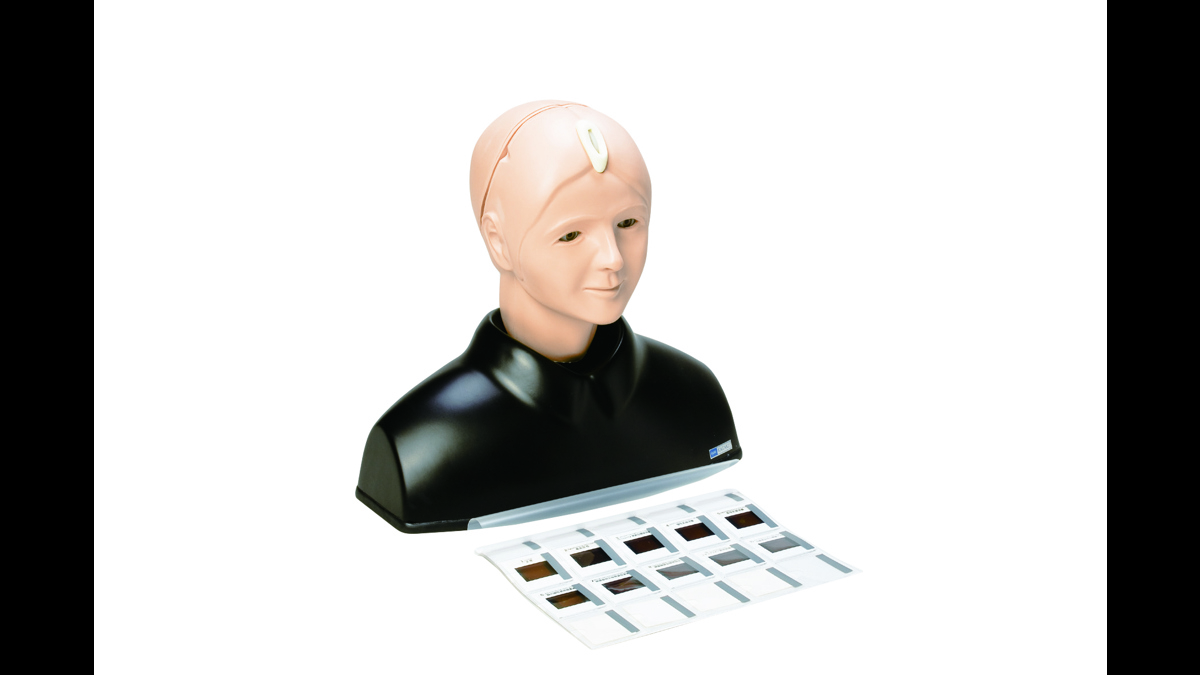
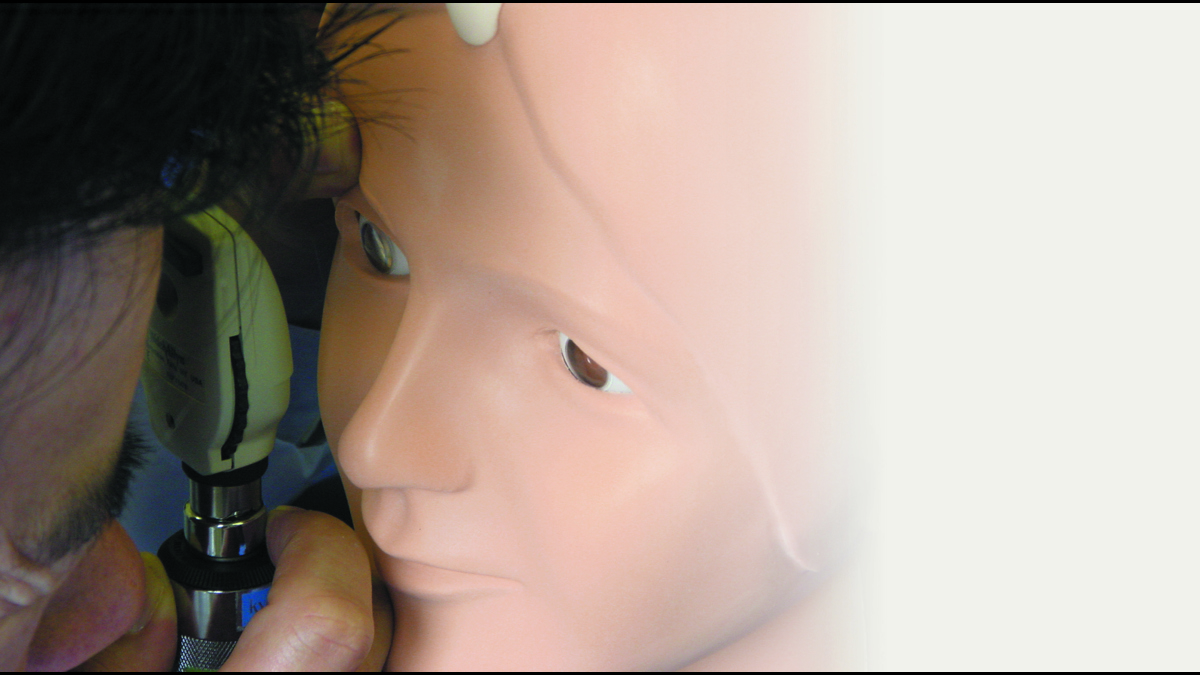
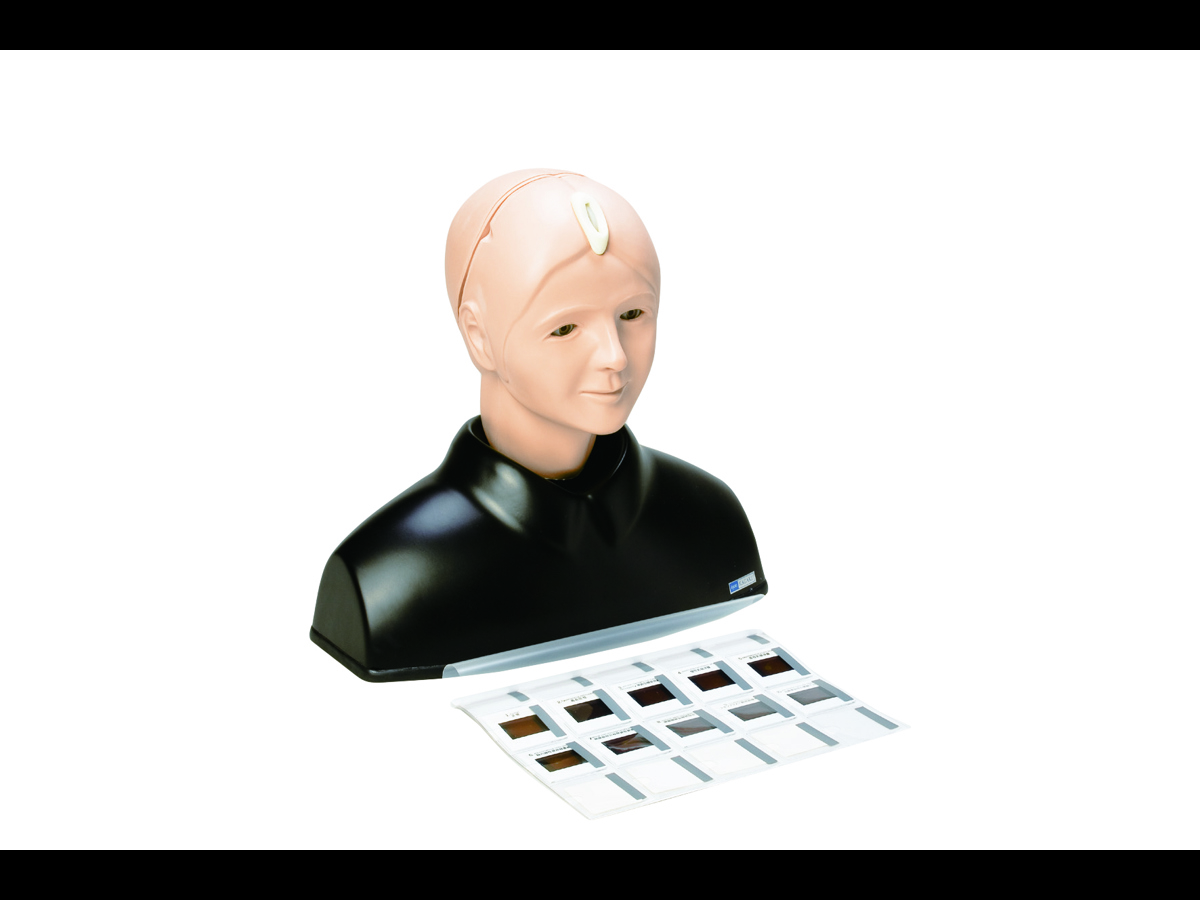
