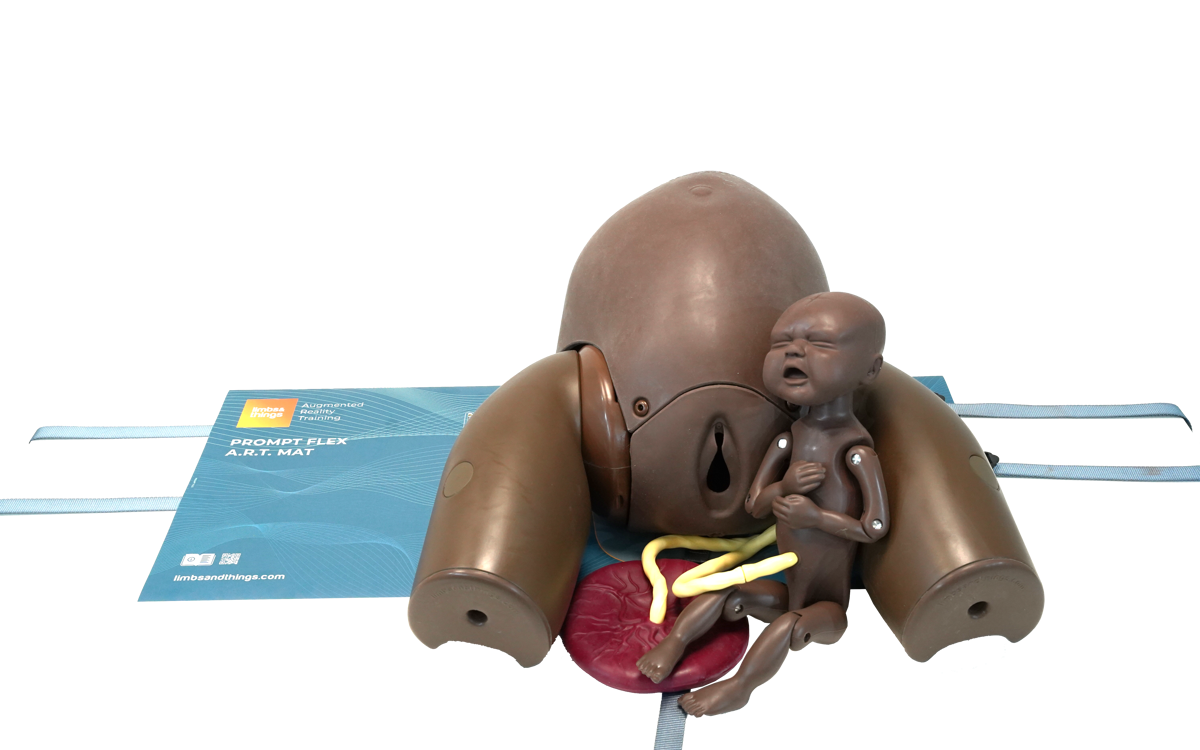

Birthing Simulator PROMPT Flex - Standard (Dark Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
Birthing Simulator PROMPT Flex - Advanced (Dark Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
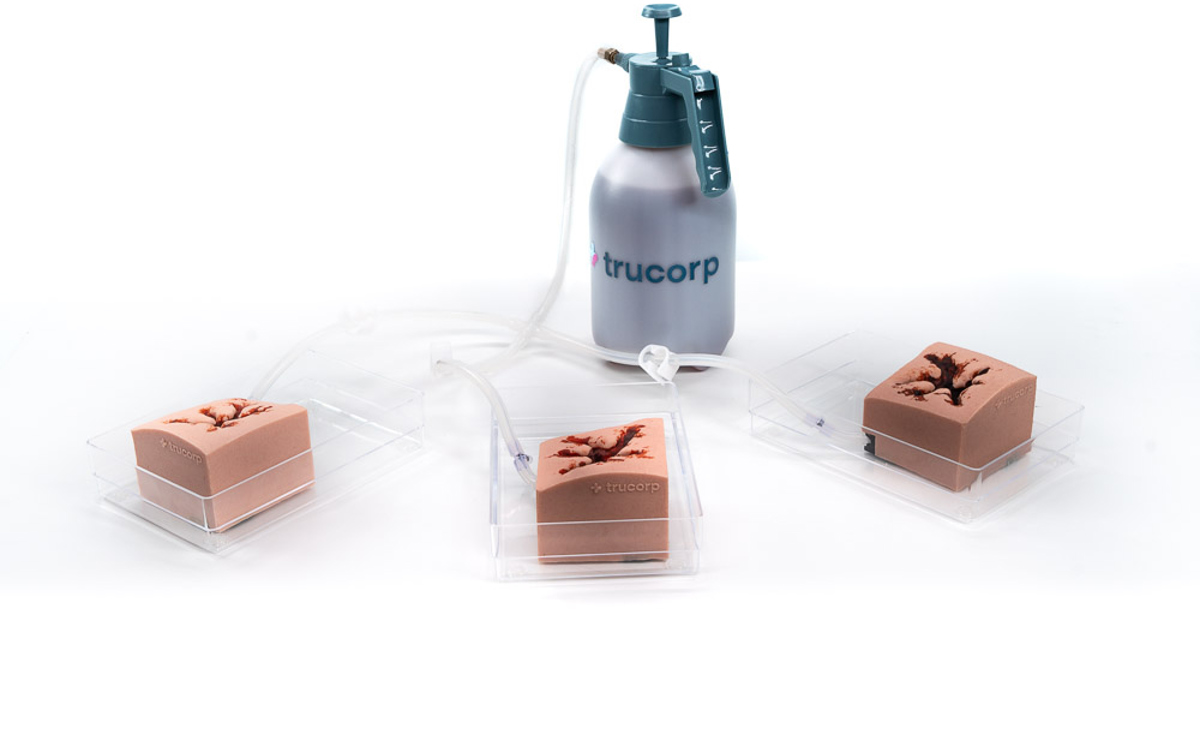

TruWound (Light Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
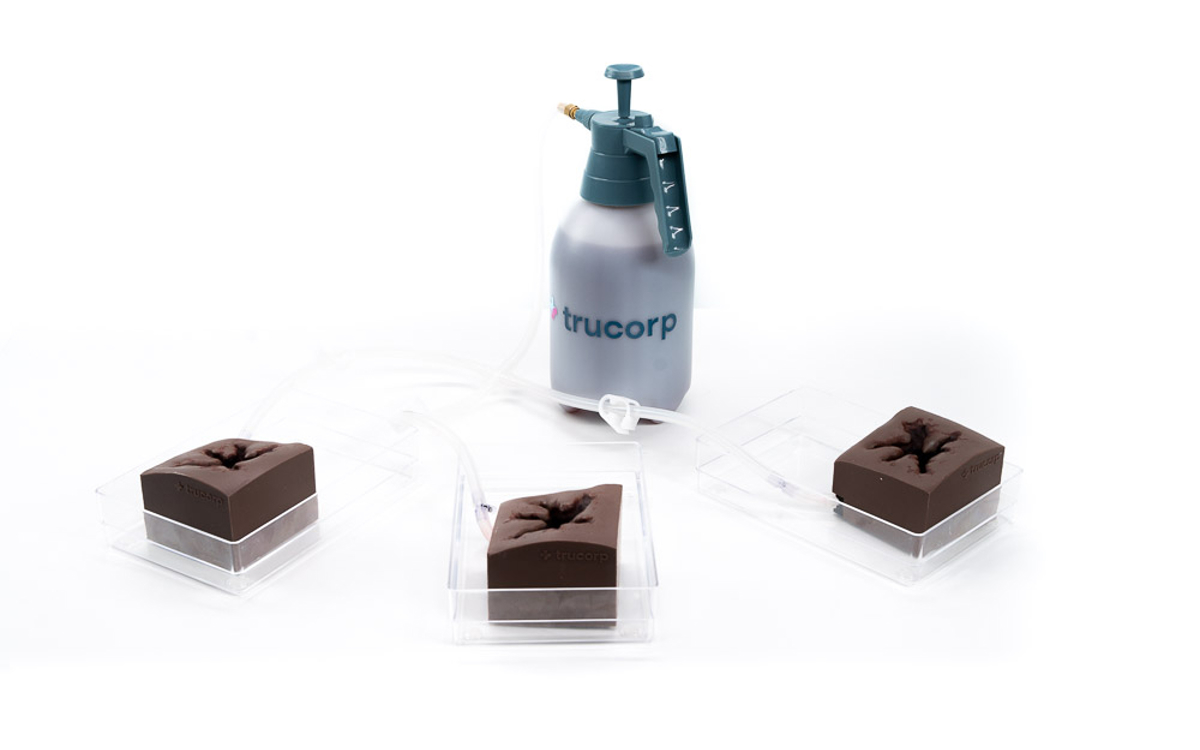

TruWound (Dark Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
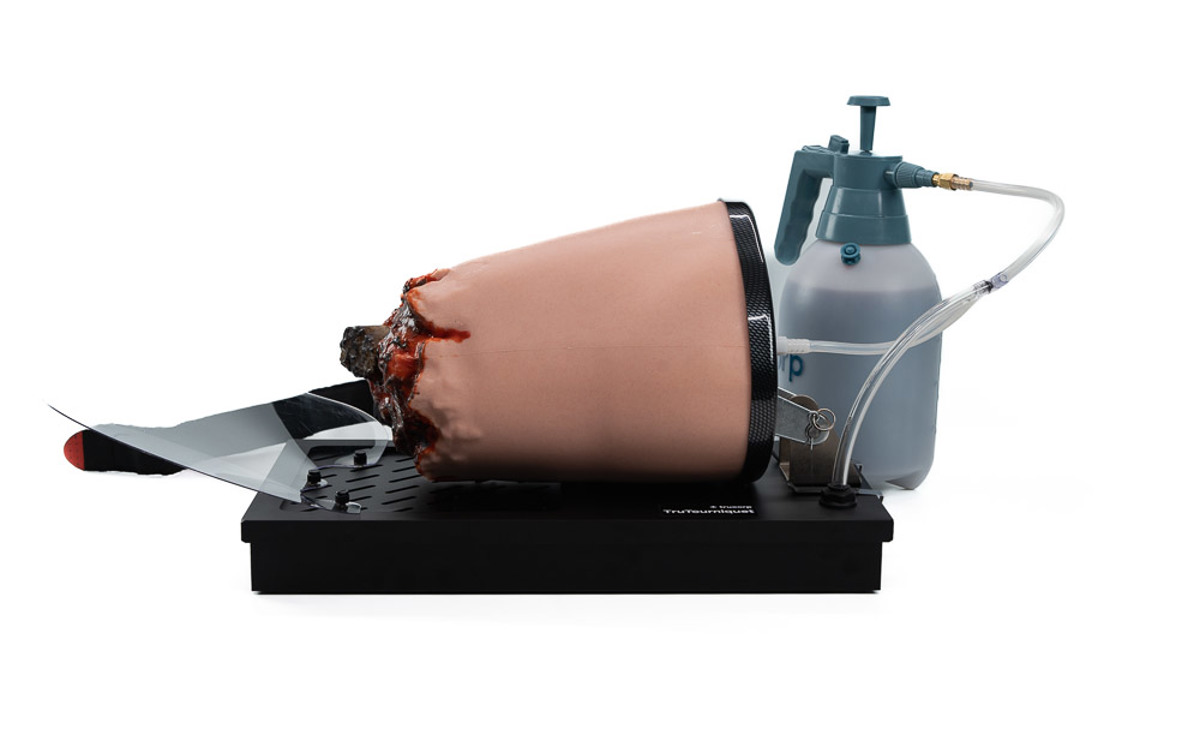
TruTourniquet (Light Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
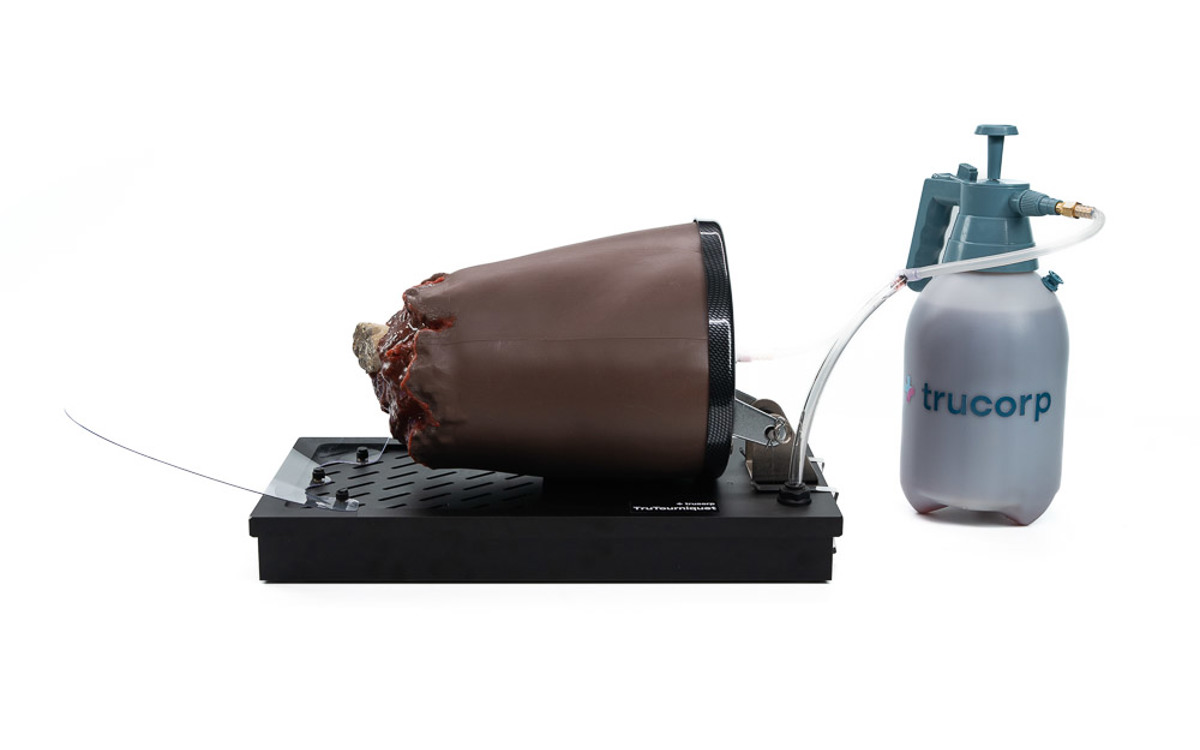

TruTourniquet (Dark Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
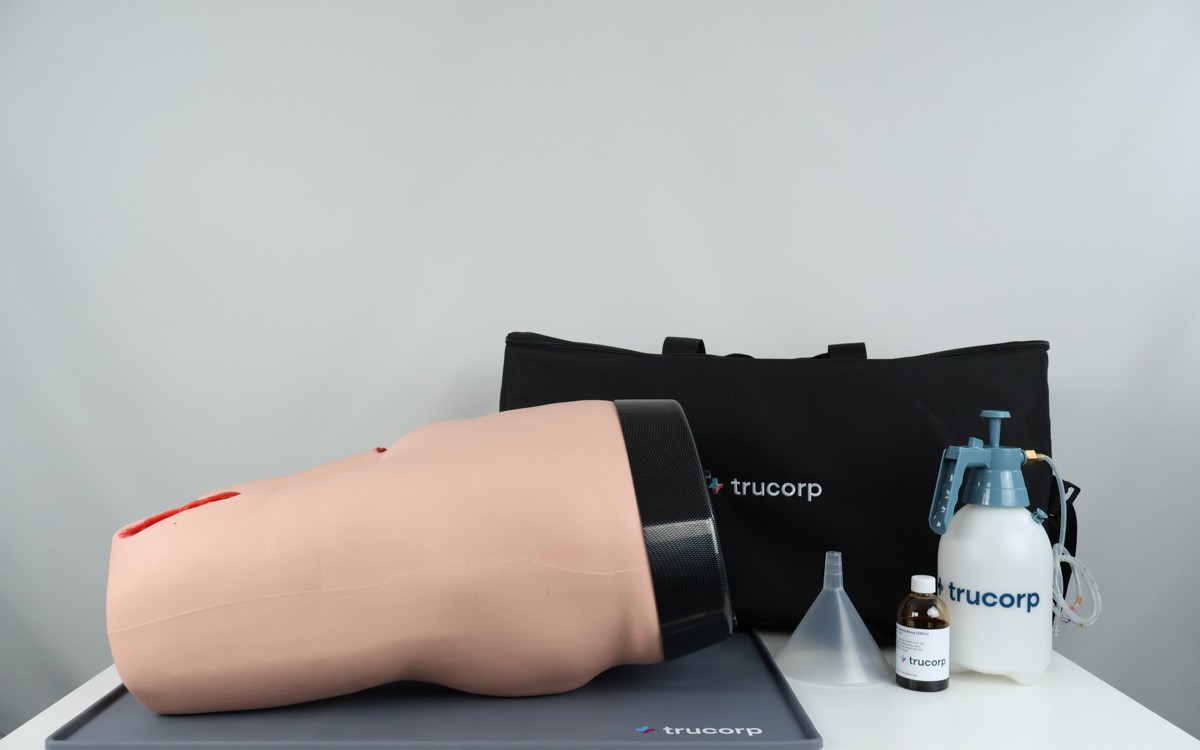
TruJunctional - Junctional Tourniquet Trainer
-
Light
-
Dark
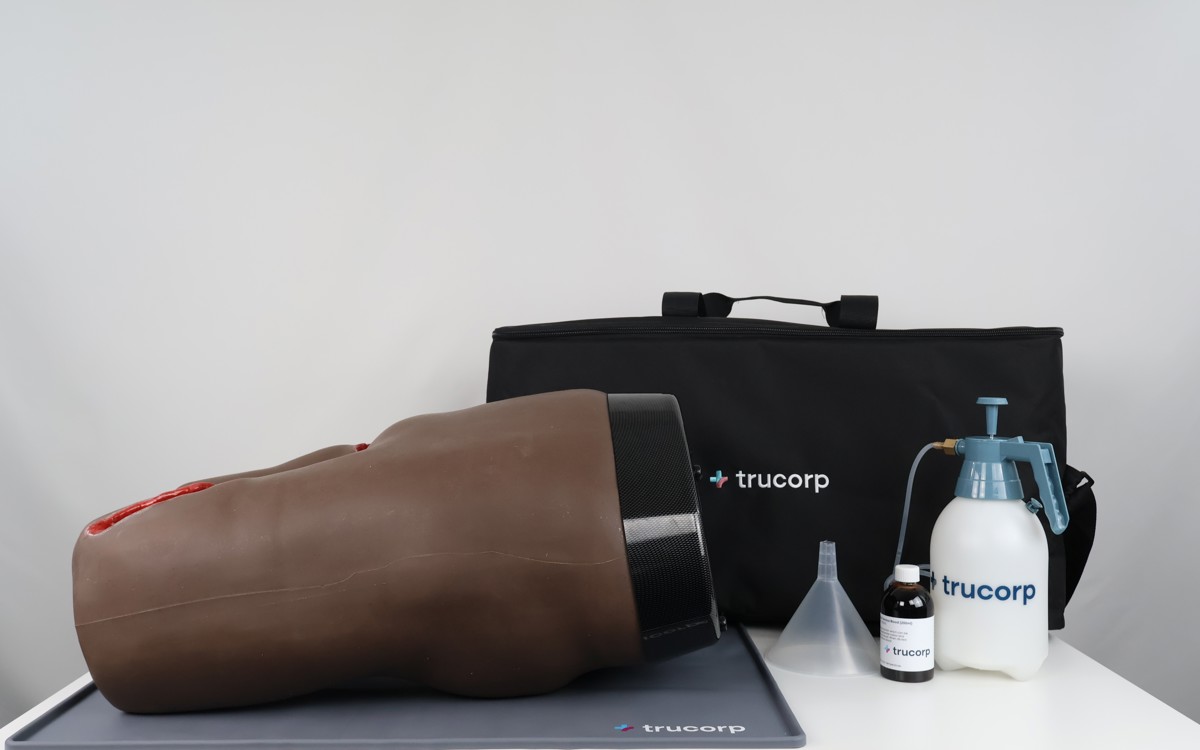
TruJunctional - Junctional Tourniquet Trainer
References
MEAC Curriculum checklist of essential competencies Post-partum haemorrhage: - manage postpartum bleeding and haemorrhage, using appropriate techniques and uterotonic agents as indicated - provide emergency treatment of late post-partum haemorrhage, and refer if necessary
Postpartum haemorrhage: - Surgical management of postpartum haemorrhage
