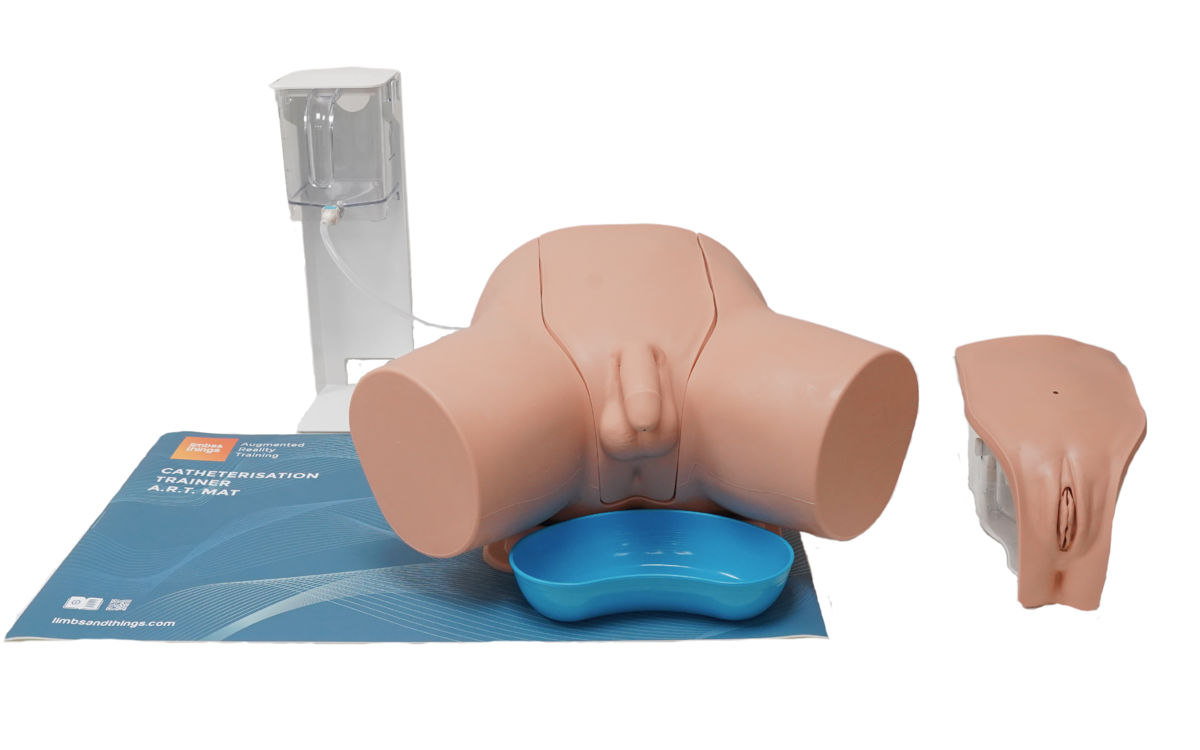





Male Catheterization Trainer with Augmented Reality
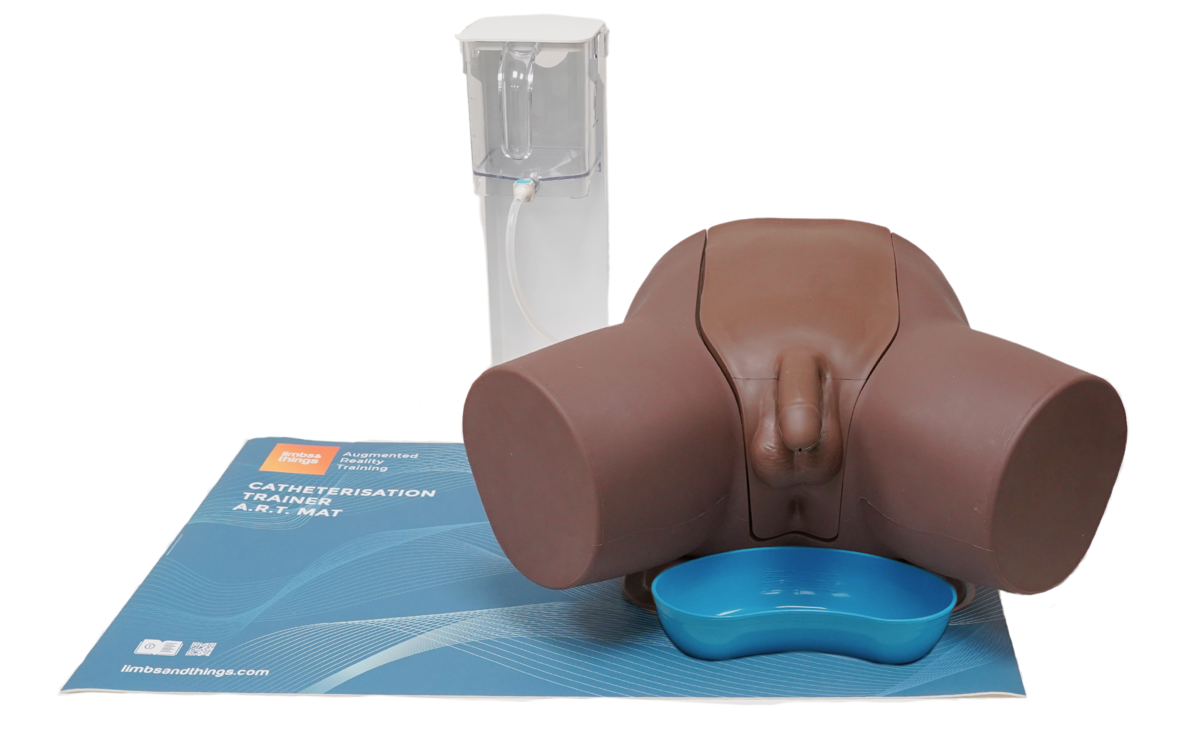
Skin Tone
Model
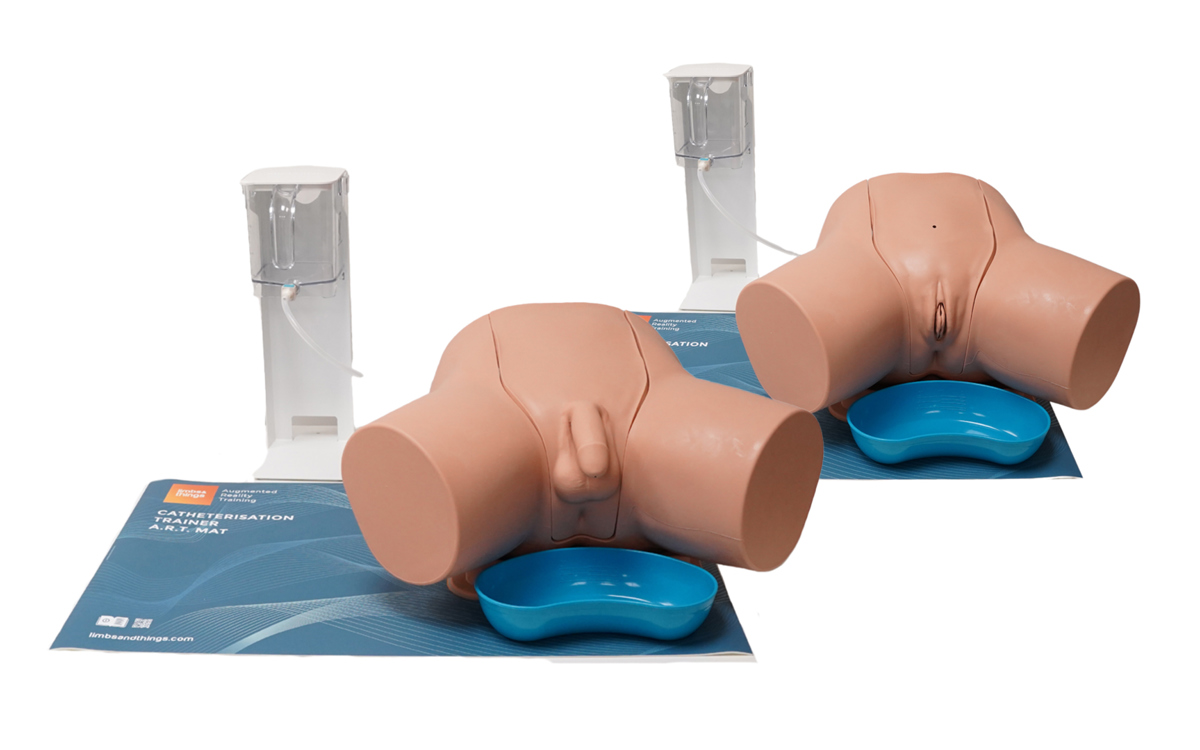
Choose between individual trainers or combined sets
Male Urinary Catheterisation trainer with Augmented Reality, for clinical accuracy and realism.
Adding to cart...
Added to cart
Sorry, something went wrong adding the product to the cart.