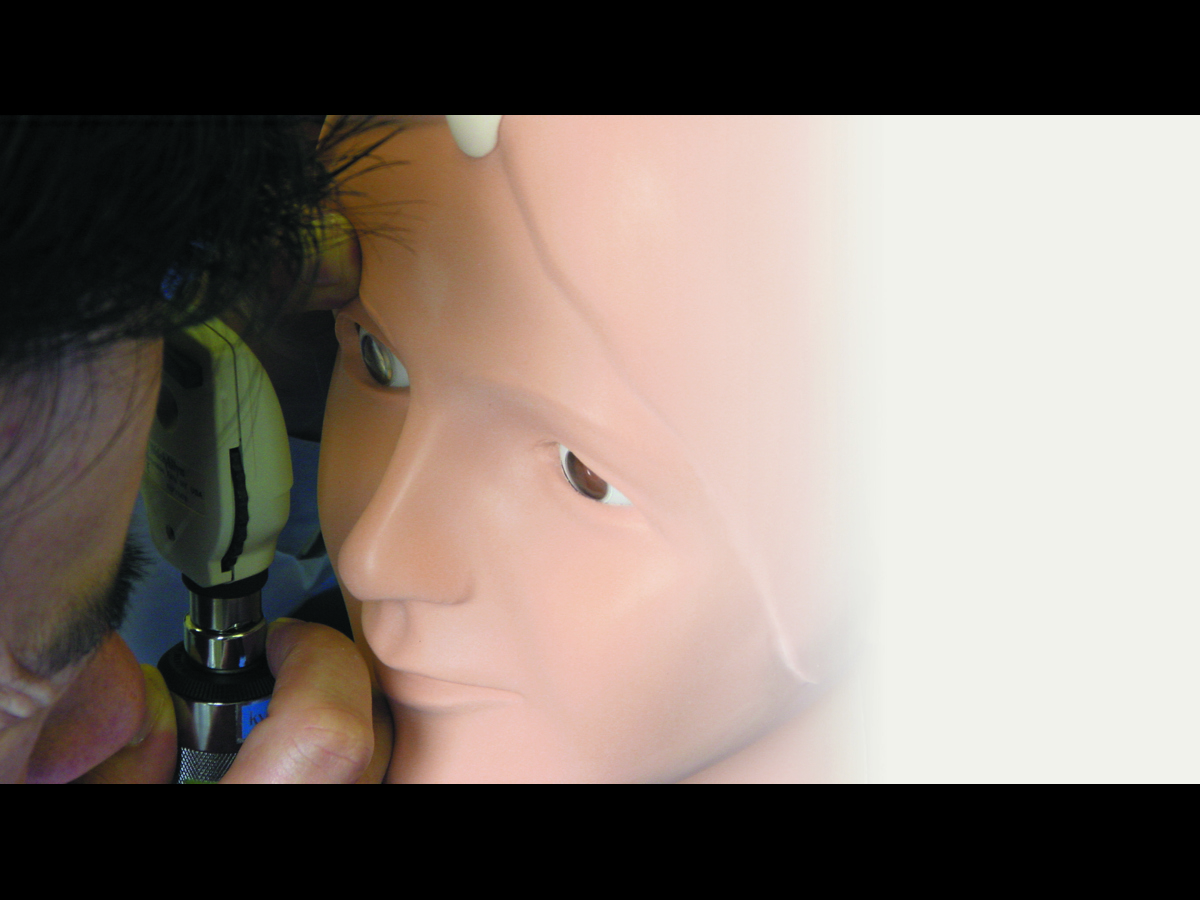
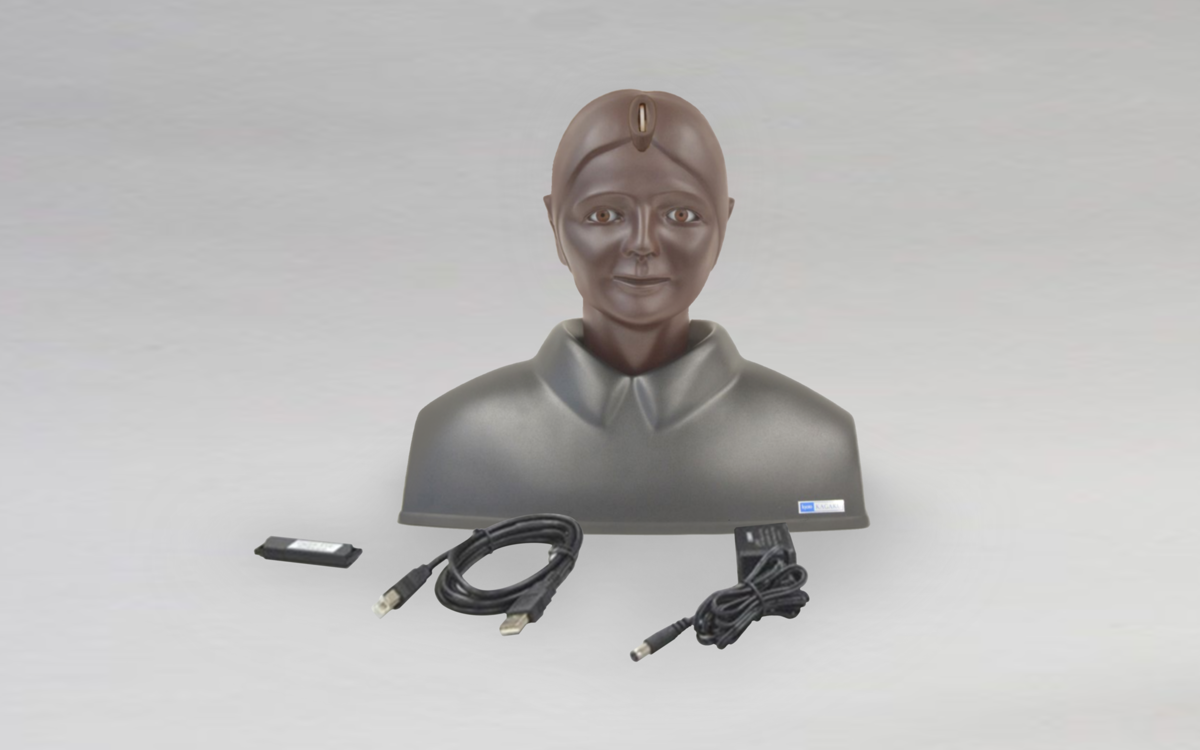