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education & The American Board of Emergency Medicine Wound Management (PC13) Assesses and appropriately manages wounds in patients of all ages regardless of the clinical situation. - Performs complex wound repairs (deep sutures, layered repair, corner stitch) - Identifies wounds that may be high risk and require more extensive evaluation (example: x-ray, ultrasound, and/or exploration) - wound using advanced techniques such as: cautery, ligation, deep suture, injection, topical haemostatic agents - Performs advanced wound repairs, such as tendon repairs and skin flaps
National EMS Core Content Listing of Conditions and Components (Patient complaints and presenting signs and symptoms) - Bleeding control - Wound closure techniques - Wound management - Multiple trauma - Trauma (incl. abdominal, chest, head & neck, lower body, upper body, trauma in pregnancy etc
ANMC Standards and Criteria for the Accreditation of Nursing and Midwifery Courses Leading to Registration, Enrolment, Endorsement and Authorisation in Australia— with Evidence Guide Postpartum Haemorrhage: - provision of care in the postnatal period
RANZCOG Curriculum Postpartum Haemorrhage: - Procedures employed for control of postpartum haemorrhage (including B Lynch suture, uterine tamponade balloon, internal iliac artery ligation and postpartum hysterectomy)
Australian College for Emergency Medicine Presentations: - Bleeding/bleeding time Wound management: - Advanced suturing techniques - Wound exploration, cleaning, irrigation, and debridement - Open wound packing References to trauma
AOA (Australian orthopaedic association) & NZOA (NZ orthopaedic association). Consequences of Trauma - Clinical Knowledge and Procedure Syllabus. - To understand the principles of treatment of vascular injuries; to include a discussion of the timing, order of treatment, indication for shunts, different options for fracture fixation both temporary and definitive treatment, consideration for amputation and interaction between the vascular surgeon and orthopaedist when treating these patients - Transfusion in trauma (including massive transfusions) - Recommended ratio of blood products given - Anticipation and management of complications of massive transfusion Review and understand the determination of the source of blood loss…
Standards for pre-registration midwifery education PPH - Undertake appropriate emergency procedures to meet the health needs of women and babies. Emergency procedures will include: - Managing post-partum haemorrhage