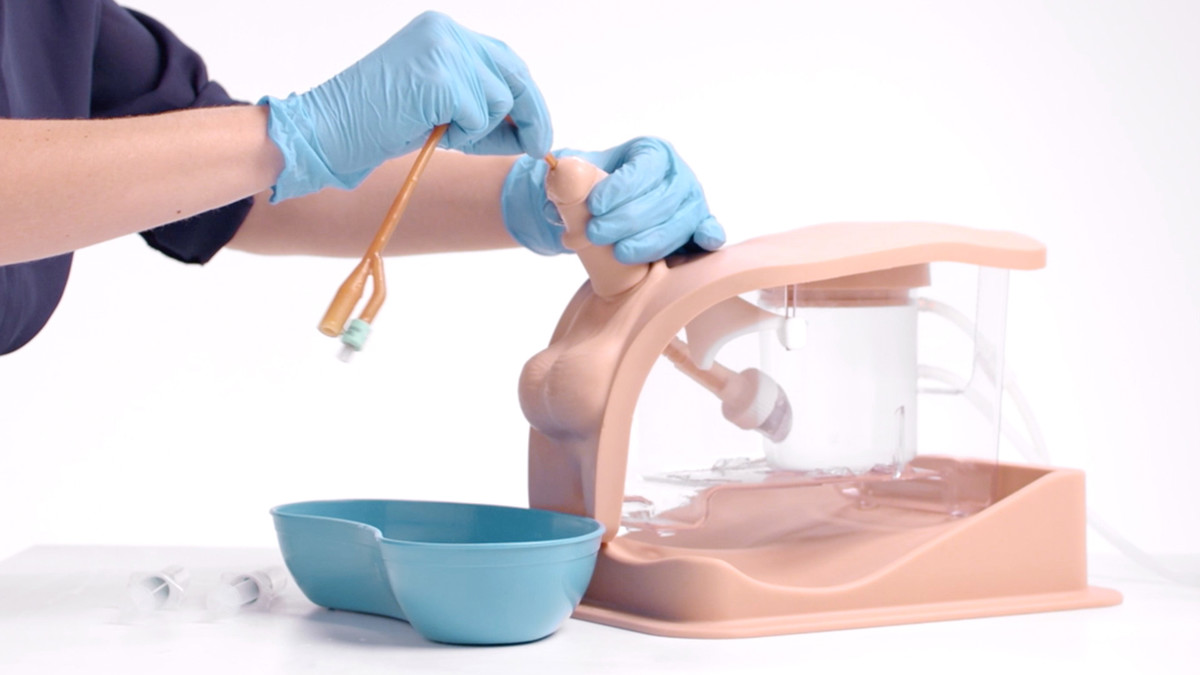
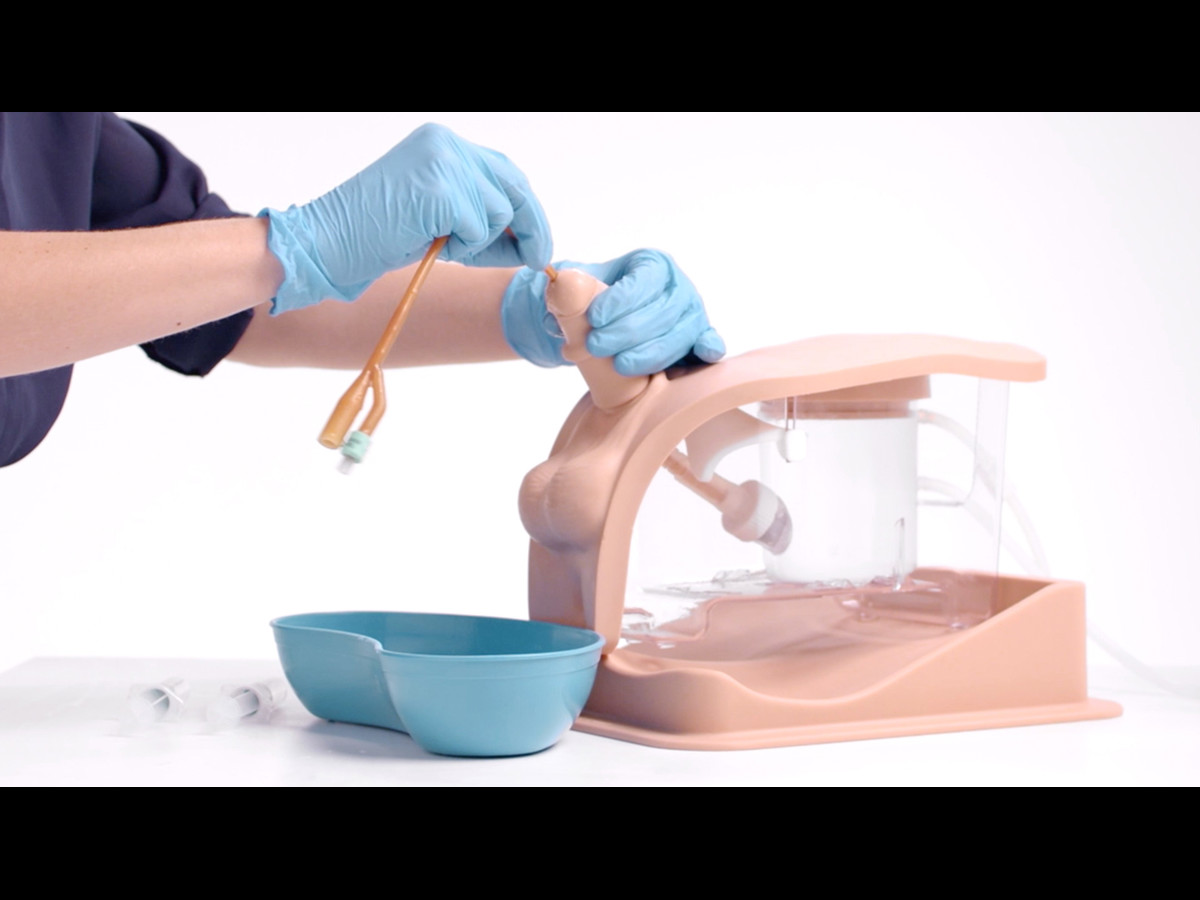
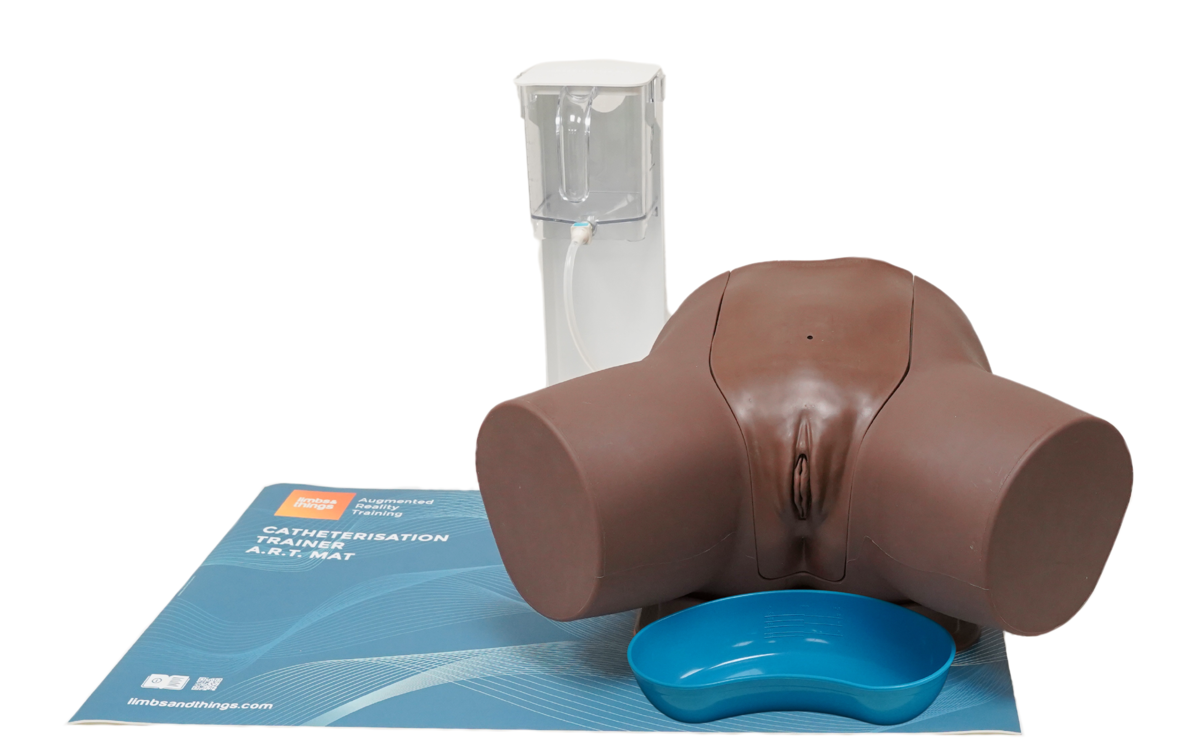
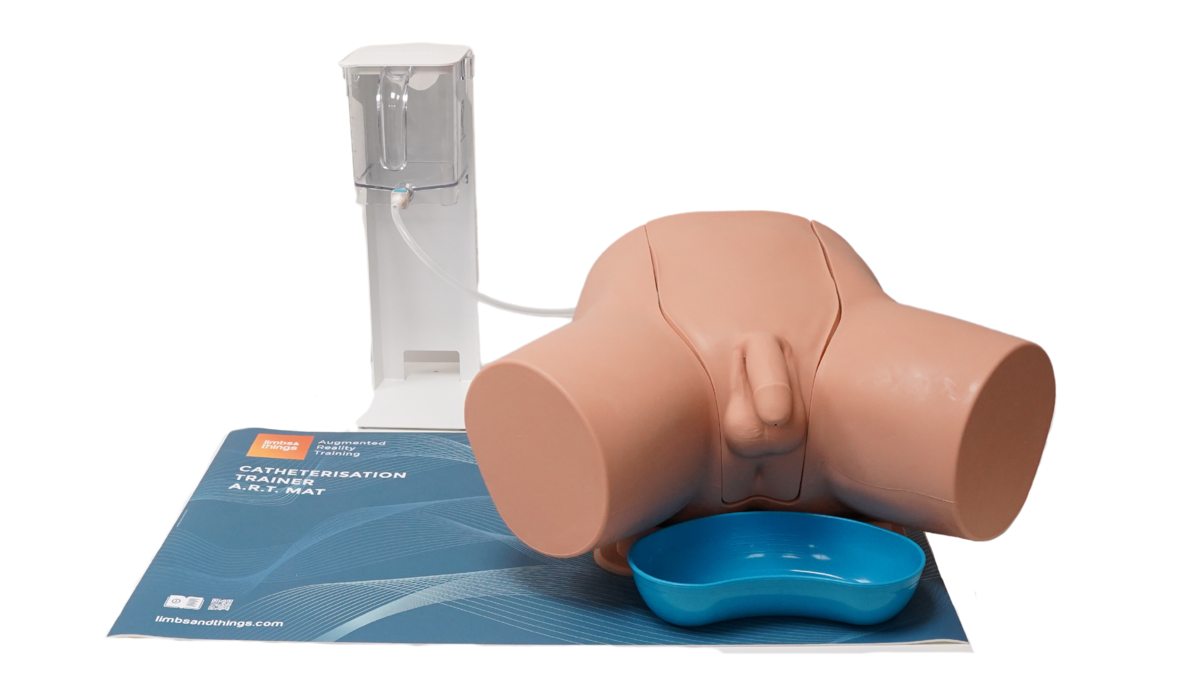
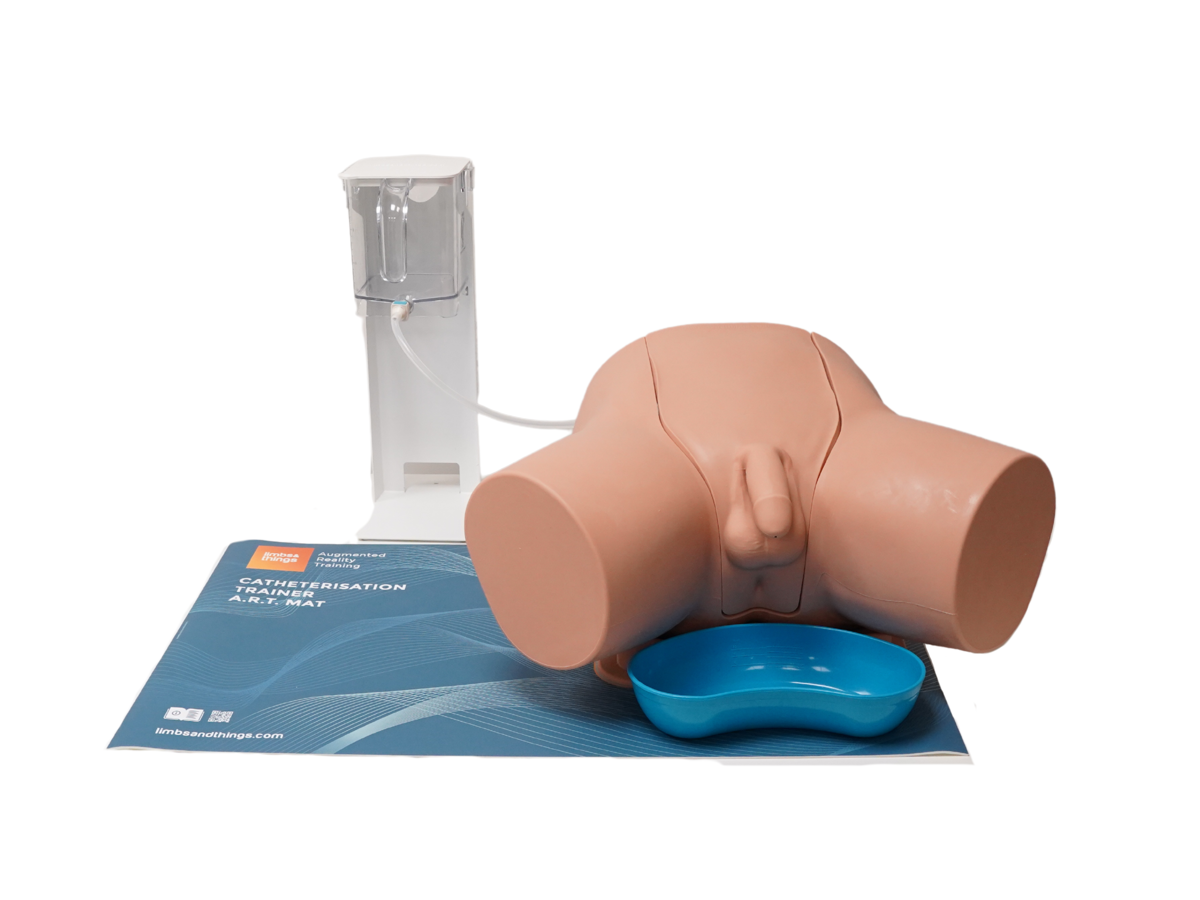
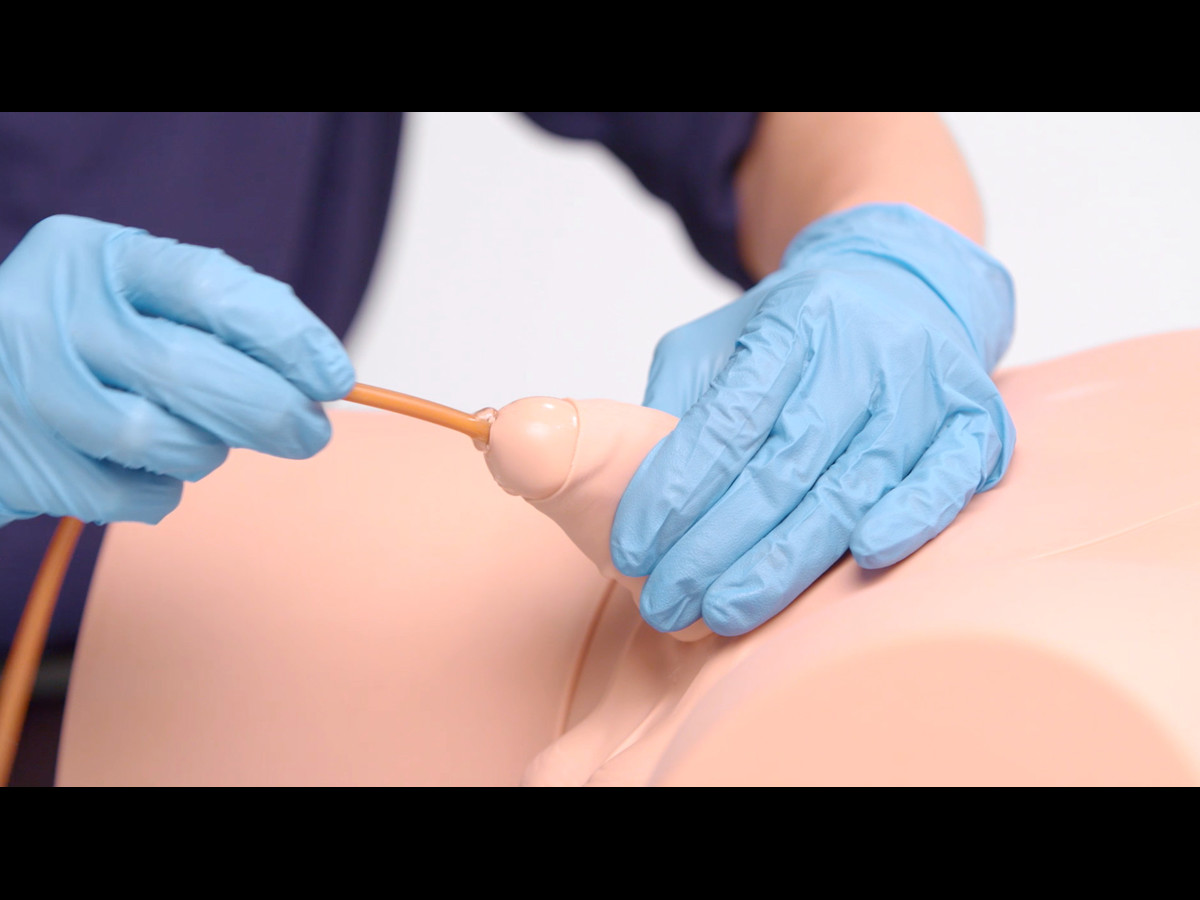
The Male Catheterization Trainer is an advanced training model designed to support healthcare professionals in mastering urinary catheterisation techniques specific to the male anatomy. With enhanced anatomical realism and features that align with best practices for CAUTI prevention, this trainer enables effective and safe clinical training in technical catheterisation skills.