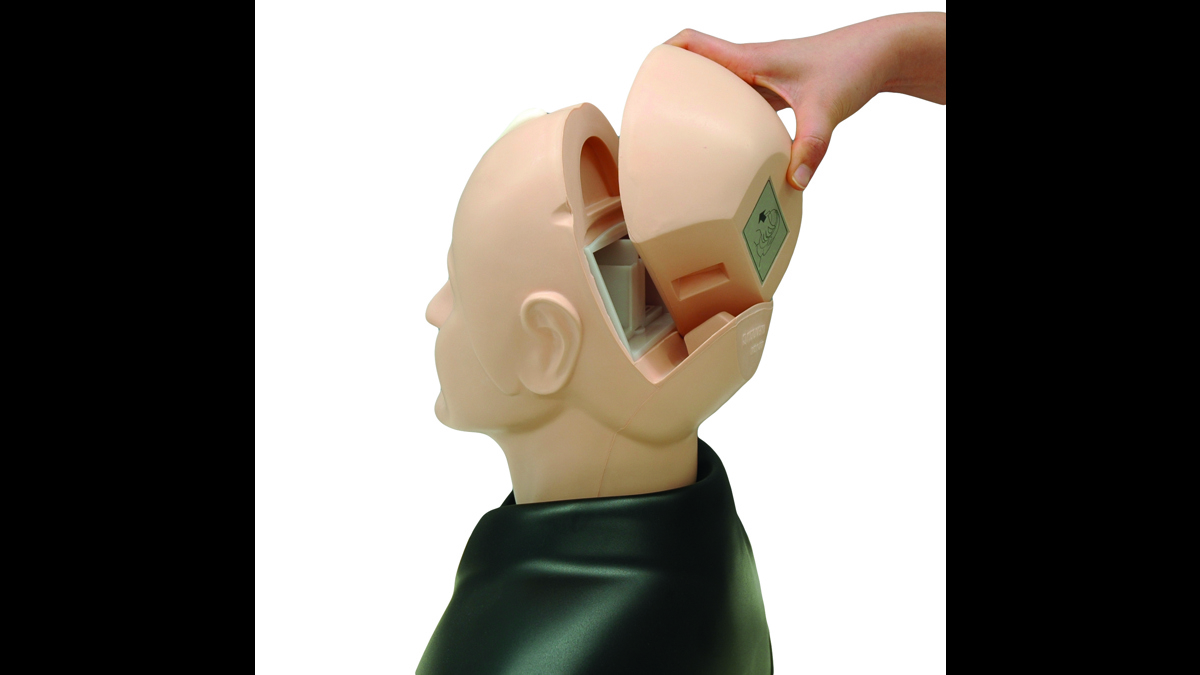

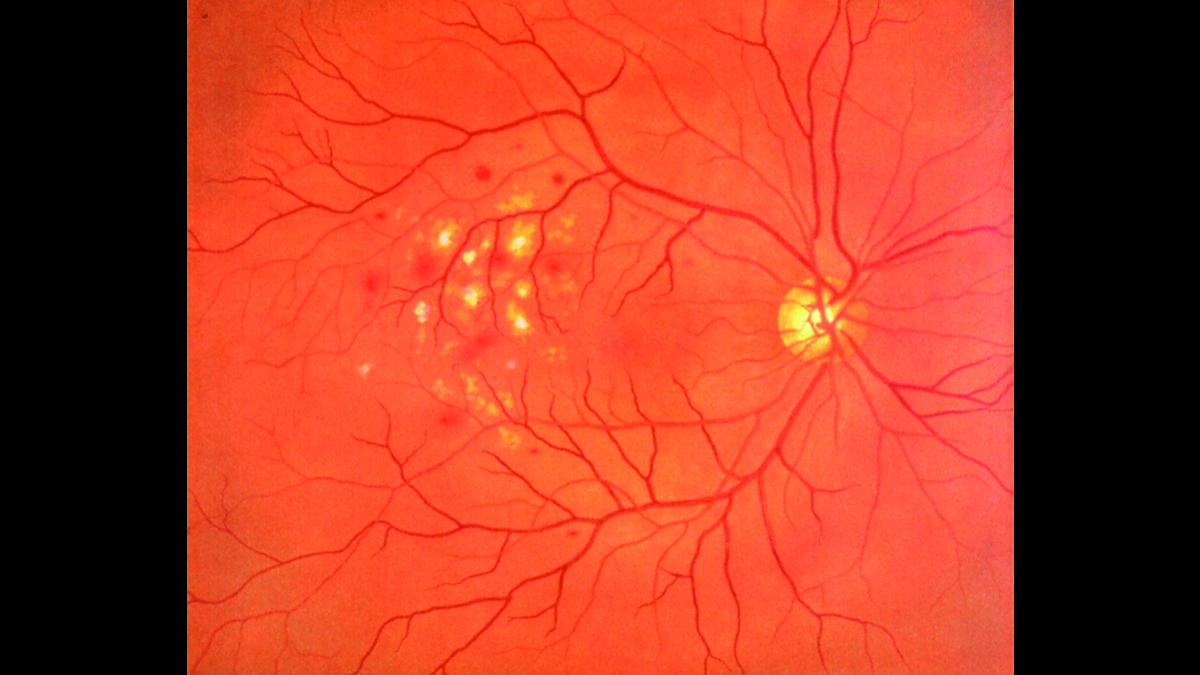
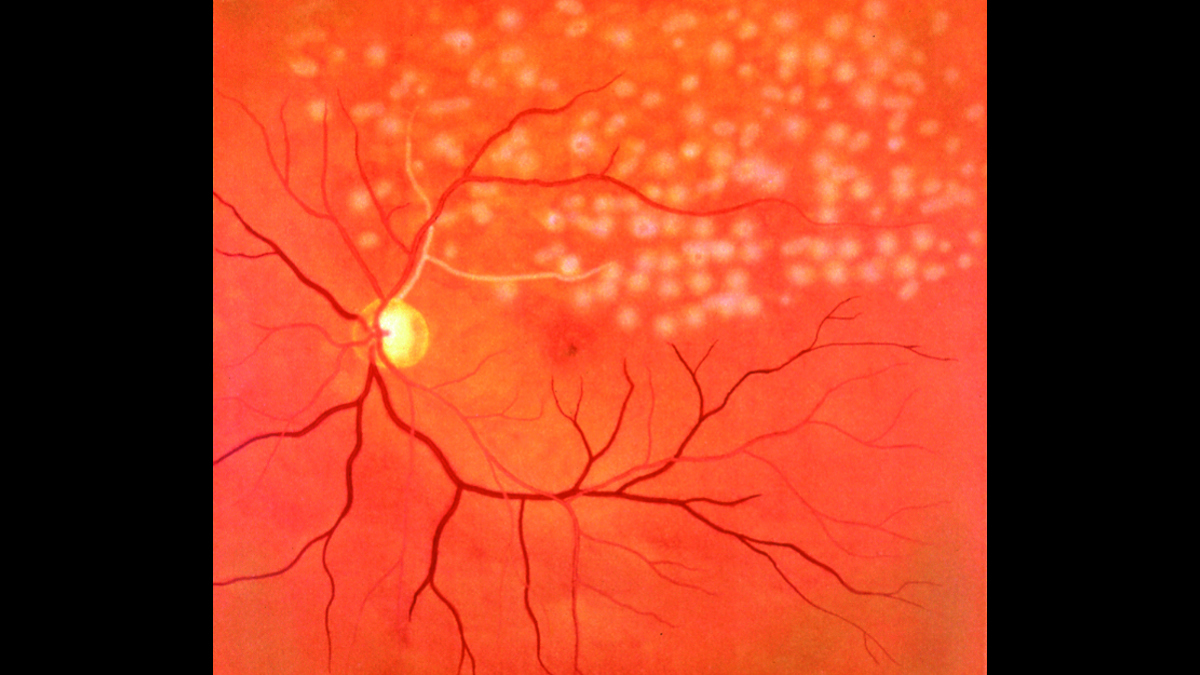