Core Module 12: Postpartum Problems (the Puerperium) To understand and demonstrate appropriate knowledge, skills and attitudes in relation to postpartum problems; Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH): - Techniques for the control of postpartum haemorrhage - Primary, secondary and other postpartum haemorrhage
The College of Emergency Medicine Wound assessment and management: - Know how to assess a wound in terms of mechanism of injury, underlying structures, and complications - Know of special types of wound: puncture, bites, amputation, de-gloving, and presence of foreign bodies - Know different wound closure techniques Wound management: - The trainee will be able to assess the patient with increasing complex wounds, providing analgesia, wound exploration, identification of damaged underlying structures, repair where appropriate and closure Major Trauma: - The trainee will be able to lead a trauma team in the assessment of the trauma victim using a systematic prioritised approach, identify and treat life-threatening conditions and arrange appropriate investigations for further management Major trauma - Chest Injuries: - The trainee will be able to evaluate the patient who presents with major trauma and to identify and treat the life-threatening presentations, to produce a valid differential diagnosis, appropriate investigation and implement a management plan. The trainee builds on previous training with more detailed knowledge, skills and behaviours Major trauma - Abdominal trauma: - The trainee will be able to evaluate the patient who presents with major trauma and to identify and treat the life-threatening presentations, to produce a valid differential diagnosis, appropriate investigation and implement a management plan. - Know the different presentations of blunt and penetrating abdominal trauma and the structures that may be damaged, Specifically, blunt splenic, hepatic, renal, pancreatic trauma, hollow viscus injury, urethral/bladder and testicular trauma Traumatic limb and joint injuries: - Know when to seek senior advice in the management of limb and joint trauma Bruising and spontaneous bleeding: - The trainee will be able to evaluate the patient who presents with bruising or spontaneous bleeding and produce a valid differential diagnosis, appropriate investigation, and implement a management plan
Intercollegiate Board for Training in Pre-hospital Emergency Medicine Working in Emergency Medical Systems - Major trauma services - Major trauma in a pregnant patient
Interventional Radiology Specialty Training Curriculum, The Royal College of Radiologists, 2019. Accute Haemorrhage