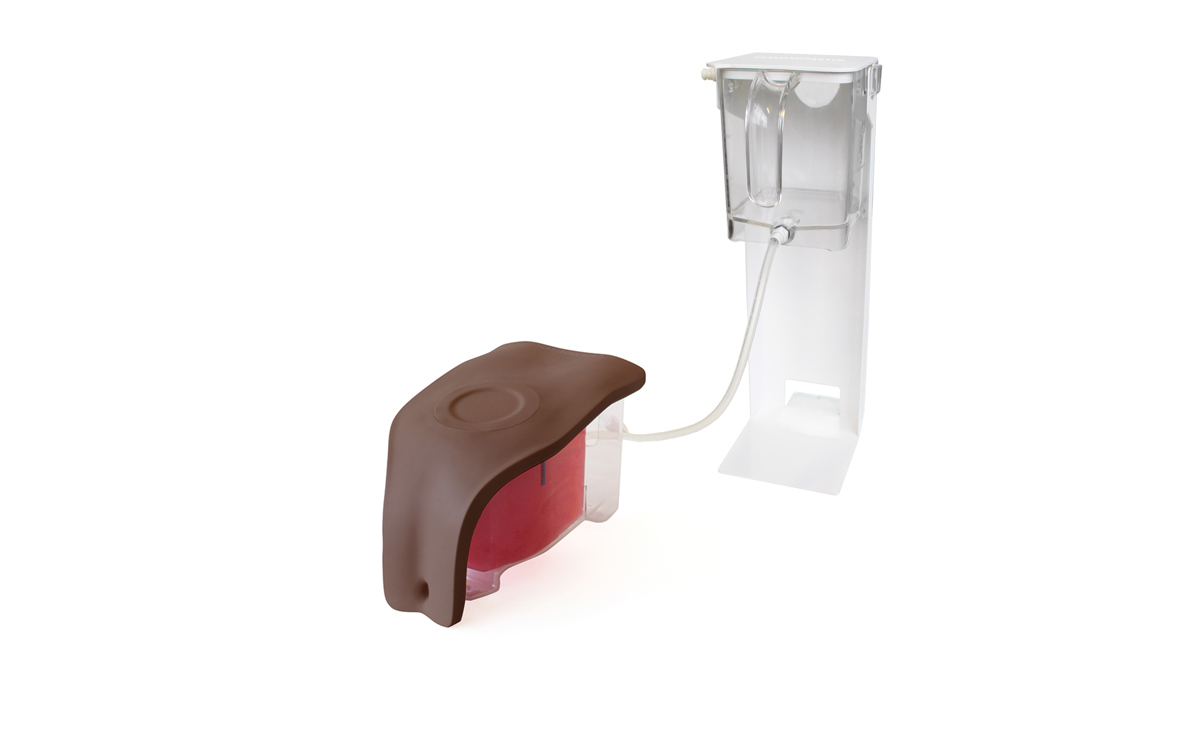
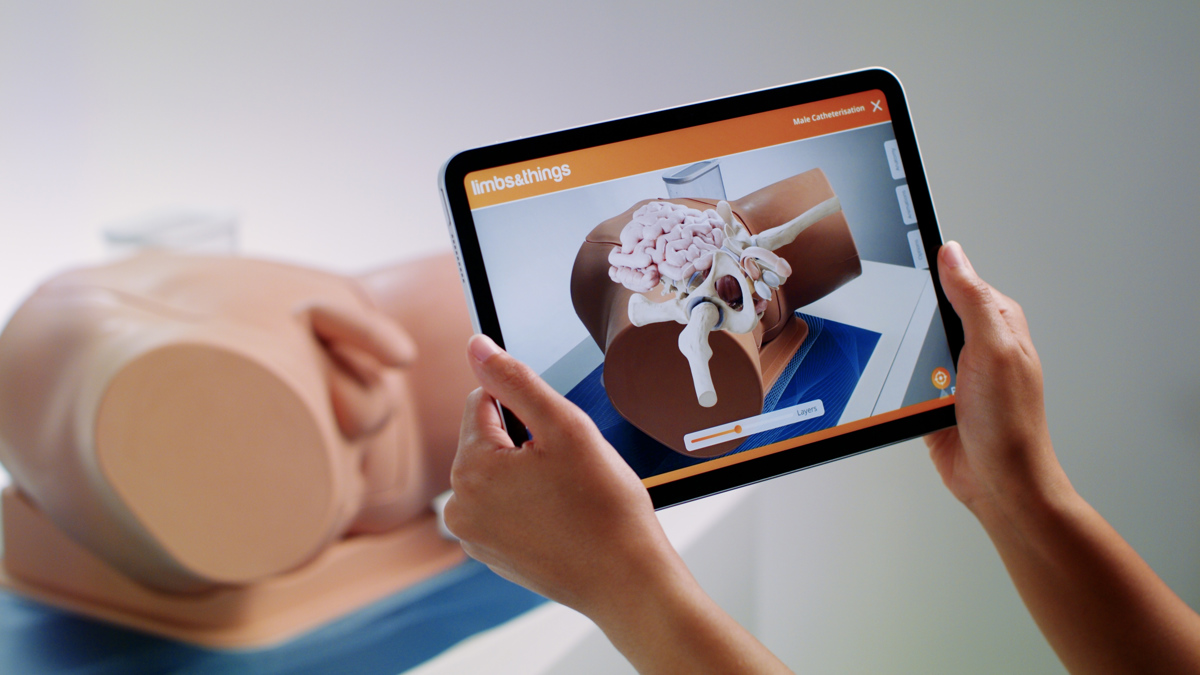
This trainer comes with Augmented Reality to add another dimension to learning. Use your smart device to interact with the internal anatomy and build deeper understanding.
Realistic Anatomy & Enhanced Training Capabilities
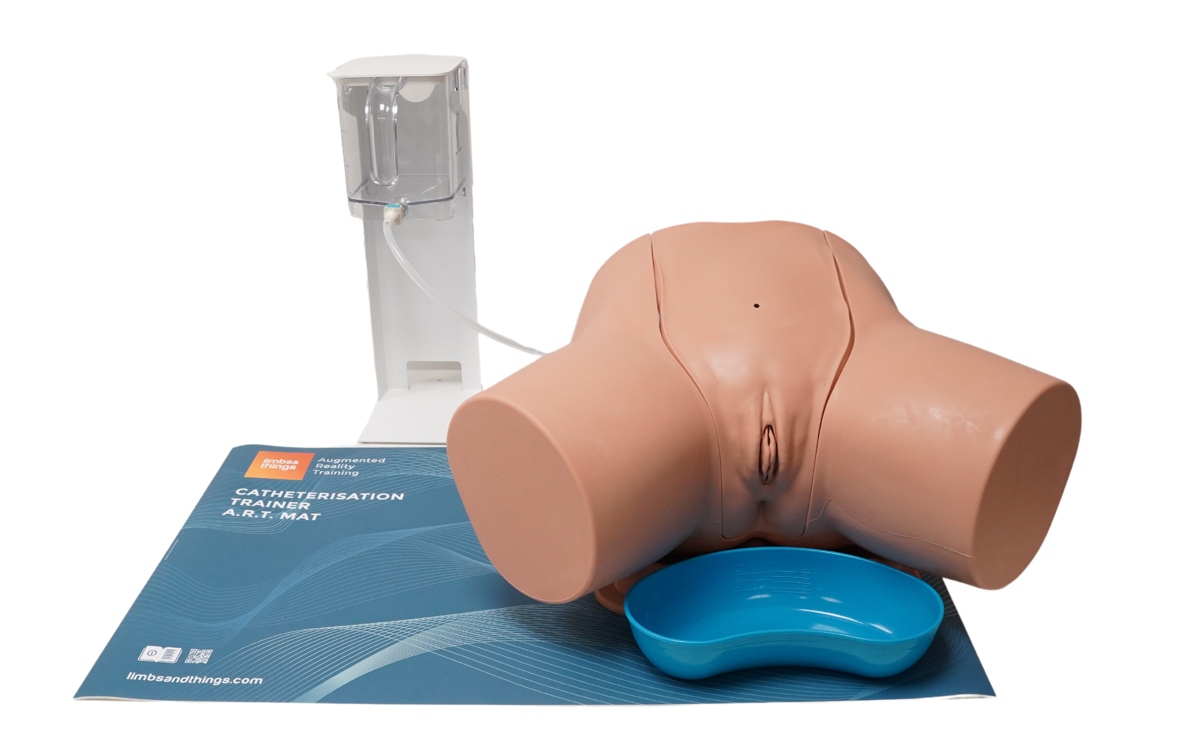
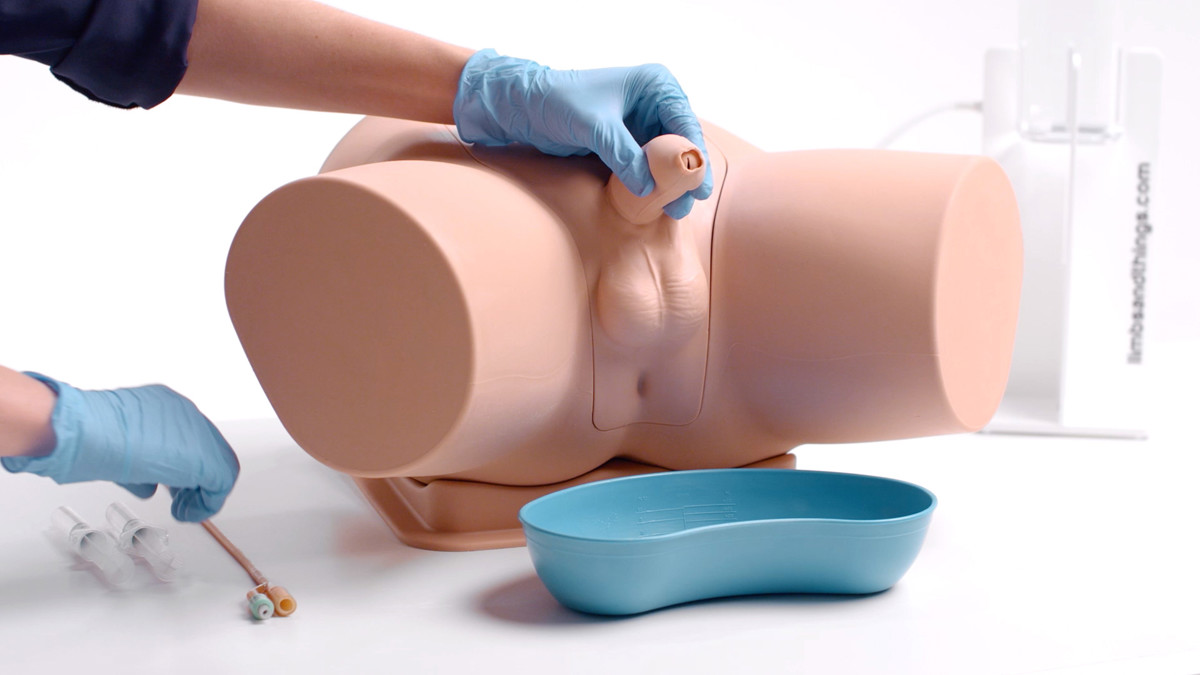
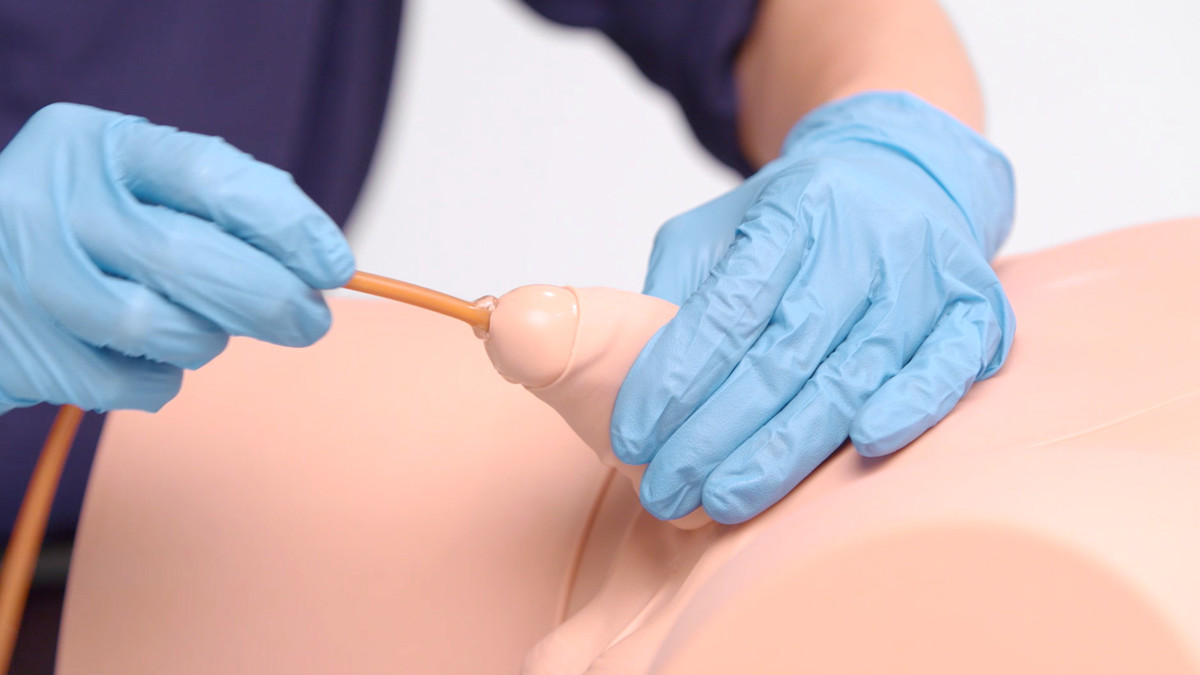
- Anatomical Accuracy: This model provides a lifelike experience, with a softer and flaccid penis, an anatomically accurate bladder, and a supple urethra that mimics natural resistance, including a realistic sphincter response during catheter insertion
The Male Catheterization Trainer is an advanced training model designed to support healthcare professionals in mastering urinary catheterisation techniques specific to the male anatomy. With enhanced anatomical realism and features that align with best practices for CAUTI prevention, this trainer enables effective and safe clinical training in technical catheterisation skills.
This trainer comes with Augmented Reality to add another dimension to learning. Use your smart device to interact with the internal anatomy and build deeper understanding.
Realistic Anatomy & Enhanced Training Capabilities