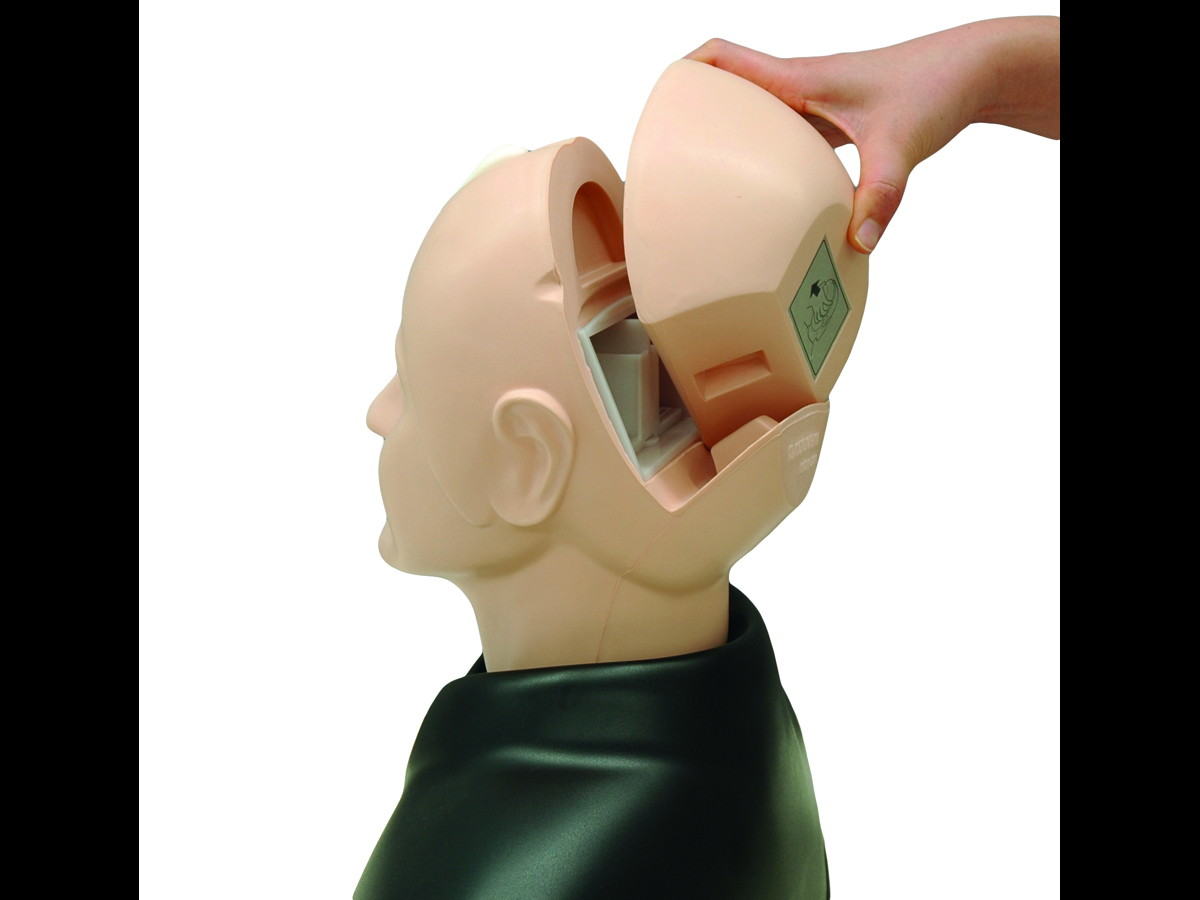


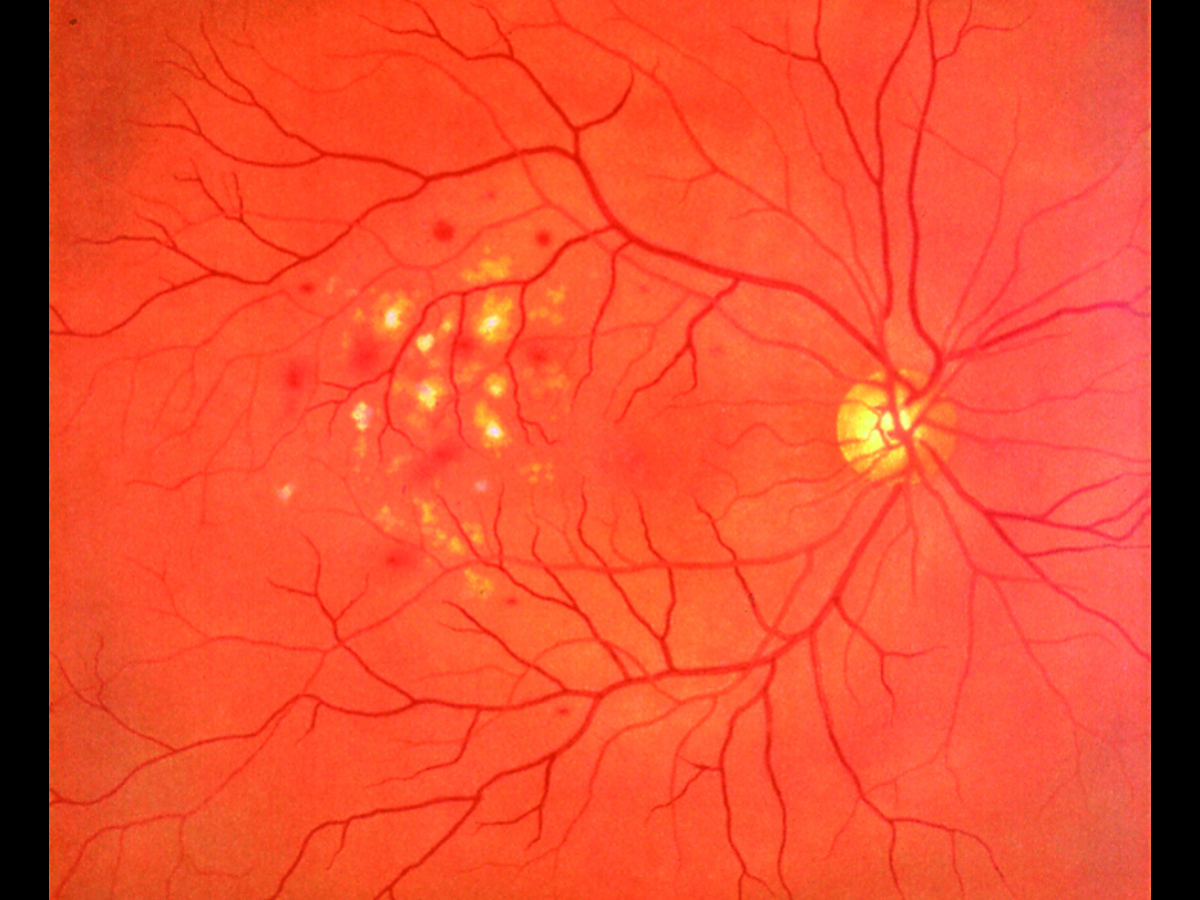
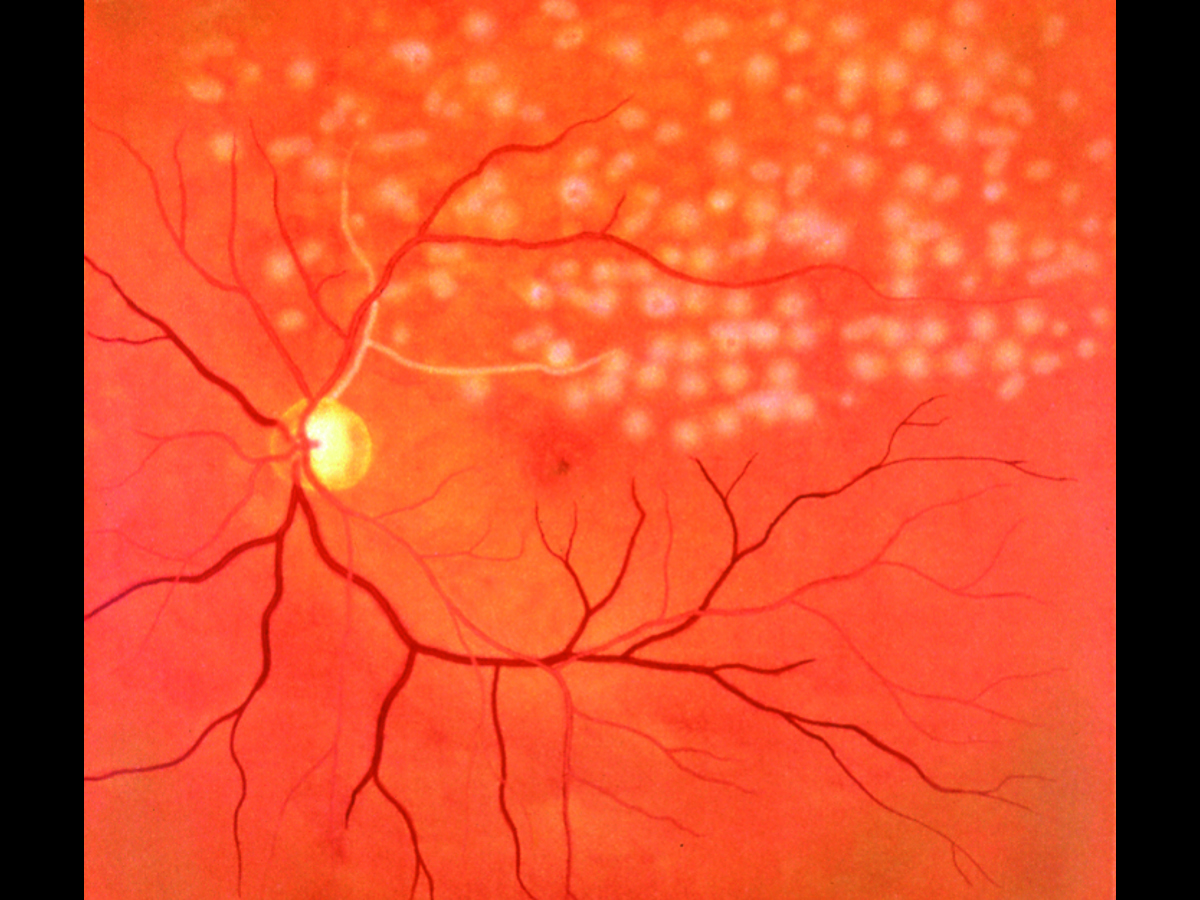
Kyoto Kagaku’s Eye Examination Simulator offers practical and repeatable training in fundal examination.
The fully adjustable ocular anatomy, with its imaging slides showing 10 real clinical fungal diseases, give trainees up to 90 different scenarios to diagnose. (Red reflex can also be detected during examinations.)