WHAT PROCEDURES CAN THE CLEAN BLEED® MAT BE USED TO DEMONSTRATE?
Any scenario or clinical procedure where the external blood flow or blood (or any other fluid) is a critical signal to act and intervene. For example, low flow bleeds from head or peripheral trauma to high flow bleeds such post-partum haemorrhages and post-operative bleeds.
____________________________________
Will the bag hold up under a variety of clinical scenarios?
The Clean Bleed® bag is produced using a durable, tear resistant material. This allows it to be used on or under medical training equipment, as well as being knelt or stood on by trainees when they perform examinations.
____________________________________
CAN YOU USE OTHER BLOOD?
Yes, but we highly recommend using Limbs & Things blood as it provides the most realistic flow characteristics and optimum pump performance. Other brands may also cause staining.
____________________________________
HOW CAN I USE THIS IF THE EDUCATOR IS NOT IN THE ROOM FOR THE SIMULATION?
Using smart plugs educators can activate the pump system remotely.
____________________________________
CAN YOU USE THIS TO SIMULATE AN INCONTINENT PATIENT?
Yes, the fluid in the blood reservoir can be substituted with simulated urine to simulate incontinence.
____________________________________
CAN WE USE CHUX/INCO PADS IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE CLEAN BLEED ® MAT?
We recommend that you use the Limbs & Things pads as they allow for a more even flow of fluids and can be used multiple times. However, if you have a supply of the standard Chux/Inco pads you will be able to use them with this product.
____________________________________
WHAT’S THE BEST WAY TO USE/SET-UP THE MAT?
For best results, lay the mat on a flat surface, if it its uneven the blood can pool at the bottom and not spread evenly.
____________________________________
WHAT’S THE BEST WAY TO USE THE MAT WITH A SIMULATED PATIENT?
The best way to use the mat with a simulated patient is to position the mat so that the end connected to the pump is underneath the simulated patient, but they are not applying pressure to the tube that could block the flow.
____________________________________
HOW FAST CAN YOU SWITCH OUT T0 A CLEAN MAT IF WE SWITCH GROUPS QUICKLY?
The mats can be replaced in around 2 minutes or for an even faster switchover the entire bag and mat can be swapped thanks to the quick-release connectors. Extra bags are available here.
____________________________________