- Anatomical Accuracy: This model provides a lifelike experience, with a softer and flaccid penis, an anatomically accurate bladder, and a supple urethra that mimics natural resistance, including a realistic sphincter response during catheter insertion
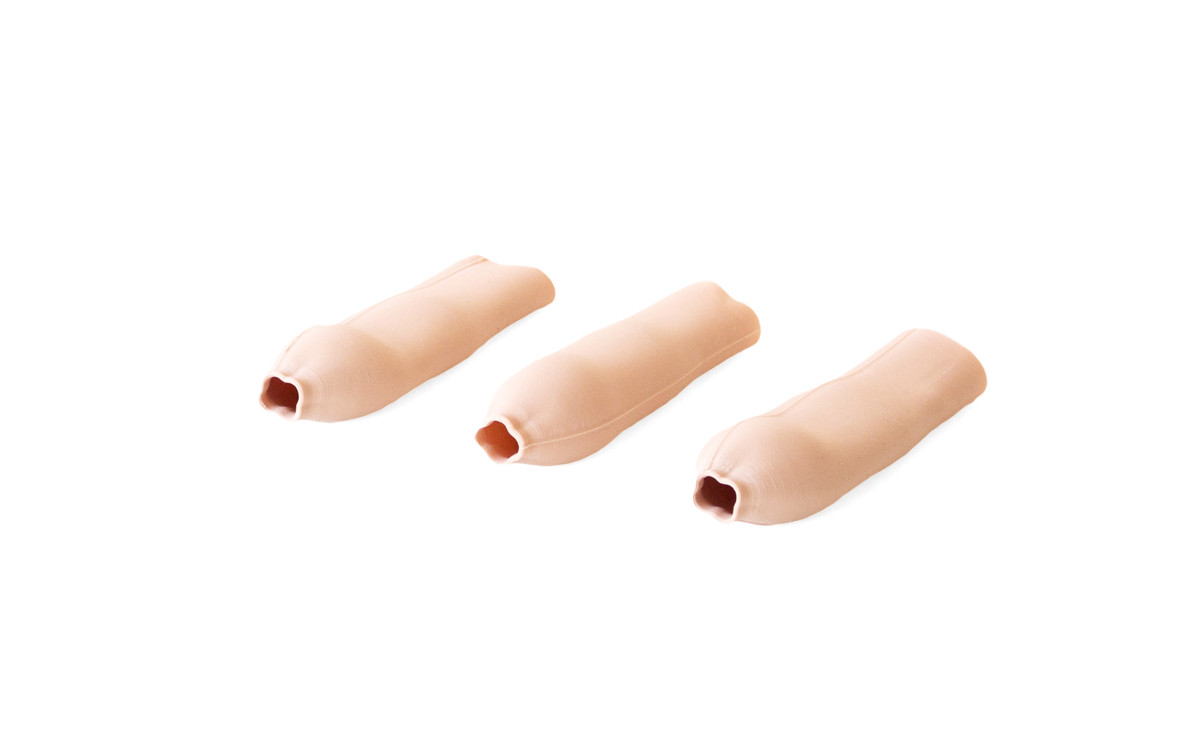
- Retractable, Removable Foreskin: Practice appropriate handling of foreskin, with the ability to simulate both circumcised and uncircumcised male genitals
- Increased Mobility: The trainer features a mobile penis, enabling trainees to handle positioning and angles realistically during catheterization practice
- Challenging, Realistic Insertion: The urethra offers realistic difficulty during catheter insertion, supporting the development of tactile sensitivity and proper technique
Communication and Soft Skills Integration
The Male Catheterization Trainer can also be used with a standardised patient to allow for simultaneous development of communication and procedural skills—encouraging holistic clinical education and reinforcing patient dignity throughout the procedure.
Built for Longevity and Cost-Efficiency
The trainer’s robust structure ensures long-term durability, reducing the need for frequent replacement and helping control ongoing training costs.
Ideal for clinical skills labs, simulation centres, and nursing or medical education programmes, the male catheter model delivers a comprehensive, realistic, and cost-effective solution for teaching male urinary catheterisation.