The innovative design of the eye exam trainer makes it possible to adjust several components of the eye, changing the complexity of the examination.
- Lens length in both left and right eyes – 3 step positioning allows for hyperopia, normal and myopia examples
- Pupil dilation – 3 step dilation/contraction of the pupil, controlled via the gear on the model’s crown
This trainer is accompanied by a study guide covering the cases included on the slides to aid in self-study.
Overview
- Identification practice for up to 90 different cases
- Easy load unit for quick change of clinical images
Realism
- Fundal slides feature real clinical images
- Adjustable dilation, visual axis and depth of fundus slides allow for different degrees of challenge
- Soft and supple material making for realistic eyelid raising
- Red reflex detectable during examination
Versatility
- Eye exam trainer has 3 options for dilation and contraction of the pupil, 2, 3.5 and 5mm
- Adjustable depth of the fundus slides to show hyperopic, normal and myopic views
- Compatible with any ophthalmoscope available on the market
Cleaning
- Wipe the surface of the eye examination trainer with a soft damp cloth
- Allow to dry before storing
- Use the blower included to remove dust from slide frames
Safety
- Included blower contains latex
- When changing the diameter of the pupil, do not force gears when turning, this can lead to damage of the model
- Hold the fundus image slides by their frames, fingerprints on the surface will show in further examinations
- During examination practice, use an anti-reflection filter on a direct ophthalmoscope
Anatomy
- Adult male head and shoulders
- Lens-equipped eyeballs that simulate the visual axis of the human eye
- Eyelids
Skills Gained
- Use of an ophthalmoscope (not supplied) to examine the optic fundus
Identification of common eye diseases:
- Normal fundus
- Grade 3 hypertensive retinopathy, arteriolar vasoconstriction
- Grade 1 hypertensive retinopathy, arteriolosclerosis
- Hypertensive retinopathy hemorrhages and cotton wool spots
- Hypertensive retinopathy, simple vein concealment
- Diabetic retinopathy: microaneurysm, hemorrhages and hard exudates
- Papilloedema, chronic phase
- Papilloedema, acute phase
- Glacomatous optic atrophy: disc cupping and nerve fiber defect
- Retinal vein occlusion, acute phase: flame-shaped hemorrhage and cotton wool spots
- Retinal vein occlusion, post retinal laser photocoagulation
- Toxoplasmosis, retinochoroiditis
- Age-related macular degeneration: macular exudates and subretinal hemorrhage
References
National Organisation of Nurse Practitioner Faculties, Nurse Practitioner Core Competencies Content , 2017 Independent Practice Competencies p.14 3.b Uses advanced health assessment skills to differentiate between normal, variations of normal and abnormal findings. 3.c Employs screening and diagnostic strategies in the development of diagnoses.
AAFP Recommended Curriculum Guidelines for Family Medicine Residents Conditions of the Eye, Reprint No. 263, 2017 p.6 1. Evaluation a. Perform specific procedures and interpret results i. Tests of visual acuity ix. Ophthalmoscopy
Undergraduate Medicine - AAMC (2008) - Recommendations for Preclerkship Clinical Skills Education for Undergraduate Medical Education p.25 Appendix 5: Patient Examination. “Perform head exam including eyes, ... “
CPMEC Australian curriculum Framework for Junior Doctors version 3.1, 2012, p.31 ...provide safe treatment to patients through competently performing certain procedures... Corneal and other superficial foreign body removal
RACGP Curriculum for Australian General Practice 2016, EY16 - Eye Medicine Contextual Unit Identification ... of acute and progressive visual loss are essential skills for general practitioners. Identification of individuals at risk of common conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration
Medical Graduate Competency Framework Stage 2 Final Report, August 2012, Appendix C Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Ophthalmoscopy
Competence and Curriculum Framework for the Physician Assistant 2012, p 12 2.3.5 ...Perform a physical examination tailored to the needs of the patient and the demands of the clinical situation, including ..ophthalmic examination
Specialty Training Curriculum for Core Medical Training, 2013 p.111: Visual Disturbance: Perform full examination including acuity, eye movements, visual fields, fundoscopy
The UK Foundation Programme Curriculum 2016. p.9: obtains history, performs clinical examination, formulates differential diagnosis and management plan (FPC 11)
Practical Skills and Procedures, General Medical Council, April 2019, p.4 Assessment of patient needs 3. Perform basic ophthalmoscopy and identify common abnormalities
RCN Competencies - Advanced Nurse Practitioners, 2012, p.4 ...receiving patients with undifferentiated and undiagnosed problems and making an assessment of their health care needs, based on highly-developed nursing knowledge and skills ... such as physical examination
Royal College of General Practitioners Online Curriculum 3.16 Care of people with eye problems Recognise ophthalmic emergencies , e.g. new visual distortion ... age-related macular degeneration, sudden loss of vision Recognise ocular manifestations of neurological disease