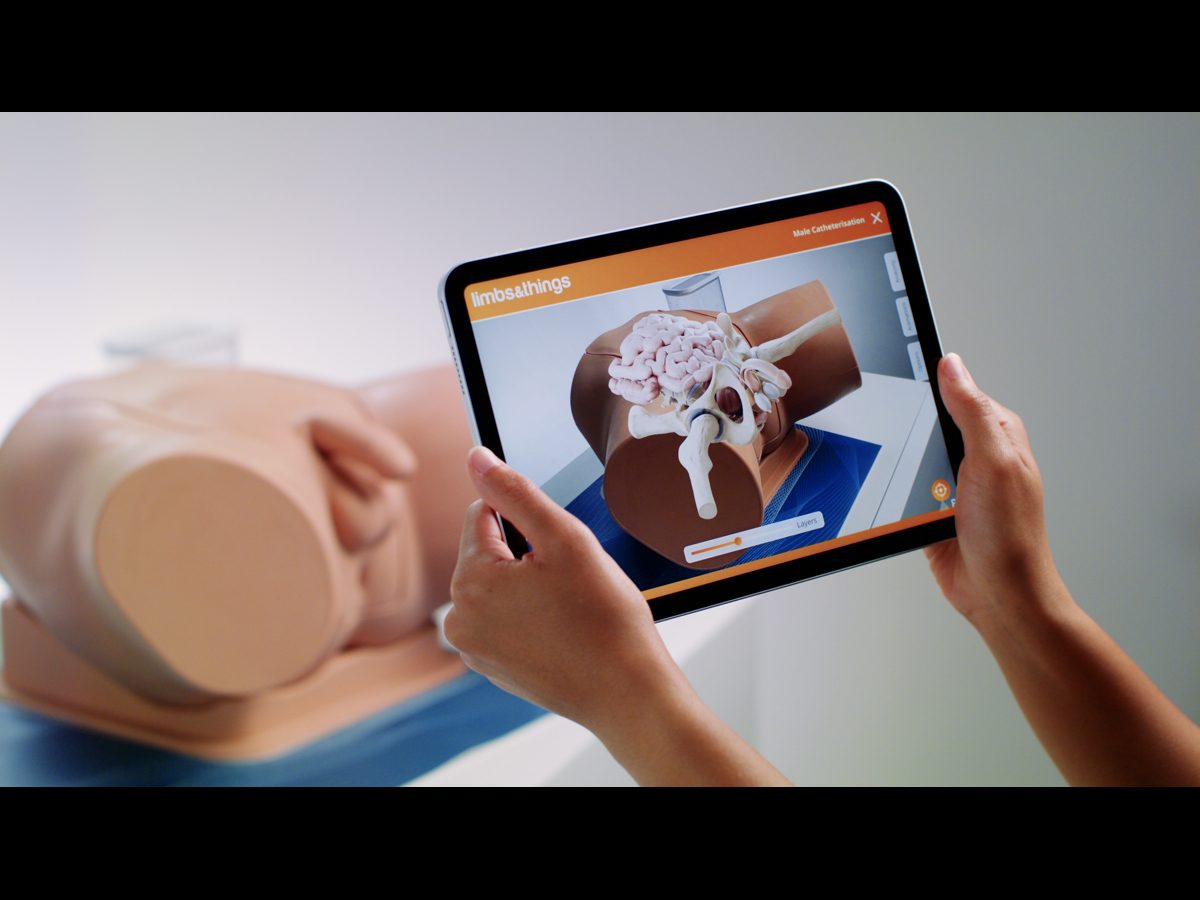
Augmented Reality. Bridging the gap between theory and practice
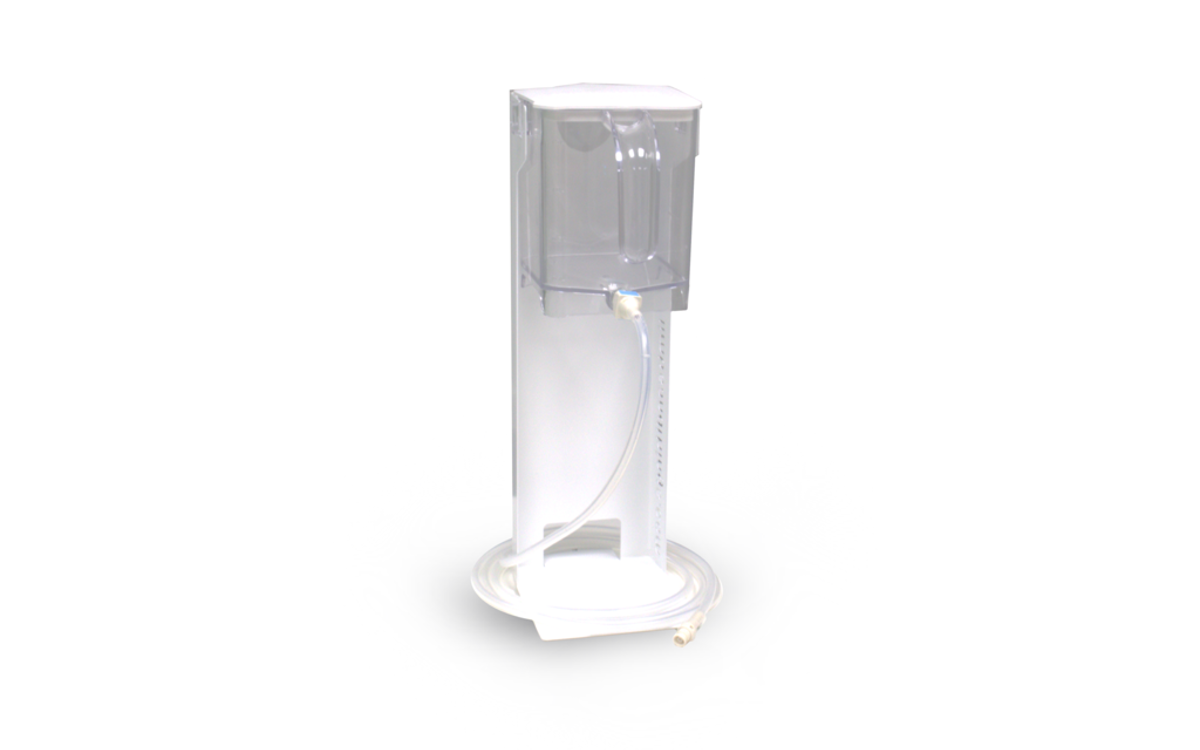
Real-world MRI and CT scan data, combined with the skills of talented medical artists and digital creators, bring the internal anatomy of our Catheterization trainers to life.
The FREE Augmented Reality app, enhances the learning experience for students. The technology provides access to highly realistic and interactive 3D images alongside engaging procedural animations. This unique feature strengthens independent learning inside and outside the classroom.
Overview
- Augmented Reality allows you to bridge the gap between theory and practice
- Robust design for long lasting models and cost-effective training
- Softer, more realistic male anatomy
- Ability to view the catheter path when modules are used outside the pelvic shell
Realism
- Supple urethra & resistant sphincter provide a realistic response
- Anatomically accurate bladder
- Flaccid penis with removable foreskin for realistic male catheterisation on circumcised and uncircumcised anatomy
- Increase mobility of the penis gives a more accurate representation of inserting the catheter
Versatility
- Modular design, allowing easy removal of inserts for cleaning and replacement
- Removable foreskins for wider training scenarios
- Ability to view the path of the catheter during procedures
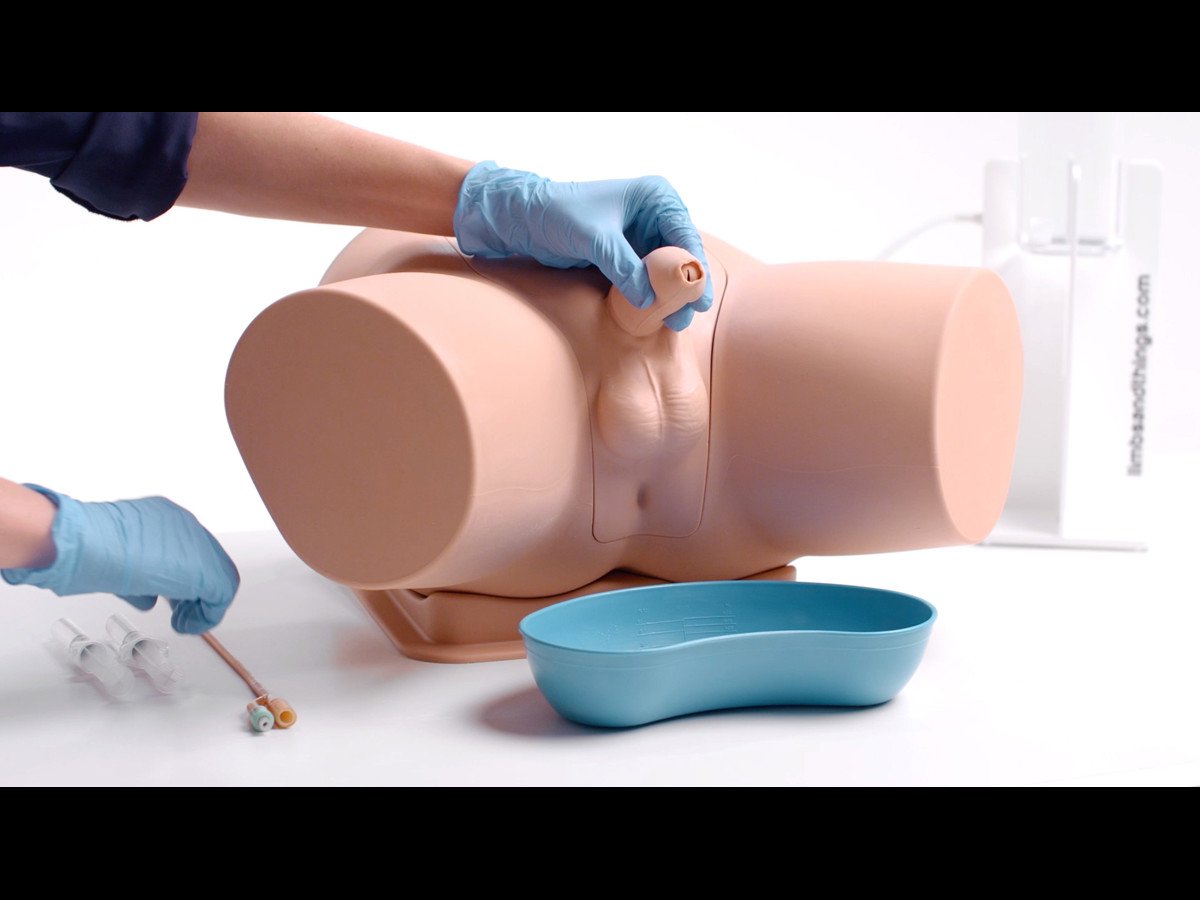
- Reusable double-sleeve catheter packaging is supplied for teaching aseptic technique
- Syringe supplied with water-based lubricant to simulate proprietary local anaesthetic gel, e.g. Instillagel®, which is used prior to catheterisation
Cleaning
- Drain all fluid from the product when not in use
- Remove catheters and foreskin from the trainer after use
- Wipe off excess lubricant
- Clean product surfaces with a soft damp cloth, warm water and mild detergent
- Allow trainer and components to dry completely before storing
Safety
- Components of the trainer are latex free
- Foley Catheter supplied is made of silicone coated latex
- Always deflate the balloon of the catheter before removing
- Only use mock gels that are supplied with the catheterisation simulator
- Always use lubricant when inserting the catheter
- To reduce the risk of bacteria and mould, add a sterilisation fluid to the water, such as Milton Antifungal agent
Simulated Patient
- This trainer can be used with a standardised patient to help improve communication skills
Anatomy
Male, lower torso to upper thigh with:
- Pubic bone
- Penis
- Testicles
- Foreskins (removable)
Skills Gained
- Correct handling of male anatomy
- Aseptic catheterization technique
- Withdrawal of catheter
- Urinary catheterization
- Fluid management
- Insertion of a urinary catheter
Product Contains
This simulation model is supplied with an antifungal agent. (Use as per instructions on the packet.)
Works with the following products:
-
Light
-
Dark
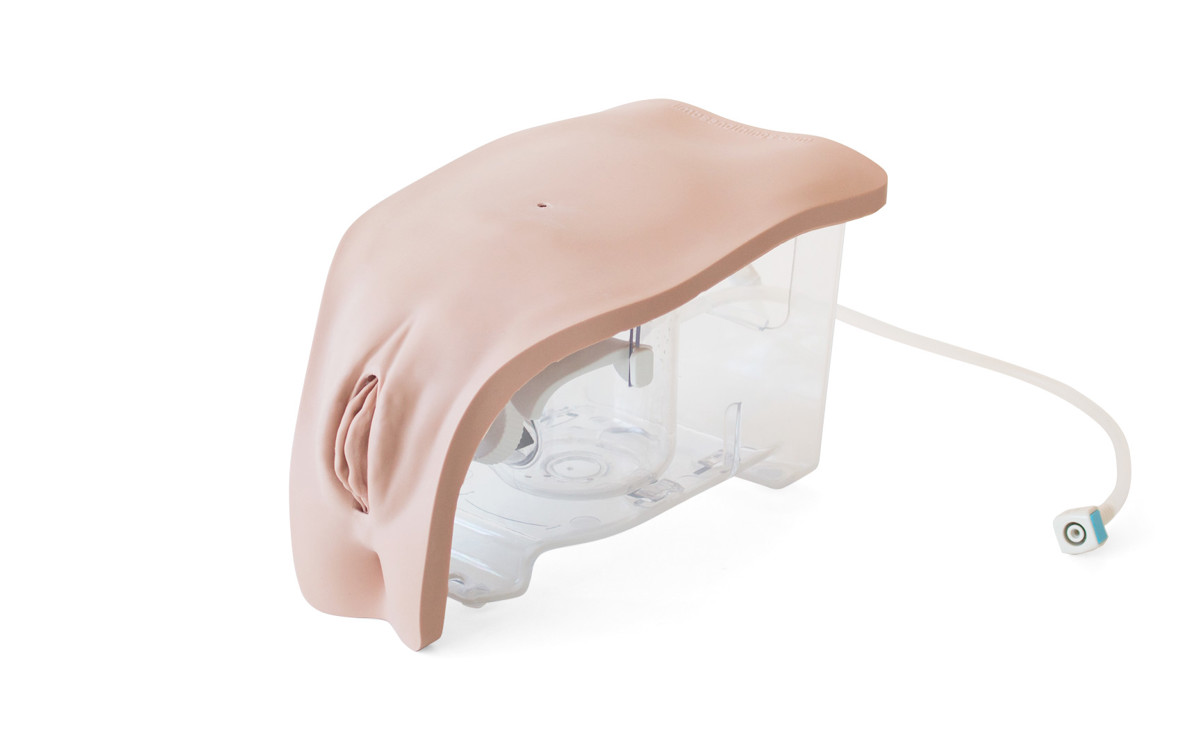

Female Catheterization Module (Light Skin Tone)
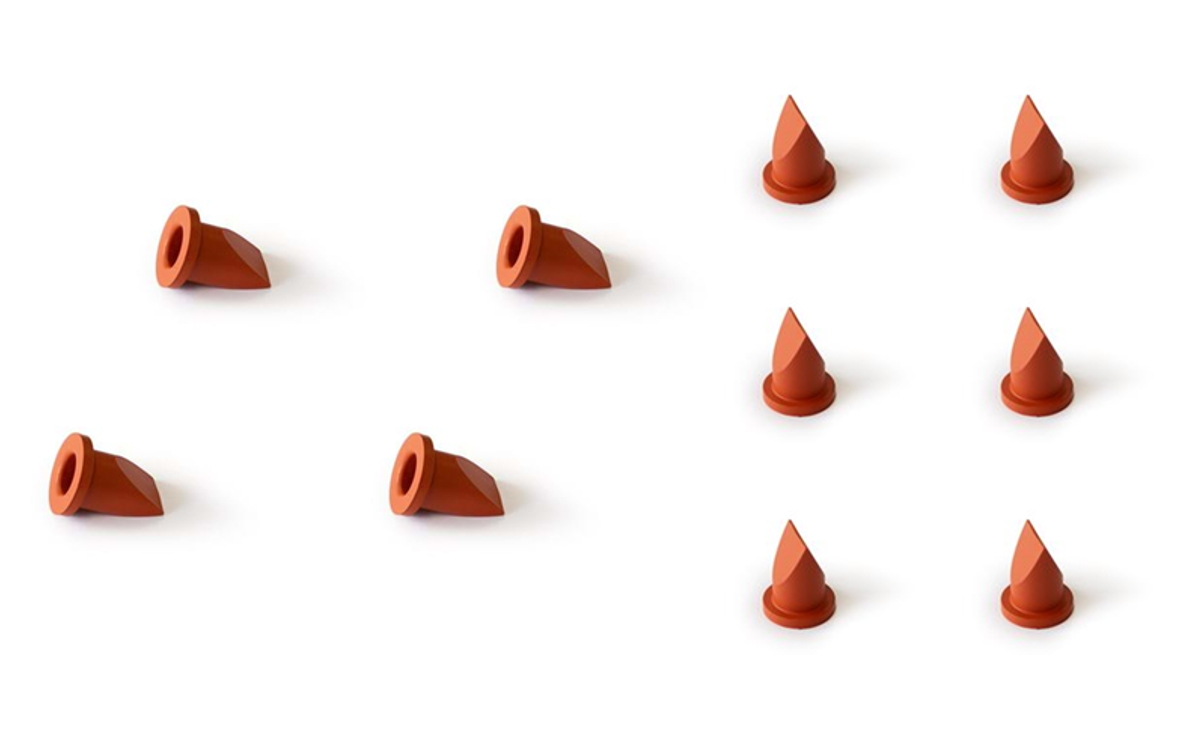

Bladder Valve (Pack of 10)
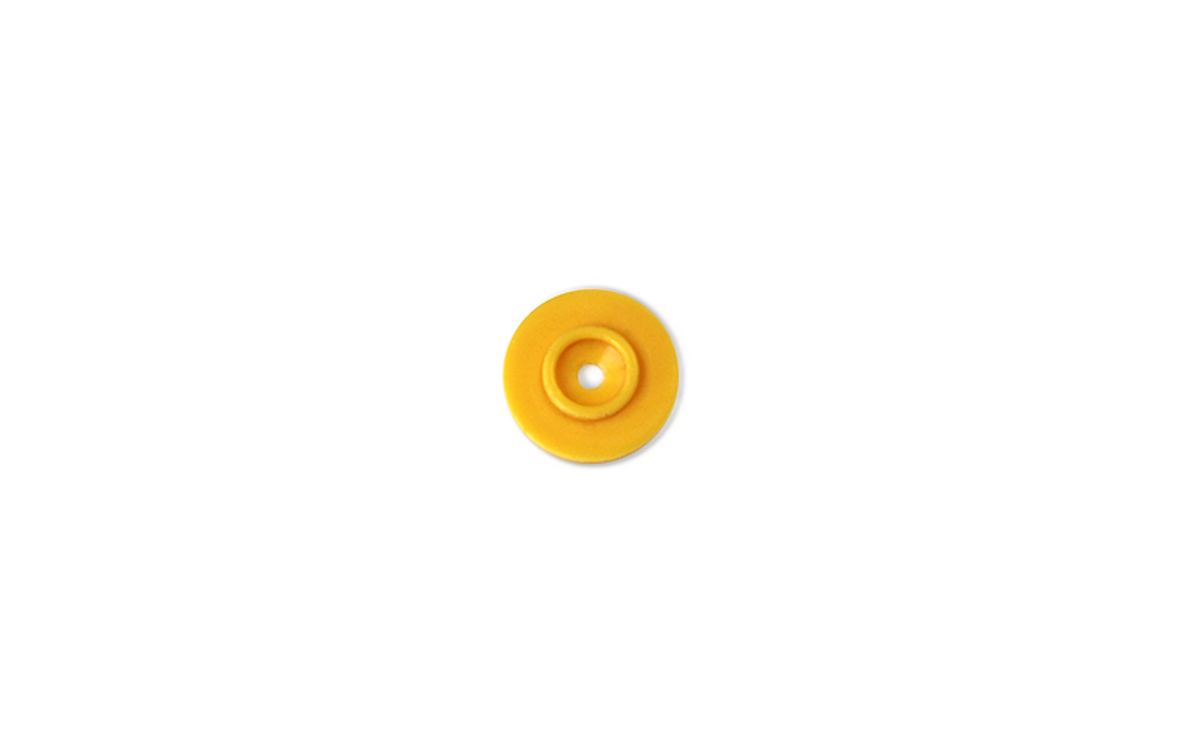

Bladder Diaphragm
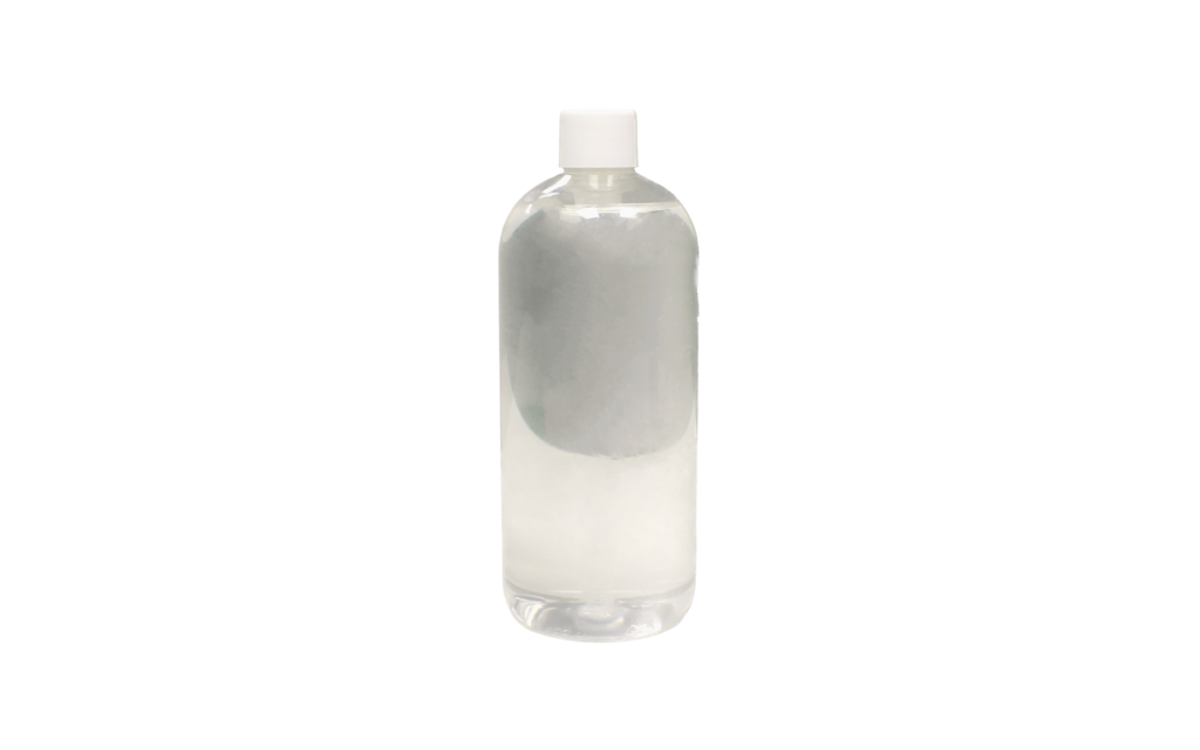

Catheterisation Lubricant
-
Light
-
Dark
Suprapubic Insertion (Ultrasound Guided) Unit (Light Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
Suprapubic (Ultrasound) Catheterization Module (Light Skin Tone)
-
Light
-
Dark
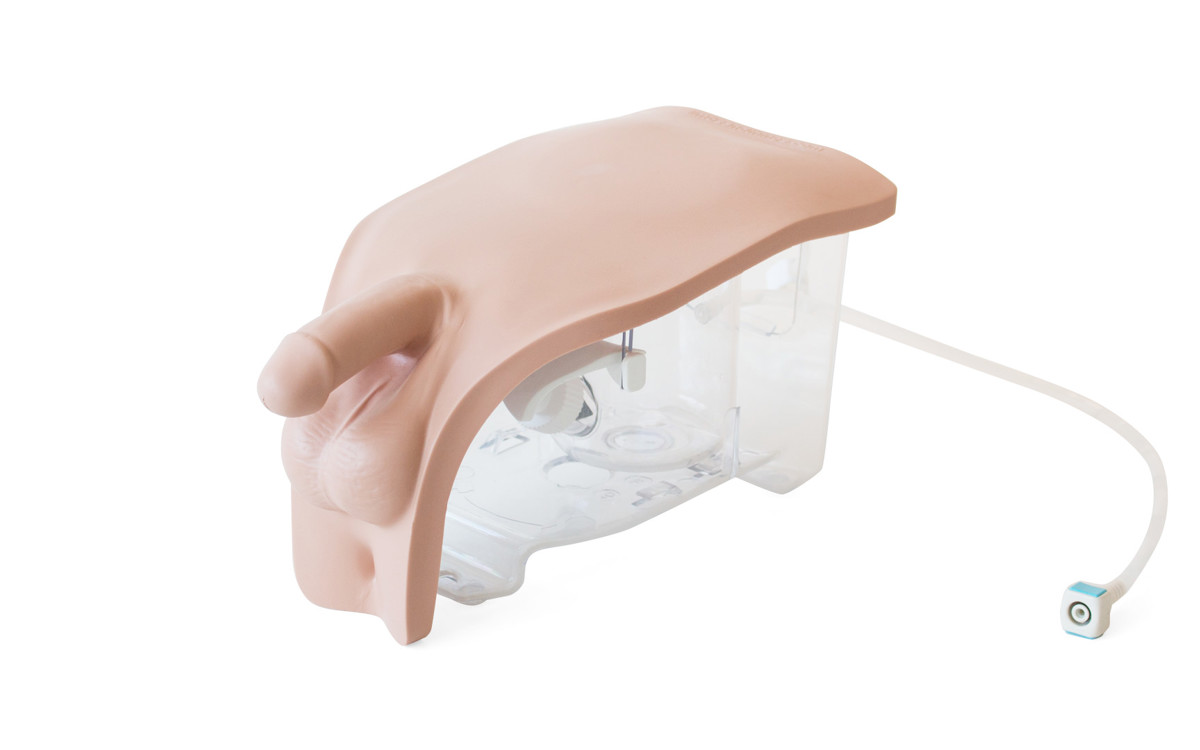
Male Catheterization Module (Light Skin Tone)

Augmented Reality Mat for Catheterisation
-
Light
-
Dark
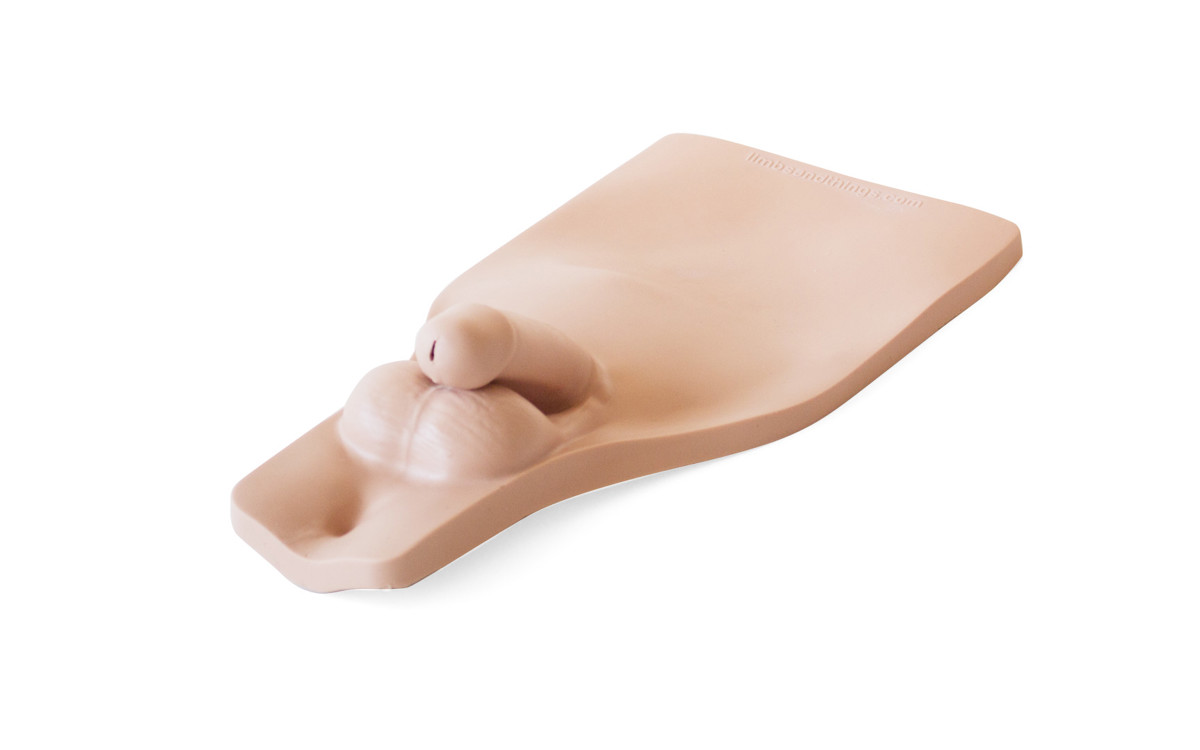
Male Perineum for Catheterization (Light Skin Tone)
References
Bladder catheterization (M&F). Confederation of Postgraduate Medical Education Councils (CPMEC) Australian Curriculum Framework for Junior Doctors: Skills and Procedure, 2007, S18.
Urinary catheter (male and female) Paramedics Australasia: Paramedicine Roles Descriptions: General Care Paramedic, 2018, P9.
Competently insert an indwelling catheter and replace suprapubic catheters. Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (RACGP) Curriculum for Australian General Practice, Kidney and urinary health, 2022.
Female and Male catheterization in a simulated environment. Medical Deans' Competencies Report, Medical Graduate Competency Framework Stage 2 Final Report, 2012, P9.
Female and Male Indwelling Urniary Catheterisation. Agency for Clinical Innovation (ACI) Urology Network - Nursing 2013.